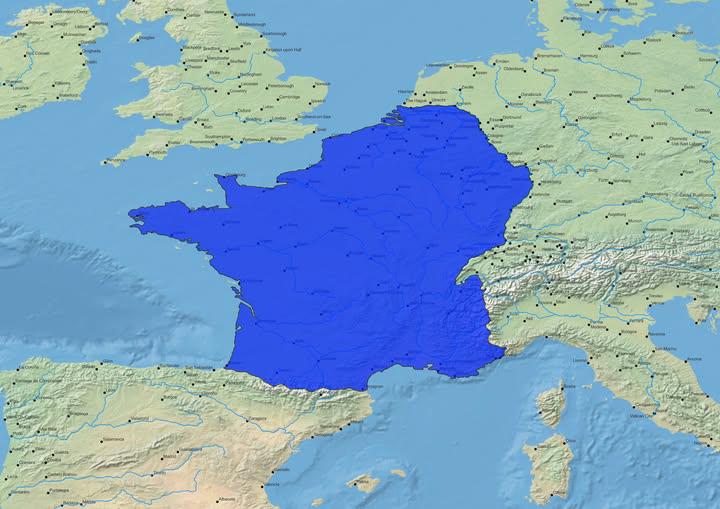
Map of the Natural Borders of France

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Map of the Natural Borders of France" illustrates the geographical features that have historically defined the boundaries of France. Originating from the Napoleonic era, this concept highlights natural formations such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines that serve as delineators of territory. These natural borders have played a crucial role in shaping not only the political landscape of France but also its cultural and historical identity.
Deep Dive into Natural Borders
Natural borders are significant geographical features that serve as boundaries between territories. In the case of France, these borders are predominantly defined by its mountain ranges, rivers, and the coastline. The concept of natural borders emerged during the Napoleonic era, promoting the idea that physical geography should dictate political boundaries. This was a departure from arbitrary lines drawn on maps, emphasizing the importance of geographical features in determining the identity and unity of a nation.
Mountains such as the Alps and the Pyrenees are prominent natural borders that separate France from its neighboring countries. The Alps, stretching along the southeastern border with Italy and Switzerland, are among the highest mountains in Europe. They not only provide a formidable barrier but also contribute to the biodiversity and climate variability in the region. Interestingly, the Pyrenees form a natural frontier between France and Spain, creating distinct cultural differences that persist to this day.
Rivers also play a critical role in defining natural borders in France. The Rhine River, for instance, acts as a boundary with Germany in the northeast. It has historically served as a trade route and a line of defense, impacting the development of towns and cities along its banks. The Loire River, while not a border with another nation, has been significant in French history, serving as a natural divider between regions and influencing settlement patterns.
The coastline of France, stretching from the northern shores along the English Channel to the Mediterranean Sea in the south, further illustrates the concept of natural borders. The various bays, estuaries, and cliffs not only define the nation's limits but also contribute to France's rich maritime heritage. The coastal regions have historically been vital for trade and cultural exchange, linking France to the broader world.
Regional Analysis
In examining the map, we can see how different regions in France are influenced by their natural borders. For example, the southeastern region, dominated by the Alps, has a unique climate and ecology compared to the northern flatlands. The high altitude of the Alps results in cooler temperatures and distinct flora and fauna, offering a stark contrast to the temperate climate of northern France.
In the region of Aquitaine, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean, the natural coastal barrier has fostered a rich maritime culture. Towns such as Bordeaux have thrived due to their proximity to the sea, relying on fishing, trade, and tourism as economic drivers. In contrast, the mountainous regions of Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes have developed economies based on agriculture and tourism, drawing visitors for skiing and hiking.
Moreover, the historical significance of these natural borders becomes apparent when looking at the cultural identities of different regions. For example, the Basque country in the Pyrenees showcases a unique blend of French and Spanish cultures, highlighting how natural barriers can influence not only political boundaries but also cultural exchanges and identity formation.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the natural borders of France is essential for grasping the historical and contemporary significance of these geographical features. These borders have shaped France's political landscape, influencing territorial claims, regional governance, and cultural identities. They remind us that geography is not merely a backdrop but an active component in the narrative of nations.
Today, the implications of natural borders are evident in discussions around environmental conservation and sustainability. Regions like the Alps face challenges related to climate change, such as glacial melting and biodiversity loss. As the effects of climate change intensify, the preservation of these natural borders becomes crucial for protecting not just the landscape but also the cultural heritage tied to these areas.
Looking ahead, the concept of natural borders may continue to influence regional planning and development in France. With increasing urbanization and environmental challenges, there’s a growing need to balance human activities with the preservation of natural landscapes. This balance will be vital for maintaining the unique characteristics of each region while addressing the needs of a modern society.
In conclusion, the "Map of the Natural Borders of France" serves as a reminder of the deep connections between geography, history, and culture. By appreciating these natural features, we can better understand the complexities of national identity and the pressing issues facing our environment today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 16, 2025
- Views
- 14
Comments
Loading comments...