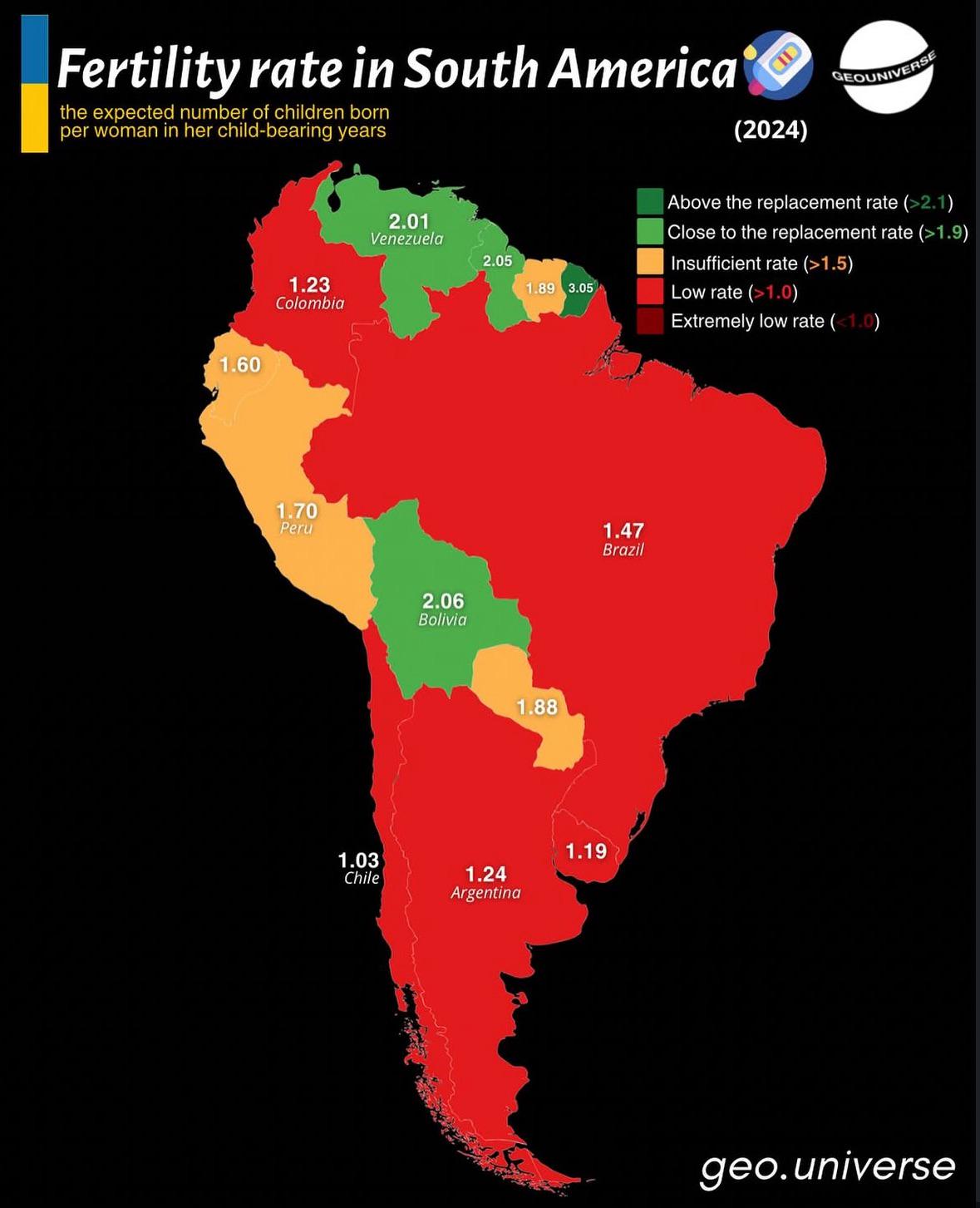
Fertility Rate Map of South America

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Fertility Rate Map of South America" provides a visual representation of the birth rates across different countries in this vibrant continent. Each country is color-coded to indicate its fertility rate, which is typically measured as the number of live births per woman over her lifetime. This map allows us to quickly grasp the disparities in fertility rates across South America, which can be influenced by various social, economic, and cultural factors.
Deep Dive into Fertility Rates in South America
Fertility rates are a crucial demographic indicator that reflect the reproductive behavior of women in a given region. In South America, the fertility rate has undergone significant changes over the past few decades. For instance, in the 1960s, many South American countries had fertility rates exceeding five births per woman. However, as of the latest data, countries like Argentina and Chile have seen rates drop to around 1.8 and 1.6, respectively, which are below the replacement level of 2.1 births per woman.
What's fascinating is how these changes mirror broader social transformations. Increased access to education, particularly for women, has played a pivotal role in lowering fertility rates. Countries like Brazil and Uruguay, which show fertility rates around 1.7 and 1.9, have made significant strides in women's education and employment opportunities. This empowerment allows women to make informed choices about family planning and childbearing.
Interestingly, the map illustrates notable outliers. Countries like Paraguay and Bolivia still report higher fertility rates—around 2.7 and 2.9 respectively. These nations often have more rural populations and traditional social structures that favor larger families. Cultural norms and economic factors, such as reliance on agriculture, can encourage higher birth rates as children are often seen as economic assets.
The decline in fertility rates also correlates with urbanization. As people migrate from rural areas to urban centers, family structures and lifestyles shift. Urban areas typically offer more resources for family planning and healthcare, which can lead to a decline in birth rates. Additionally, countries with stronger healthcare systems and family planning policies, like Colombia, which has a fertility rate of about 1.9, tend to have lower fertility rates compared to their neighbors.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing South America regionally, clear patterns emerge. The Southern Cone, which includes Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, displays some of the lowest fertility rates on the continent. This region benefits from economic stability and access to healthcare, contributing to family planning initiatives that promote smaller family sizes.
Conversely, in the Andean region, which includes Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador, fertility rates tend to be higher. Bolivia, for instance, stands out with a fertility rate nearing three births per woman, reflecting its more traditional societal norms and challenges in access to education and healthcare. Peru is in transition, with fertility rates dropping from 3.1 in the early 2000s to around 2.4 today, showcasing the impact of education and urbanization as well.
In the Northern region, countries like Venezuela and Guyana present a mixed picture. Venezuela's fertility rate has been fluctuating due to economic crises, but it remains above the replacement level. Guyana, with a fertility rate of approximately 2.4, reflects a blend of traditional values and modern influences, echoing the complexities of fertility trends across the continent.
Significance and Impact
Understanding fertility rates in South America is crucial for several reasons. High fertility rates can strain resources, impacting economic development, healthcare systems, and education. For policymakers, these statistics are vital for planning public services and anticipating future demographic shifts. For instance, countries with declining fertility rates may face challenges related to an aging population, while those with higher rates might need to enhance their infrastructure to support growing populations.
As we look to the future, trends in fertility rates will likely continue to evolve due to factors such as globalization, economic changes, and shifts in cultural perspectives on family and child-rearing. The implications of these changes are profound, affecting everything from economic growth to environmental sustainability. Ever wondered how demographic shifts might impact political landscapes in these countries? The interplay between fertility rates and governance is an area ripe for exploration and discussion.
As we navigate through the complexities of fertility rates in South America, it's clear that this map is not just a tool for visualization; it’s a window into the evolving dynamics of society, culture, and economics across the continent.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 26, 2025
- Views
- 94
Comments
Loading comments...