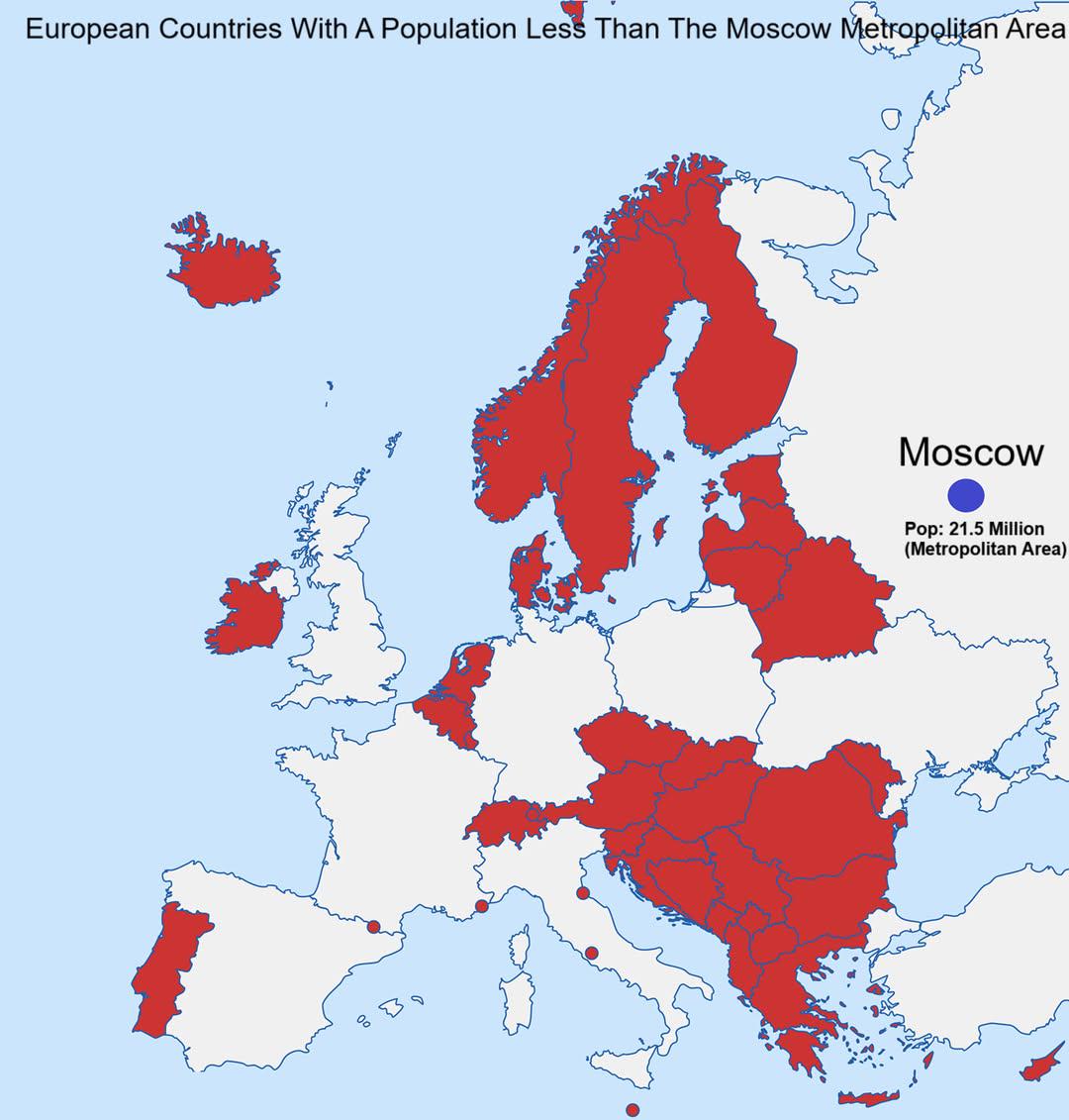
European Countries With Population Less Than Moscow Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map visualizes the European countries whose populations are smaller than that of the Moscow metropolitan area, which boasts a staggering population of around 12 million people. By highlighting these countries, we gain insight into the demographic disparities across Europe. While some nations are bustling with life, others remain less populated, presenting a fascinating picture of urbanization and population distribution.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution in Europe
Population distribution is a key factor in understanding the socio-economic landscape of a region. In Europe, the population is not evenly spread out; instead, it is concentrated in urban areas, particularly in capitals and major cities. For instance, Moscow stands as a major metropolis, drawing people from across Russia and beyond due to its economic opportunities, cultural attractions, and educational institutions.
