Soviet Annexations in 1939-1940 Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
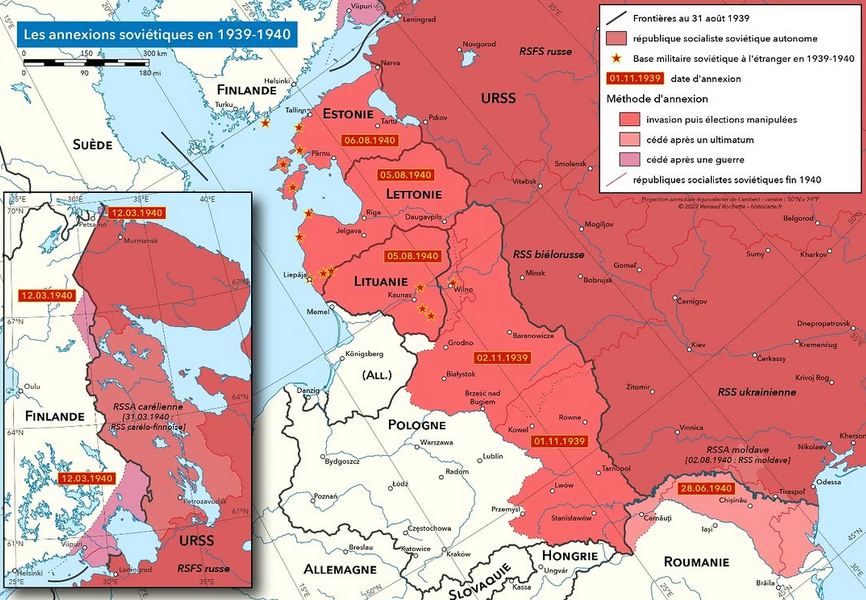
What This Map Shows\nThis map illustrates the significant territorial changes that occurred during the Soviet annexations between 1939 and 1940. It highlights the regions that the Soviet Union incorporated into its territory following the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, a secret agreement between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. The visualization details how various territories, including parts of Poland, the Baltic States, and regions of Finland, were absorbed into the Soviet sphere, reshaping the geopolitical landscape of Eastern Europe.
Deep Dive into Soviet Annexations\nThe period of 1939 to 1940 was marked by dramatic shifts in territorial boundaries, largely influenced by the ideological and strategic objectives of the Soviet regime under Joseph Stalin. Following the signing of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact in August 1939, which delineated spheres of influence between the two totalitarian regimes, the Soviet Union began its aggressive expansion into neighboring territories, culminating in the onset of World War II.
One of the most significant events was the invasion of Poland in September 1939. The Soviet forces entered from the east, occupying the areas defined in the secret protocols of the pact. This annexation not only altered Poland's borders but also led to the division of the country between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, profoundly affecting the Polish populace and setting the stage for future conflicts.
In the Baltic States, the Soviets quickly moved to establish control over Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. By mid-1940, these nations were fully annexed, and the Soviet government imposed its political and economic systems, effectively erasing their independence. Interestingly, this annexation was met with varying degrees of resistance and compliance among the local populations, highlighting the complex interplay of nationalism and Soviet power.
Finland also faced the brunt of Soviet expansionism. Although the Winter War (1939-1940) presented a fierce resistance from Finnish forces, the conflict ultimately resulted in territorial concessions. The Soviet Union gained significant territories in Karelia, including cities like Viipuri (Vyborg), which were strategically important and rich in resources.
What’s fascinating is how these annexations were not just about land but were also efforts to spread Soviet ideology and reshape the social fabric of the occupied territories. The imposition of Soviet governance often involved the suppression of local cultures and political dissent, leading to long-lasting tensions and conflicts that would resonate in the decades to follow.
Regional Analysis\nExamining the map reveals distinct regional patterns in the Soviet annexations. In Poland, for instance, the eastern regions were integrated into the Ukrainian and Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republics, significantly impacting the ethnic composition of these areas. The Polish population faced repression, forced deportations, and a complete overhaul of their societal structures.
In the Baltic States, the annexation resulted in a swift and brutal transformation. Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania were subjected to significant Sovietization efforts, including the suppression of local languages, cultures, and political institutions. Interestingly, the local responses varied; while some people collaborated with the Soviet authorities, others engaged in resistance movements that would continue throughout the Soviet era.
Conversely, Finland’s experience during this period was characterized by a fierce defense of sovereignty. The Winter War, despite its eventual territorial losses, showcased Finnish resilience and garnered international sympathy, setting the stage for Finland's unique position in post-war Europe. This resistance helped Finland maintain a degree of independence that many of its neighbors did not achieve.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the Soviet annexations of 1939-1940 is crucial for grasping the historical context of Eastern European geopolitics. These events were not isolated but rather set a precedent for future conflicts in the region, influencing the Cold War dynamics and the eventual fragmentation of the Soviet Union itself.
Moreover, the legacy of these annexations continues to be felt today. The borders drawn and the populations displaced during this tumultuous period contribute to ongoing ethnic tensions and political disputes in Eastern Europe. For example, the Baltic States have worked tirelessly to reclaim their national identities and strengthen their sovereignty in the face of historical oppression.
As we look to the future, the repercussions of these territorial changes remind us of the importance of understanding history in shaping contemporary relationships among nations. The map not only serves as a historical reference but also as a reminder of the complex narratives that define modern Eastern Europe. Have you noticed how historical events like these continue to influence discussions about national identity and sovereignty today?
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 11, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...