Italy Land Cover Map 2024

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
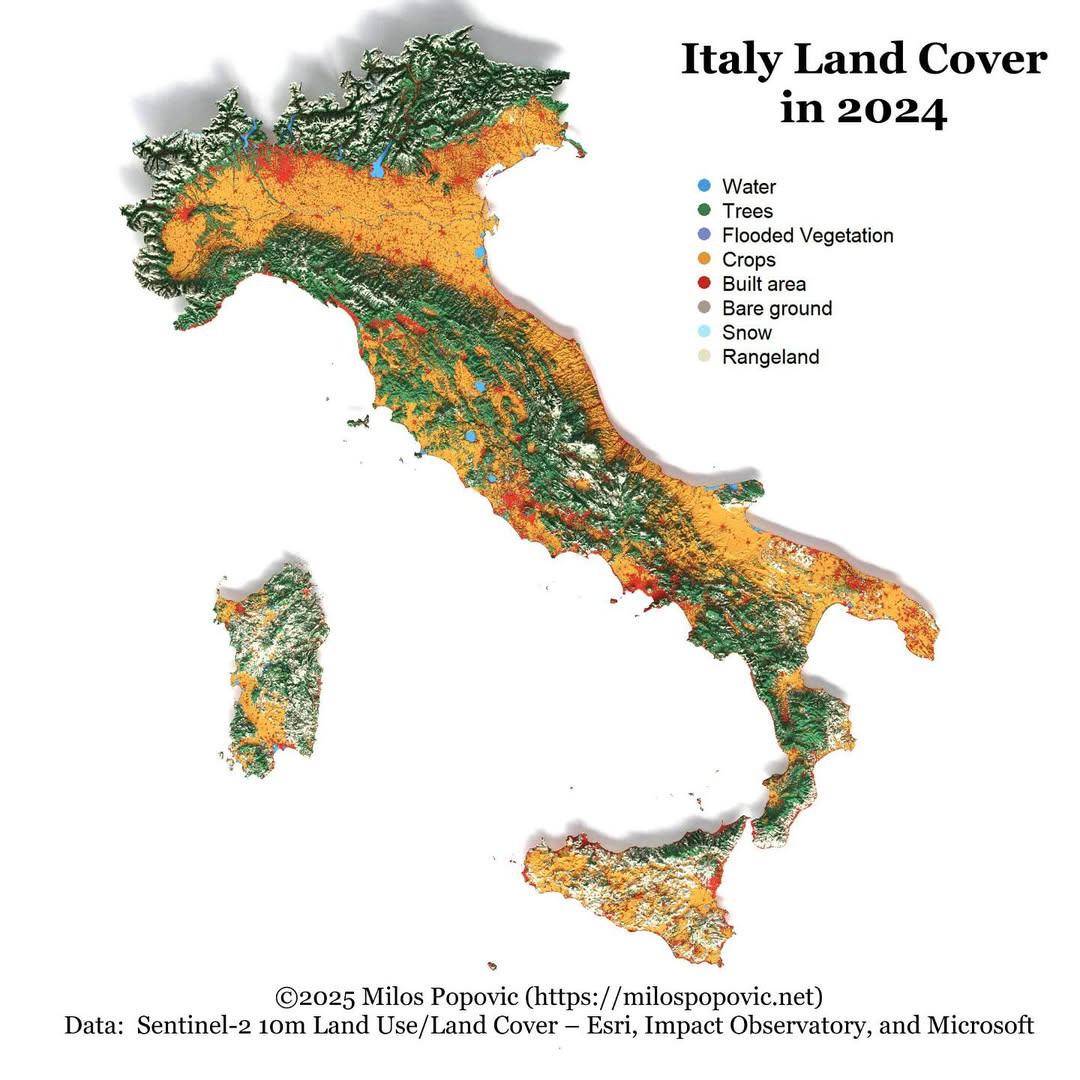
What This Map Shows
The "Italy Land Cover Map 2024" provides a comprehensive visualization of the various land cover types across Italy, illustrating how different areas are utilized and the natural landscapes that dominate the country. This map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the distribution of forests, agricultural land, urban areas, wetlands, and other land cover categories. Each color-coded section represents a distinct type of land cover, allowing viewers to quickly assess the ecological and anthropogenic features of Italy's diverse regions.
Deep Dive into Land Cover in Italy
Land cover refers to the physical and biological cover on the Earth's surface. In Italy, the variety of land cover types reflects the nation’s rich biodiversity and varied climate zones. This map highlights several key components of Italy’s land cover.
Firstly, forests play a significant role in Italy's landscape, covering approximately 35% of the country. These woodlands, primarily found in the Apennine Mountains and the northern regions such as Trentino-Alto Adige and Friuli Venezia Giulia, are essential for maintaining biodiversity and supporting various wildlife habitats. Interestingly, Italy is home to a range of tree species, including the iconic Italian pine and various deciduous trees, which are vital for carbon sequestration and combating climate change.
Agricultural land is another prominent feature of the map, accounting for about 24% of Italy’s total land cover. The northern regions, especially Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna, are known for their intensive agricultural practices. These areas thrive on fertile plains and are celebrated for producing a variety of crops, from grains to fruits and vegetables. Have you ever wondered why Italy is famous for its wine? Regions like Tuscany and Piedmont showcase extensive vineyards that contribute to both local economies and cultural identity.
Urban areas, depicted in stark contrast to the surrounding green spaces, make up approximately 7% of Italy’s land cover. Major cities like Rome, Milan, and Naples exhibit significant urban sprawl, which has implications for land use and environmental sustainability. The growth of urban areas often encroaches on agricultural and natural lands, raising concerns about habitat loss and the balance between development and conservation.
Wetlands and water bodies, while less prominent on the map, are critical for maintaining ecological balance. Regions like the Po Delta are known for their rich biodiversity, supporting various aquatic species and acting as natural flood barriers. However, these ecosystems face challenges from pollution and climate change, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts.
Regional Analysis
Italy's land cover varies significantly from region to region, influenced by geography, climate, and human activity. For instance, the northern regions are characterized by a higher percentage of forest cover and agricultural land compared to the southern parts. In Trentino-Alto Adige, forests dominate the landscape, while Emilia-Romagna showcases vast agricultural fields.
In contrast, southern regions like Calabria and Sicily have a more diverse land cover, with a mix of agricultural areas and natural landscapes. Interestingly, these areas are often more arid, which leads to different agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of Mediterranean crops like olives and citrus fruits.
Urbanization trends also differ across regions. Northern cities have experienced rapid growth due to industrialization, while southern cities face challenges related to migration and economic opportunities. The map illustrates these differences, showing how land cover is shaped by socio-economic factors.
Significance and Impact
Understanding land cover is essential for various reasons. It informs land management policies, conservation efforts, and urban planning. As Italy faces challenges from climate change and urbanization, monitoring land cover changes becomes increasingly critical. For instance, the ongoing trend of urban expansion threatens agricultural lands, necessitating careful planning to balance development with sustainable practices.
Moreover, land cover has direct implications for biodiversity. With habitat loss due to urban sprawl and agricultural expansion, many species are at risk. Conservation initiatives must focus on preserving vital ecosystems and promoting sustainable land use practices. The future of Italy's landscapes depends on how effectively these challenges are managed, making discussions around land cover not only relevant but essential for the nation's ecological health and cultural heritage.
In conclusion, the "Italy Land Cover Map 2024" is not just a visual representation; it encapsulates the intricate relationship between nature and human activity across Italy. Understanding these dynamics can help inform better decisions for the future of this beautiful country.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 17, 2025
- Views
- 48
Comments
Loading comments...