Cities with Over 100,000 Inhabitants in 1700 Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
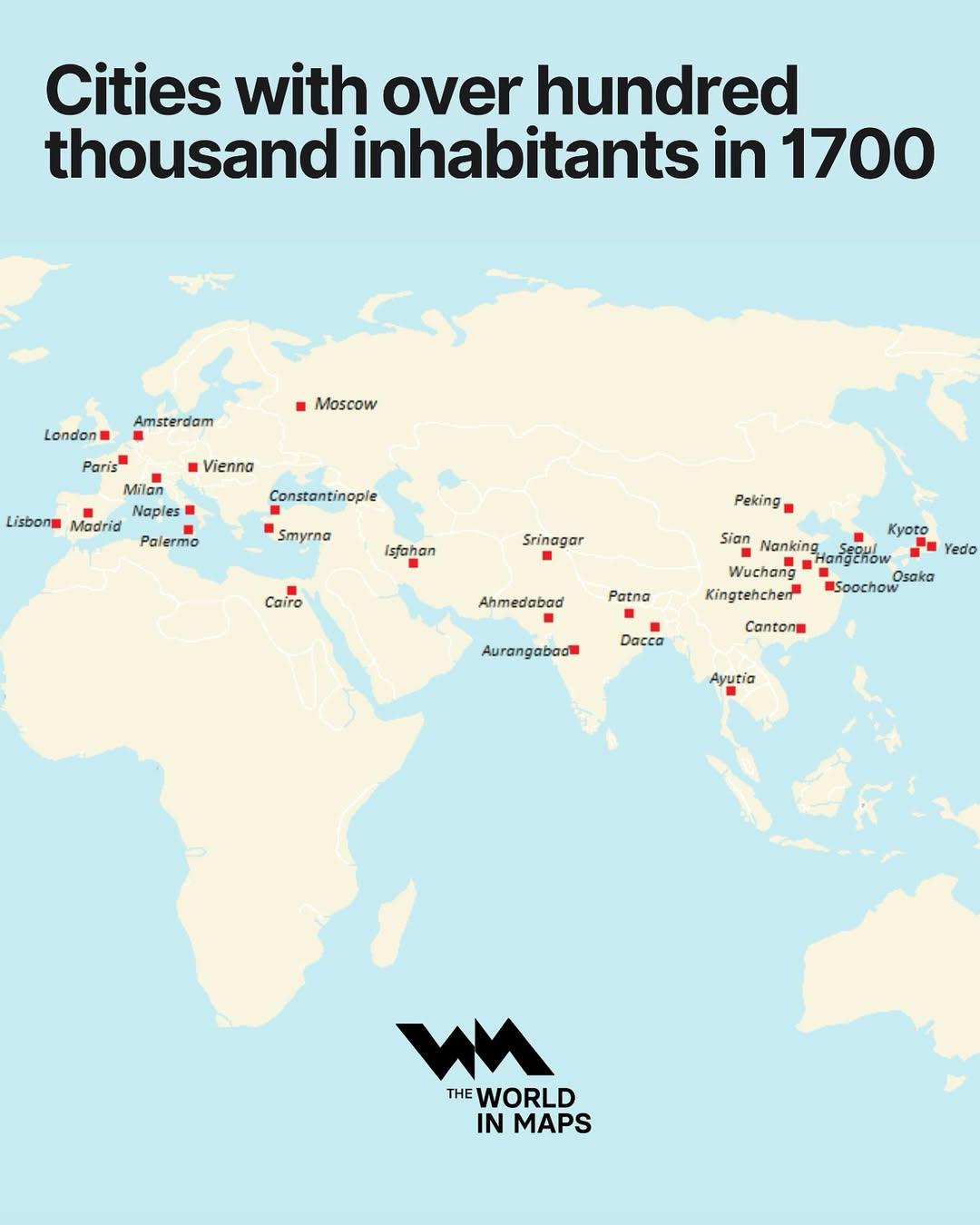
What This Map Shows
The "Cities with Over 100,000 Inhabitants in 1700 Map" provides a fascinating glimpse into urbanization during the early modern period. It highlights the cities that reached this demographic milestone, offering insights into population distribution and the centers of commerce, culture, and power at that time. As we delve into the specifics of urban development, we can appreciate how these cities laid the groundwork for the modern urban landscape.
Deep Dive into Urban Population in 1700
In 1700, the world was undergoing significant transformations, particularly in its urban centers. Cities were not merely collections of buildings; they were hubs of economic activity, political power, and social interaction. The map indicates that only a select few cities around the globe surpassed the 100,000 inhabitant mark, showcasing the stark contrast between urban and rural life during this era.
For instance, cities like Beijing, Istanbul, and Paris were among the largest, each boasting populations well into the hundreds of thousands. Interestingly, Beijing, with its rich history and status as the capital of the Qing Dynasty, was likely the largest city globally at the time, with estimates around one million inhabitants. The density of the population in such cities was crucial for trade and governance, as they served as critical nodes in international trade networks.
Additionally, demographic factors played a pivotal role in shaping these urban centers. Migration patterns significantly influenced population sizes, with many individuals moving to cities for economic opportunities or fleeing from rural hardships. Urbanization was also driven by advancements in agriculture, which allowed fewer people to produce more food, thereby supporting larger urban populations.
Moreover, the social fabric of these cities was rich and diverse. Major urban centers often became melting pots of cultures, as people from various backgrounds converged. This diversity fueled innovation, economic growth, and the exchange of ideas, ultimately contributing to the Enlightenment and the eventual industrial revolution.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes apparent that Europe and Asia dominated the list of cities with populations exceeding 100,000 in 1700. In Europe, cities like London, Paris, and Amsterdam were not just large; they were also influential. London, with a population estimated between 575,000 and 700,000, was a burgeoning center of trade, politics, and culture. The Thames River facilitated commerce, making London a significant player in global trade networks.
In contrast, the situation in Asia revealed a different story. While cities like Beijing and Istanbul were large, their growth was often tied to imperial and dynastic ambitions. For example, Istanbul, formerly known as Constantinople, was not only the seat of the Ottoman Empire but also a vital crossroads for trade between Europe and Asia. Its population was around 700,000, reflecting its importance in connecting diverse cultures and economies.
Interestingly, the Americas were just beginning to see the emergence of larger urban centers in 1700. Cities like Mexico City and Lima were growing but were still far behind their European and Asian counterparts. Mexico City, with its strategic position and rich resources, started to climb the ranks but had not yet reached the hundred-thousand mark.
Significance and Impact
Why does understanding the population distribution of cities in 1700 matter? For one, it sheds light on the historical context of urbanization and the evolution of cities into the bustling metropolises we know today. The concentration of populations in these early cities laid the groundwork for future developments in infrastructure, governance, and social structures.
Furthermore, the patterns of urban growth observed in 1700 continue to resonate in today's world. Modern cities face challenges such as overpopulation, resource management, and sustainability—all issues that can trace their origins back to the dynamics established in these early urban centers. As we look toward the future, understanding these historical population trends can provide valuable insights into managing contemporary urban challenges effectively.
Have you ever considered how the population dynamics of the past influence our present? The connections are indeed profound, and as cities continue to expand and evolve, reflecting on their history can offer guidance on navigating future complexities. The cities that flourished in 1700 were not just statistical points on a map; they were vibrant ecosystems that shaped human civilization and continue to impact our lives today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 22, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...