Interestingly, when we look at countries with populations smaller than Moscow's metropolitan area, we find nations like Iceland, Malta, and Luxembourg. These countries often have unique characteristics that influence their demographic profiles. For example, Iceland, with a population of roughly 370,000, is known for its stunning landscapes and low population density, which can be attributed to its geography and the harsh climate. On the other hand, Malta, with about 514,000 residents, is one of the world's smallest and most densely populated countries, showcasing a very different demographic reality.
Moreover, the population sizes of these countries can be influenced by various factors, including economic opportunities, migration patterns, and historical contexts. For instance, nations like Luxembourg, which has a population of around 634,000, have seen significant growth due to their favorable economic conditions and the influx of expatriates seeking work. This contrasts sharply with countries like Estonia or Slovenia, which, while having larger populations than the smallest nations, still fall short when compared to the bustling life of Moscow.
Diving deeper, it’s crucial to consider the implications of these differences. Smaller populations can mean fewer resources, which might affect infrastructure development, healthcare, and education systems. For example, Iceland excels in providing quality healthcare and education despite its small population, largely due to its substantial investment in social welfare systems. However, this can also lead to challenges, like a limited labor market or difficulties in sustaining certain industries.
Regional Analysis
Breaking this down regionally, we can observe some interesting trends. For instance, the Nordic countries—like Iceland and Finland—tend to have smaller populations relative to their land area. This is largely due to their geographical features, such as mountains and extensive forests, which create a natural division in settlement patterns. Interestingly, Finland, with a population of about 5.5 million, is still significantly smaller than Moscow, despite hosting a well-developed urban infrastructure in cities like Helsinki.
In contrast, Southern European countries such as Malta and Monaco have high population densities, which can be attributed to their limited land area and attractive climates. Monaco, with a population density of over 25,000 people per square kilometer, illustrates how urban environments can thrive under certain geographical constraints.
Additionally, Eastern European nations like Latvia and Lithuania often find themselves in this category, with populations below 3 million. These countries have dealt with significant demographic shifts due to emigration and historical events such as the Soviet era, which have shaped their current population landscapes. The challenges these nations face regarding population decline and aging demographics are significant, as they seek to attract talent and maintain economic growth.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the population dynamics of these smaller European countries is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the varying challenges faced by different nations, particularly in terms of economic development, social services, and governance. Countries with smaller populations often need to devise innovative solutions to maintain their viability in a rapidly changing world. For instance, they might focus on enhancing tourism, diversifying economies, or investing in technology.
Moreover, as Europe grapples with issues such as migration, climate change, and economic inequality, the demographic profiles of these smaller nations can serve as case studies. They often provide unique insights into how countries can thrive despite limited resources. The ongoing trends of urbanization and population movement will likely continue to shape the European landscape, making it essential to monitor these developments closely.
In conclusion, the map of European countries with populations smaller than that of the Moscow metropolitan area offers a fascinating glimpse into the diverse demographic realities of the continent. It propels us to consider how geography, economy, and societal factors intertwine, influencing the lives of millions. As we navigate the future, understanding these dynamics will be critical to addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for Europe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 21, 2025
- Views
- 50
Comments
Loading comments...