Obese Adults in India Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
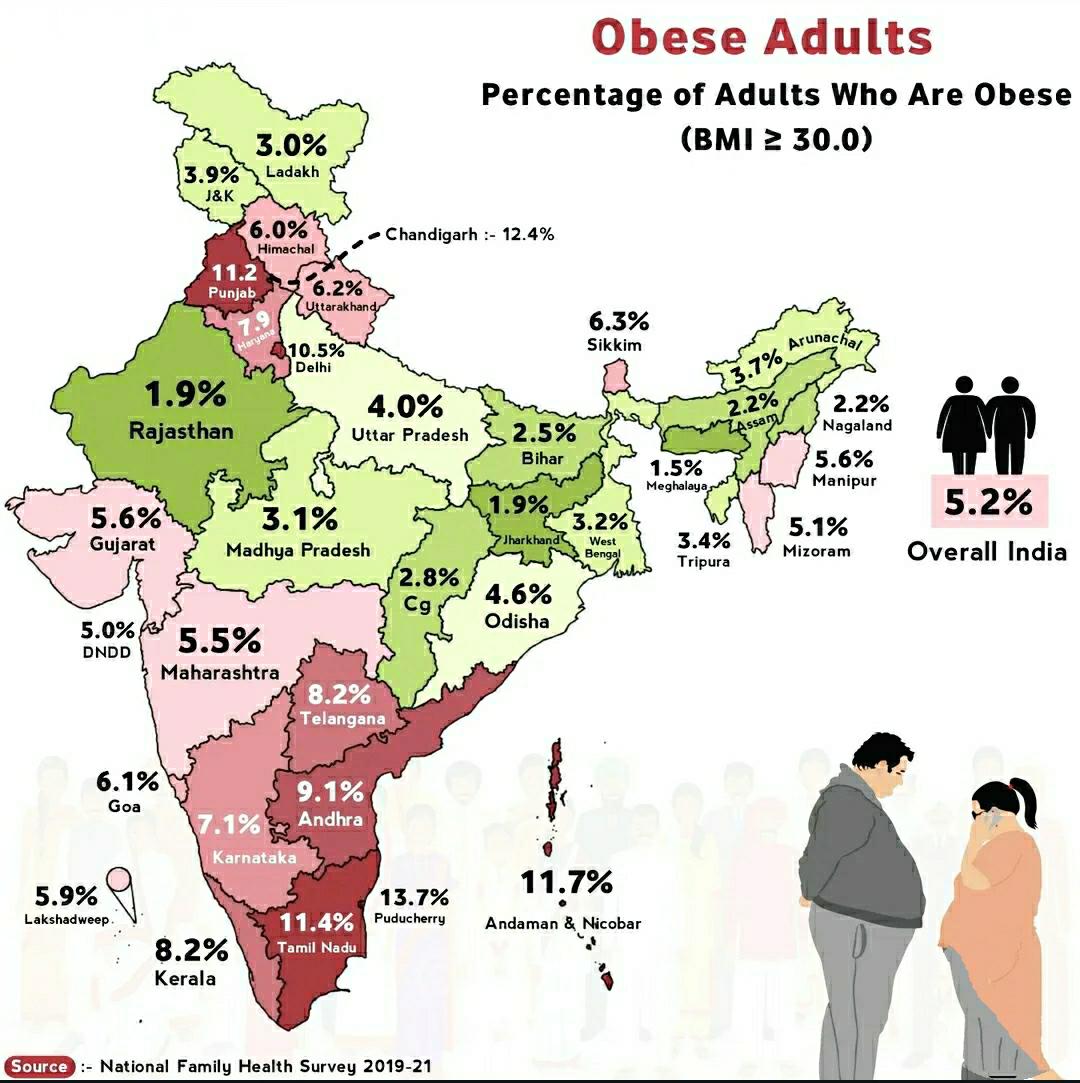
The "Obese Adults in India Map" provides a visual representation of the prevalence of obesity among adults across various states in India. It highlights the disparities in obesity rates, showcasing regions with higher and lower proportions of obese adults. This map serves as a critical tool for understanding the public health crisis of obesity in India, a country experiencing rapid changes in lifestyle and dietary habits.
Deep Dive into Obesity in India
Obesity has become a significant health concern in India, where the rise in overweight and obese adults has been alarming. As per the World Health Organization, obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. Interestingly, the increasing prevalence of obesity in India reflects a multifaceted issue involving urbanization, dietary transitions, and socio-economic factors.
In recent years, the obesity rate among Indian adults has surged. According to the 2019-2020 National Family Health Survey (NFHS), approximately 23% of men and 24% of women aged 15 years and older are classified as obese. This increase is primarily linked to changes in lifestyle, such as sedentary behavior and the consumption of high-calorie, processed foods. Ever wondered why such a rapid shift has occurred? The answer often lies in urbanization, where traditional diets are replaced by fast food and convenience items, leading to a higher caloric intake.
Moreover, the economic landscape plays a crucial role. Regions with greater economic development often report higher rates of obesity. For instance, urban areas like Delhi and Mumbai show alarming obesity rates due to higher incomes and easier access to unhealthy food options. On the other hand, rural areas, where access to such foods is limited, tend to have lower obesity rates. However, this is changing as global fast-food chains expand their reach into rural markets, potentially altering dietary patterns.
Additionally, cultural factors contribute to the obesity epidemic. In many Indian communities, a fuller body can be associated with wealth and prosperity. This perception can lead to normalized unhealthy eating habits, further exacerbating the issue. Interestingly, while India is still grappling with undernutrition, the rise of obesity presents a dual burden of malnutrition that complicates public health strategies.
Regional Analysis
The map vividly illustrates the stark differences in obesity rates across India’s diverse states. For example, states like Punjab and Haryana showcase some of the highest obesity rates, often attributed to affluent lifestyles and dietary habits rich in carbohydrates and fats. In contrast, states such as Bihar and Jharkhand have lower obesity rates, which can be linked to economic constraints and limited access to fast food.
In the southern states, Kerala and Tamil Nadu have notable obesity statistics as well. Kerala has seen increasing obesity rates, possibly due to a combination of urbanization and the adoption of Western dietary patterns. Tamil Nadu, while facing similar challenges, also sees a rising trend in obesity, particularly in urban centers like Chennai.
Interestingly, the northeastern states of India generally report lower obesity rates, as traditional diets that are rich in vegetables and lower in fats remain prevalent. However, there's a growing concern that as globalization impacts these regions, their obesity statistics may begin to shift.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the obesity landscape in India is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, the health implications are significant; obesity is a risk factor for numerous non-communicable diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. With India's healthcare system already under strain, rising obesity rates could lead to increased healthcare costs and a greater burden on health services.
Moreover, the socio-economic impact of obesity cannot be overlooked. A workforce that suffers from obesity-related health issues may lead to decreased productivity and economic output. This reality raises questions about the long-term sustainability of India’s economic growth.
Looking ahead, projections indicate that if current trends continue, India could see a further increase in obesity rates, necessitating urgent public health interventions. Initiatives promoting healthier lifestyles, better nutrition education, and increased physical activity are essential to combat this growing crisis.
In conclusion, the "Obese Adults in India Map" serves as a vital tool for understanding the complex public health issue of obesity in the country. By examining regional patterns and the underlying factors contributing to this epidemic, stakeholders can work towards effective strategies to promote healthier lifestyles and improve the overall health of the population.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 24, 2025
- Views
- 152
Comments
Loading comments...