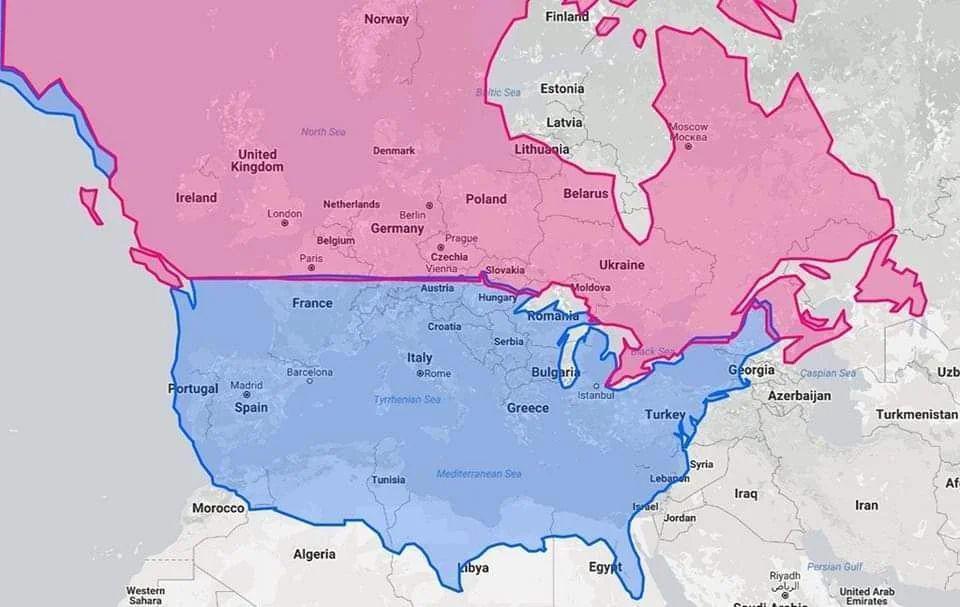
Latitude Map of United States, Canada, and Europe

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "United States & Canada in same latitude w/ Europe" highlights the parallels of latitude that connect these regions. It visually demonstrates how certain areas in the United States and Canada share the same latitudinal lines as specific parts of Europe. This is crucial because it allows us to understand how location influences climate, agriculture, and even cultural similarities despite being separated by vast distances.
Deep Dive into Latitude and Its Impact
Latitude plays a vital role in determining climate, biodiversity, and human activities. It influences everything from temperature ranges to precipitation patterns, making it a fundamental aspect of geography. Ever wondered why certain crops thrive in one region but not in another? The answer often lies in latitude. For instance, areas at higher latitudes, like northern Canada and parts of Scandinavia, experience colder climates that impact the types of agriculture possible in those regions. In contrast, areas at lower latitudes, such as the southern U.S. and southern Europe, enjoy warmer climates that are conducive to growing a wider variety of crops.
Interestingly, the map shows that cities like Seattle, Washington, and Copenhagen, Denmark, share similar latitudinal positions. Both cities experience maritime climates, characterized by mild, wet winters and cool summers. This similarity in latitude allows for comparable weather patterns, even though they are located on different continents. The influence of latitude extends beyond just weather; it also affects the types of flora and fauna that can thrive in these regions. For example, the Pacific Northwest of the United States boasts lush temperate rainforests, while northern Europe is home to diverse ecosystems that adapt to its cooler temperatures.
Moreover, latitude affects human activities and settlement patterns. The farther north one goes, the less hospitable the environment often becomes, leading to lower population densities. In the map, we can observe that while cities in the U.S. share latitudes with European counterparts, the population distribution is markedly different due to historical, economic, and social factors. For instance, the population density in the U.S. is higher in areas like the Midwest and Northeast, compared to the sparsely populated regions of northern Canada, despite their similar latitudinal lines.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the regions highlighted by the map provides insight into the nuances of climate and population distribution. In the northern U.S. and southern Canada, such as in cities like Minneapolis and Calgary, we see a continental climate with significant seasonal variation. Winters are long and harsh, while summers can be quite warm. This climate supports agriculture like wheat and barley, which requires distinct growing seasons.
In contrast, moving eastward to cities like New York and London, which are also on similar latitudes, we notice a more temperate maritime climate. The Atlantic Ocean moderates temperatures, leading to milder winters and more consistent rainfall throughout the year. This climate is excellent for growing crops like corn and soybeans in the U.S. and barley and oats in the U.K.
Interestingly, as we look at southern Europe, for example, Spain and Italy, which share latitudes with parts of the U.S. such as southern Texas, we see a shift towards a Mediterranean climate characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is perfect for growing olives, grapes, and citrus fruits, showcasing how latitude can lead to diverse agricultural practices even among regions that are aligned on the same parallel.
Significance and Impact
Understanding how latitude influences various factors is crucial for addressing real-world challenges. As climate change continues to affect weather patterns globally, regions sharing similar latitudes may experience shifts in agricultural viability, biodiversity, and even migration trends. For instance, if certain areas become less hospitable due to climate shifts, populations might move toward regions with similar latitudinal climates that are still conducive to agriculture and livability.
Moreover, the interconnectedness brought about by globalization means that regions at similar latitudes might also share economic ties and cultural exchanges, further emphasizing the importance of geographic understanding. As we approach the challenges of the 21st century, recognizing these latitudinal relationships will be key to fostering sustainable development and resilience in the face of environmental changes. In conclusion, this map is not just a collection of lines; it represents a complex web of interactions that shape our world, from climate to culture, agriculture to urbanization.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 18, 2025
- Views
- 58
Comments
Loading comments...