Australia’s Climate Compared to Other Countries Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
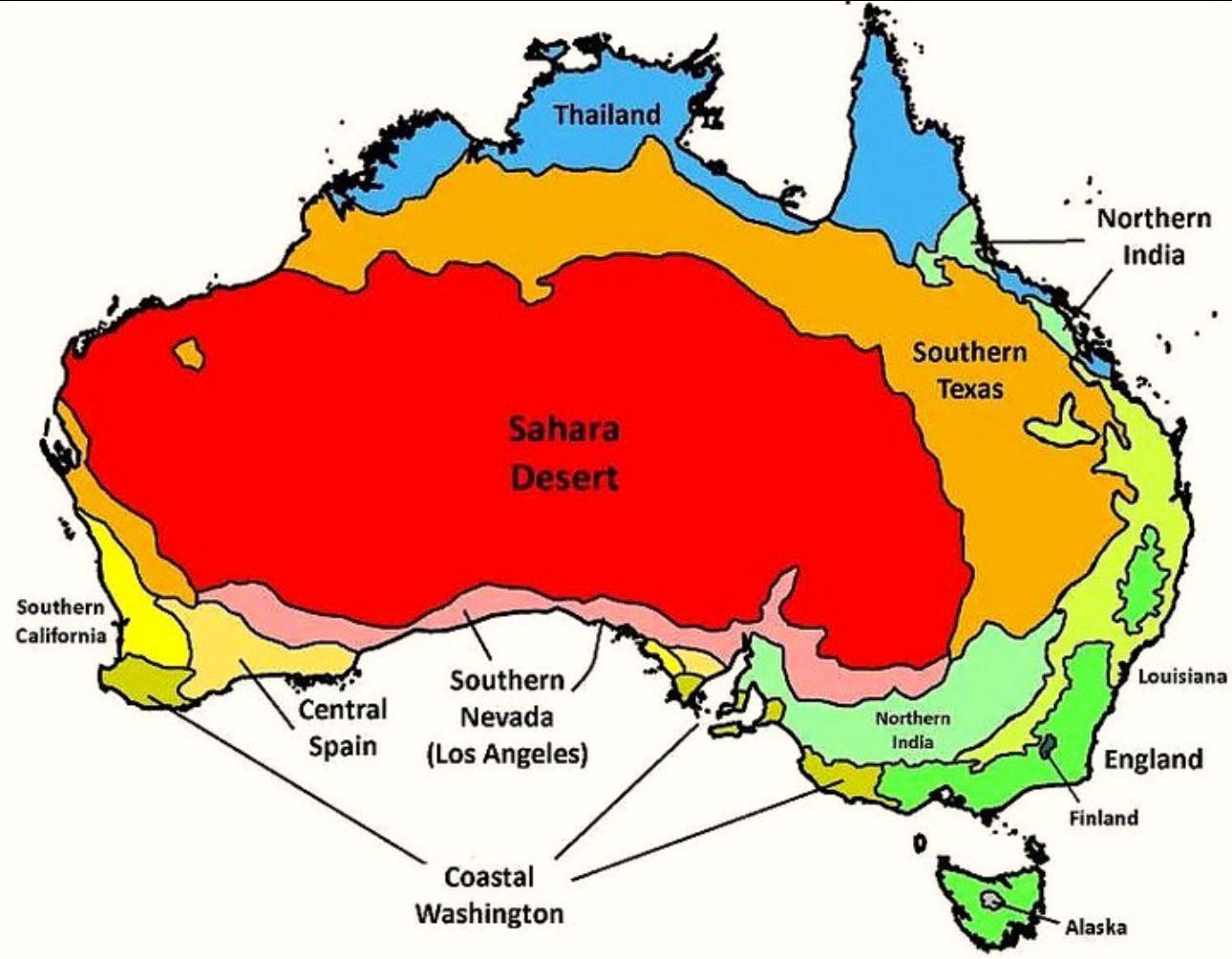
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Australia’s Climate Compared to Other Countries" provides a detailed look at how Australia's climate stacks up against various nations across the globe. It visually represents different climate zones, average temperatures, and precipitation patterns, allowing us to see not just how Australia fits into the global climate picture, but also how its unique environmental conditions compare to those of other countries.
