Map of the West Bank

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
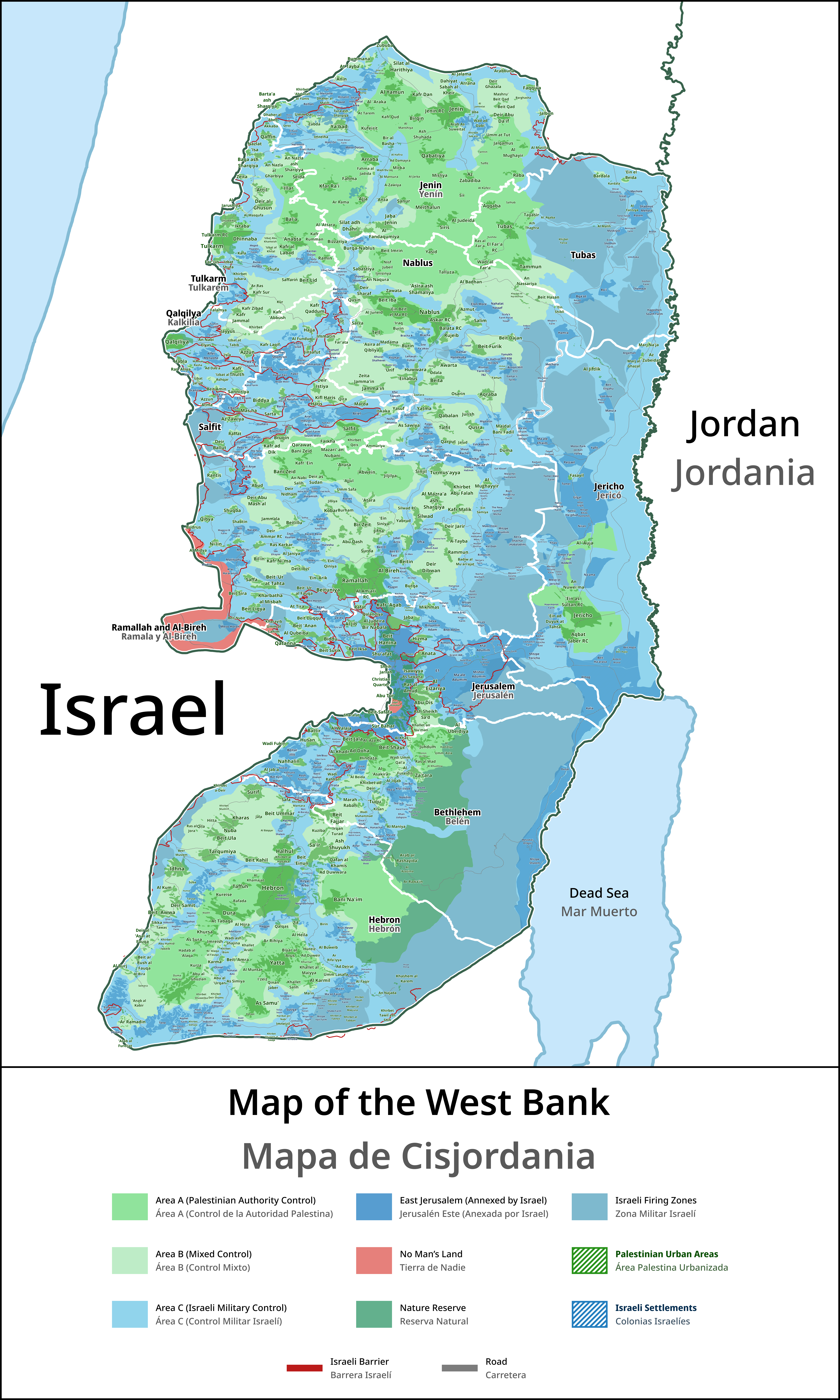
What This Map Shows
This visualization presents a detailed map of the West Bank, highlighting its geographical features, urban centers, and the complex layout of administrative boundaries. Covering an area of approximately 5,860 square kilometers, the map delineates key locations, including major cities like Ramallah, Hebron, and Bethlehem, as well as significant geographical landmarks and the intricate network of roads that connect various regions. The West Bank is situated in a politically sensitive area, bordered by Israel to the west and Jordan to the east, making it a focal point for both geographic and geopolitical discussions.
Deep Dive into the West Bank’s Geography
The West Bank is characterized by a diverse landscape that includes hills, valleys, and plateaus. The geography of the region plays a crucial role in its climate, agriculture, and settlement patterns. The northern part of the West Bank is predominantly hilly, with elevations reaching up to 1,000 meters above sea level, while the southern regions feature more rugged terrain. This variation in topography has significant implications for agriculture, as the fertile land in the valleys supports various crops, including olives, grapes, and citrus fruits.
Interestingly, the West Bank's climate is classified as a Mediterranean climate, with wet, mild winters and hot, dry summers. Average annual rainfall varies, with northern areas receiving more precipitation than the arid southern regions. This climatic diversity contributes to the rich agricultural potential of the area, but it also poses challenges, especially in terms of water resources, which are scarce and often contested.
The population of the West Bank is approximately 2.8 million, primarily composed of Palestinian Arabs. Urban development has been concentrated in cities like Nablus and Jenin, which serve as economic and cultural hubs. However, urban sprawl and the expansion of Israeli settlements have raised concerns about land use and demographic shifts. The map illustrates the distribution of these settlements, which are a significant aspect of the West Bank's socio-political landscape.
In terms of transportation, the West Bank is crisscrossed by a network of roads that connect cities and towns, but many of these routes are subject to restrictions and checkpoints, impacting mobility and trade. The map provides a clear view of these transportation arteries, highlighting how geography intertwines with daily life and commerce in the region.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the West Bank through this map, distinct regional characteristics emerge. For instance, the northern West Bank, particularly around Nablus, is known for its agricultural richness and historical significance, hosting ancient sites and vibrant markets. In contrast, the southern regions, including Hebron, have a more complex socio-political environment, with prominent historical and religious sites that draw both locals and tourists.
Furthermore, the central region, dominated by Ramallah, has become the administrative center for the Palestinian Authority. This area has seen significant urban development and economic growth, reflecting a shift towards modernization. However, the ongoing Israeli occupation and settlement expansion create stark contrasts between regions, affecting everything from resource distribution to social cohesion.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geography of the West Bank is crucial for grasping the broader socio-political dynamics at play in the region. The map not only highlights the physical landscape but also serves as a reminder of the challenges faced by the Palestinian population, including access to resources and movement restrictions.
Moreover, the implications of this geography extend into the realm of international relations, as the West Bank remains a focal point in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Future projections indicate that as urban areas continue to expand and demographic patterns shift, the pressures on land and resources will only intensify. This makes the understanding of the West Bank's geography not just an academic exercise, but a vital component of discussions surrounding peace, development, and sustainability in the region. Have you ever considered how geography shapes not only the landscape but also the lives of those who inhabit it? The West Bank is a compelling case study in this regard, rich with lessons on resilience and adaptability in the face of ongoing challenges.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 8, 2025
- Views
- 26
Comments
Loading comments...