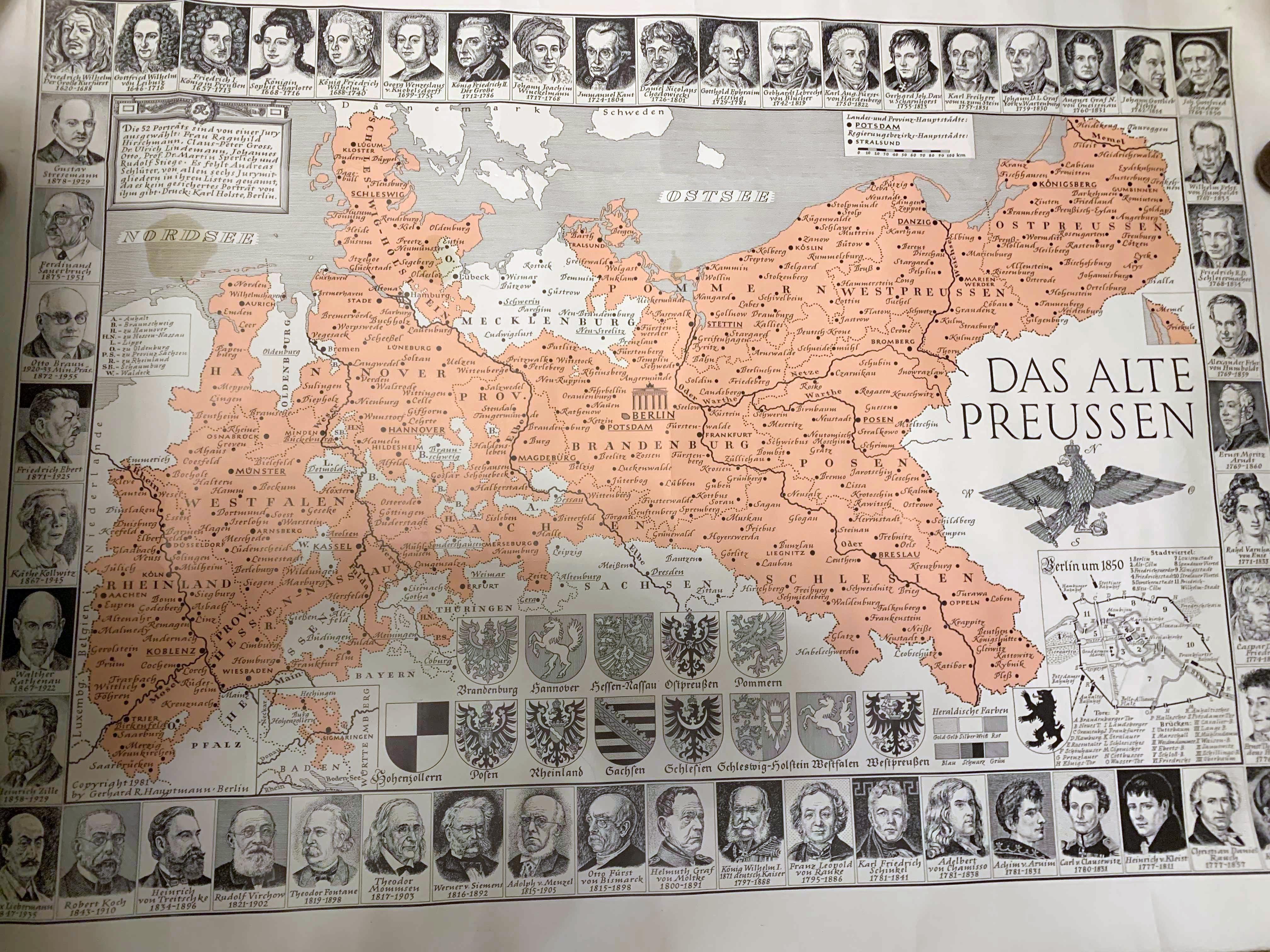
Map of Old Prussia Before World War I

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This illustrated map of Prussia, created in the 1980s, depicts the historical boundaries and territories of Prussia before the tumultuous events of World War I. The map vividly illustrates not just geographical features but also the distribution of key cities, towns, and the cultural landscape of a region that played a significant role in European history.
As we delve deeper into the topic of Prussia, it’s essential to understand the historical significance of this region and how its geography influenced political dynamics, economic activities, and cultural developments.
Deep Dive into Prussia's Geography and Historical Context
Prussia, at its height, was a powerful state in Europe, known for its military might and significant contributions to European politics and society. The territory of Prussia encompassed parts of present-day Poland, Russia, and Germany, showcasing a complex tapestry of cultural and linguistic diversity.
Interestingly, the geographical layout of Prussia included vast plains, dense forests, and a long coastline along the Baltic Sea. These features not only provided resources such as timber and fish but also shaped the settlement patterns of various groups over centuries. The northern regions, often influenced by maritime trade, developed bustling ports like Danzig (modern-day Gdańsk), which became vital for commerce.
Have you ever wondered how the rivers in Prussia influenced its development? The Vistula River, for example, served as a crucial waterway for trade and transport, linking inland areas to the sea. The navigable rivers facilitated the movement of goods and people, enhancing economic prosperity and cultural exchange.
Moreover, the population density in Prussia varied significantly across regions. The eastern parts, rich in agricultural land, were home to a predominantly rural population, while the western regions, particularly around cities like Königsberg (now Kaliningrad), experienced rapid urbanization and industrial growth. By the early 20th century, Prussia was witnessing significant demographic shifts, with urban centers expanding and populations migrating for jobs in emerging industries.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map, we see distinct regions within Prussia that highlight interesting contrasts. For instance, in the West, areas like Posen (Poznań) were characterized by a mix of Polish and German populations, leading to cultural tensions that would later play a role in the region's historical narrative. In contrast, the northern coastal areas, influenced by Germanic settlers, maintained a more homogeneous cultural identity, reflecting the language and traditions that persisted there for centuries.
The eastern territories of Prussia, particularly East Prussia, exhibited a unique blend of cultures, including Lithuanian and Polish influences. This diversity enriched the region's cultural landscape, visible in language, cuisine, and architecture. However, it also created friction among ethnic groups, which became more pronounced as nationalist movements gained momentum in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Interestingly, the map also reflects the significant impact of World War I on the region's borders and demographics. The Treaty of Versailles in 1919 drastically altered the map of Europe, leading to the loss of territories that were once part of Prussia and setting the stage for future conflicts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geography and historical context of Old Prussia is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to contextualize the rise and fall of national identities in Central and Eastern Europe. The borders established and altered during this period continue to influence modern geopolitical landscapes.
Additionally, the cultural legacies of Prussia, such as its contributions to education and military organization, are still felt today, particularly in the fields of governance and public administration. The Prussian model of education, which emphasized discipline and rigor, has influenced educational systems worldwide.
As we look towards the future, the lessons from Prussia's history can inform current discussions on nationalism, regional autonomy, and cultural identity in Europe. The complex interplay between geography and human experience in Prussia serves as a reminder of how past events shape present realities.
In conclusion, the illustrated map of Old Prussia not only serves as a historical artifact but also as a lens through which we can better understand the intricate relationship between geography, culture, and politics in shaping the course of European history.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 23, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...