Deep Dive into Australia’s Climate
Australia is renowned for its diverse climate, which ranges from arid deserts to tropical rainforests. This vast continent experiences a wide variety of weather patterns, influenced by its geographic location and topography. The country primarily falls within four major climate zones: tropical, arid, temperate, and alpine. Interestingly, this classification helps us understand the different ecosystems and agricultural practices present across regions.
The northern part of Australia is characterized by a tropical climate, with warm temperatures year-round and a distinct wet and dry season. For example, cities like Darwin experience average yearly temperatures around 30°C (86°F) and significant rainfall during the wet season, which can exceed 1,800 mm (71 inches). In contrast, the southern regions, such as Tasmania, enjoy a temperate climate, marked by cooler temperatures and higher rainfall, particularly in winter.
Inland Australia, known as the Outback, is primarily arid. This region is famous for its extreme temperature variations, often exceeding 40°C (104°F) in summer and plummeting below zero in winter nights. The map highlights these stark differences, illustrating how areas like Alice Springs receive less than 250 mm (10 inches) of rain annually, making them some of the driest places in the world.
When we compare Australia's climate to other countries, noteworthy patterns emerge. For instance, countries like Brazil and Indonesia, which also have tropical climates, experience more consistent rainfall compared to Australia’s bimodal rainfall pattern. Conversely, countries like Egypt and Saudi Arabia, which share arid zones with Australia, may not have as diverse a climate range, largely due to their geographical constraints.
Climate change is an increasingly critical factor affecting Australia, leading to more frequent and severe weather events, such as droughts, bushfires, and flooding. Recent studies indicate that average temperatures in Australia have risen by 1.44°C (2.59°F) since 1910, significantly impacting agriculture and biodiversity. The map serves as a stark reminder of these changes and their implications for the future.
Regional Analysis
Diving deeper into the map, we can analyze specific regions of Australia and how they compare to other countries. For example, the coastal regions of Queensland, known for their tropical climate, are similar to parts of Southeast Asia, such as Vietnam and the Philippines. However, while Queensland enjoys a relatively stable climate, these Southeast Asian countries face more significant impacts from typhoons and monsoons.
In contrast, Western Australia, particularly the region around Perth, experiences a Mediterranean climate. This is comparable to the climate found in parts of California, USA. Both areas have dry summers and wet winters, yet Western Australia often faces unique challenges such as more prolonged drought periods, which can affect water supply and agriculture.
The southern regions of Australia, including Victoria and Tasmania, showcase a temperate climate that can be compared to regions in New Zealand and parts of the UK. While these areas share similarities in temperature and rainfall, the unique flora and fauna of Australia’s temperate zones set it apart, making it a biodiversity hotspot.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Australia’s climate in relation to other countries is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps inform policies on agriculture and water management, especially as climate conditions continue to evolve. Farmers rely on accurate climate data to make decisions about crops and livestock, and with climate change altering traditional patterns, having a comparative understanding can provide insights into adaptive strategies.
Moreover, awareness of Australia’s climate can drive discussions about global climate change impacts. As one of the countries most vulnerable to climate fluctuations, Australia's experience serves as a case study for other nations facing similar challenges.
As we look to the future, projections indicate that Australia will continue to experience more severe weather conditions, impacting its ecosystems, economy, and communities. This map not only serves as a visual representation of current climates but also as a tool for understanding the potential future scenarios that could emerge due to ongoing environmental changes. Have you noticed how interconnected our world’s climates really are? The trends highlighted by this map remind us that what happens in one part of the globe can have far-reaching effects everywhere else.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 2, 2025
- Views
- 58
Comments
Loading comments...