European Population Growth Map During Cold War

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
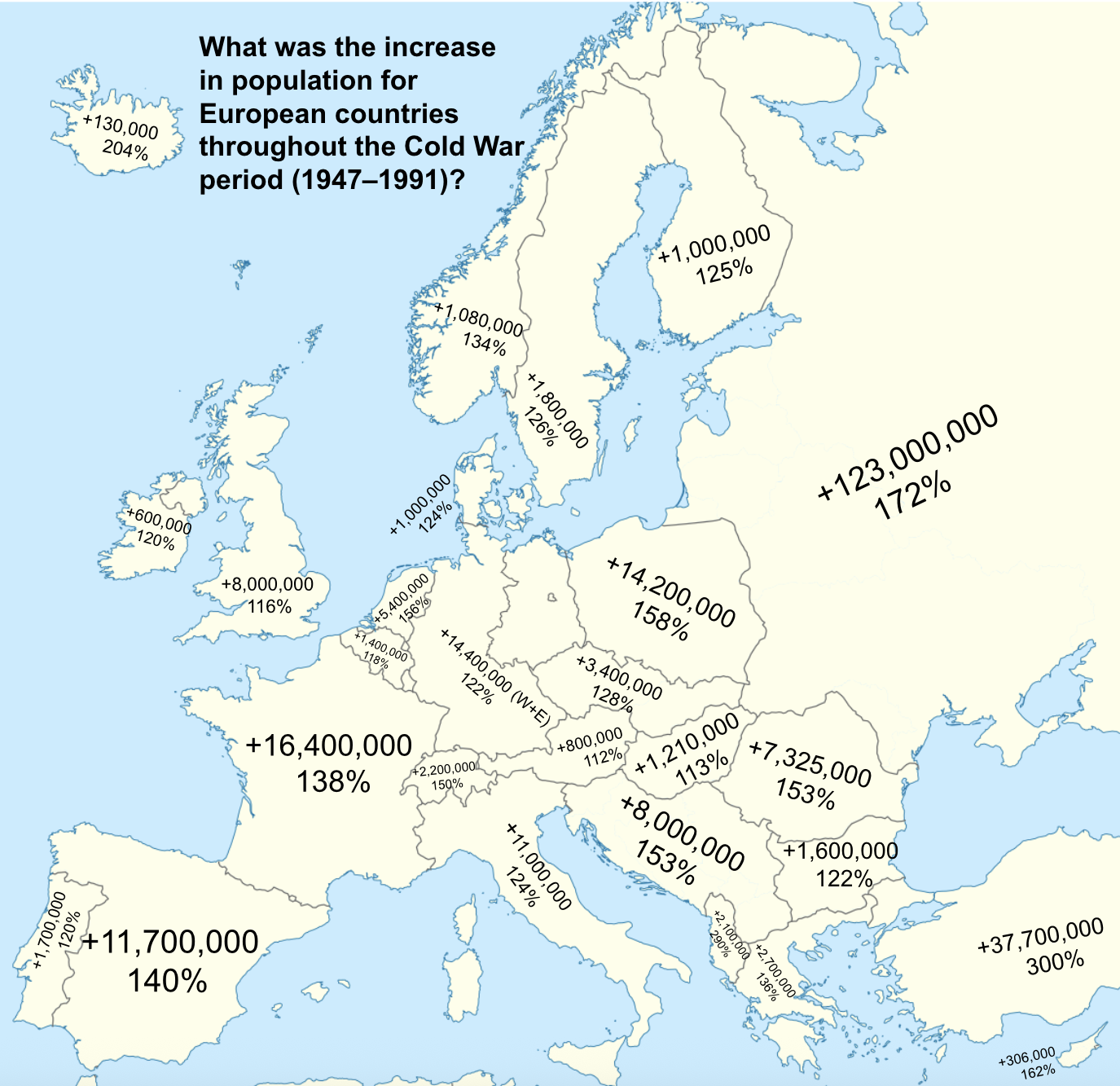
The map titled "What was the increase in population for European countries throughout the Cold War period (1947-1991)" visually represents the changes in population across various European nations during one of the most pivotal eras in modern history—the Cold War. This period, marked by ideological conflict between the Eastern and Western blocs, not only influenced political landscapes but also had significant demographic consequences. The visualization highlights the percentage increase in population for each European country, revealing trends that reflect broader social, economic, and political dynamics.
Deep Dive into Population Growth in Europe
Population growth is a critical factor in understanding a country's development and future prospects. During the Cold War, Europe experienced varied demographic changes influenced by several factors, including migration, birth rates, and economic conditions. In general, Western European countries saw a significant increase in population during this period, attributed largely to post-war recovery and economic prosperity. Countries like West Germany and France experienced notable growth rates, with the population in West Germany increasing by approximately 30% from 1947 to 1991.
Conversely, Eastern European nations faced different challenges. For instance, the Soviet Union's influence often led to political instability and economic challenges that inhibited population growth. Countries like East Germany and Poland exhibited slower growth rates, with several experiencing stagnation or even decline in population due to emigration and low birth rates. Interestingly, while the West was thriving, many Eastern European countries struggled to provide adequate living conditions, which discouraged population retention.
Demographic shifts during the Cold War were also marked by significant migration patterns. The post-World War II era saw millions of people displaced, and many sought refuge in Western Europe. This influx contributed to the population booms in countries like the United Kingdom and France, which welcomed immigrants from former colonies and other nations. For example, the UK’s population grew steadily, fueled by both domestic birth rates and international immigration.
The late 1980s witnessed the beginning of a dramatic shift in Eastern Europe, culminating in the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. This event not only symbolized the end of the Cold War but also initiated new waves of migration, as people sought better opportunities in Western Europe. The impacts of these changes would be felt long after the Cold War ended, reshaping the demographic landscape of Europe.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map by regions, distinct patterns emerge. In Northern Europe, countries like Sweden and Finland enjoyed a healthy population increase, primarily due to strong social welfare systems that supported families and encouraged higher birth rates. In contrast, the Baltic states, which were under Soviet control, saw much slower growth due to oppressive political regimes and economic hardships.
Western Europe, characterized by strong economies and political stability, showed robust growth. The Netherlands and Belgium, for example, recorded significant population increases thanks to urbanization and industrial growth. Interestingly, urban centers in these countries became magnets for both domestic and international migrants, contributing to their population surges.
Eastern Europe presents a starkly different picture. Countries like Hungary and Romania experienced population declines post-1980 due to economic difficulties and emigration. The political turmoil that marked the late Cold War years further exacerbated these trends, leading to a demographic crisis that many Eastern European nations are still grappling with today.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population dynamics during the Cold War is crucial for several reasons. First, it provides insight into how political ideologies can influence demographic trends. The stark differences in population growth between Eastern and Western Europe reflect the broader economic and social disparities that existed during this time.
Moreover, the demographic shifts initiated during the Cold War continue to shape Europe today. The ongoing challenges of an aging population in many Western European countries are a direct consequence of the population growth patterns established during this period. Countries that experienced high growth rates now face the need to address issues related to healthcare, pensions, and workforce sustainability.
Additionally, the migration patterns established during the Cold War have laid the groundwork for today’s multicultural societies in many European nations. The integration of diverse populations presents both opportunities and challenges, influencing social cohesion and economic development.
As we look to the future, it’s essential to consider how historical population trends will impact Europe in the coming decades. With current challenges such as climate change, economic shifts, and ongoing migration, the lessons learned from the Cold War era remain relevant in navigating the complexities of today’s global landscape.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 3, 2025
- Views
- 26
Comments
Loading comments...