Greenland vs. Africa Size Comparison Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
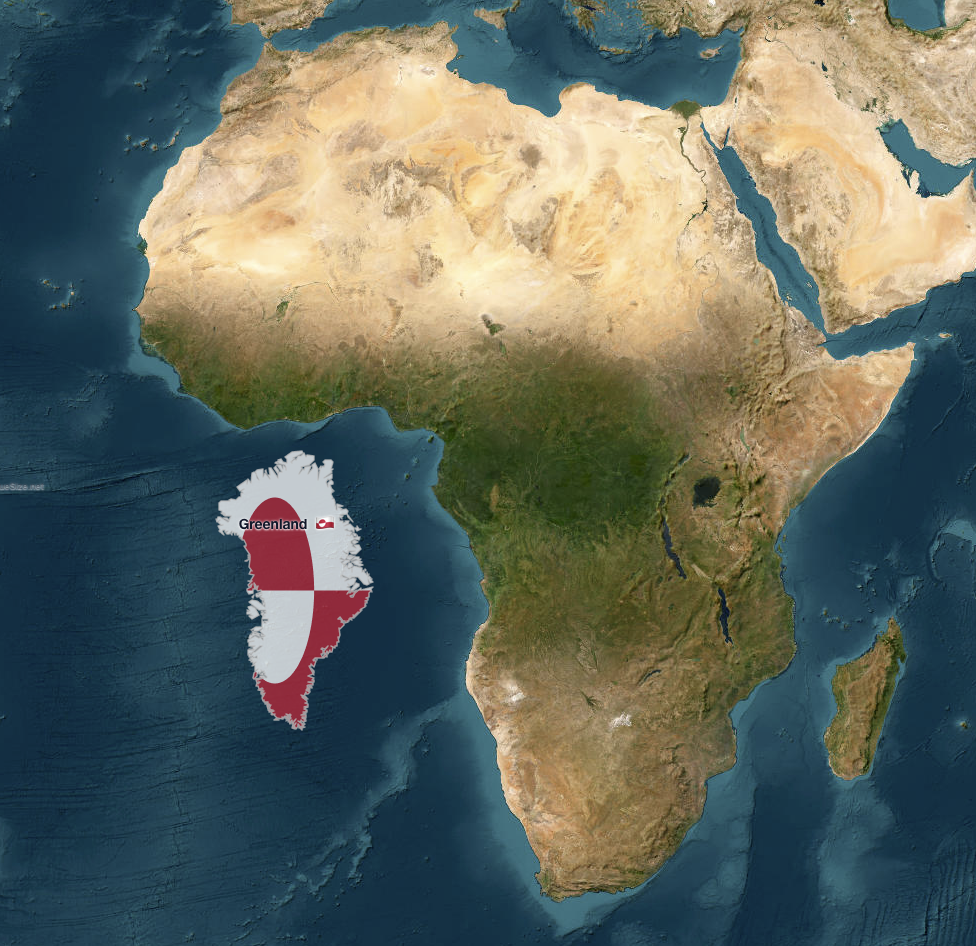
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Greenland vs. Africa — the real scale" provides a striking visual comparison of the land areas of Greenland and Africa, highlighting a common misconception about the relative sizes of these two regions. While Greenland is often depicted as a large landmass in maps, its true size is dwarfed by the vast continent of Africa. This visualization serves not only to correct the geographic misrepresentation but also to invite a deeper understanding of the geographical context and significance of these areas.
Deep Dive into Land Areas and Geography
When it comes to land area, Africa is impressively large, covering approximately 30.37 million square kilometers. In contrast, Greenland, the world's largest island, measures around 2.16 million square kilometers. This means that Africa is roughly 14 times larger than Greenland. Interestingly, many maps, especially those that utilize the Mercator projection, can exaggerate the size of Greenland relative to Africa and other landmasses. This is primarily due to the way the Mercator projection distorts areas further from the equator, making regions like Greenland appear disproportionately large.
Africa is not just a vast landmass; it is incredibly diverse in terms of geography, ecosystems, and climates. The continent is home to deserts, rainforests, savannas, and mountain ranges. For instance, the Sahara Desert, which spans approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, is the largest hot desert in the world. In contrast, Greenland's landscape is predominantly characterized by its ice sheets, glaciers, and tundra. These geographical features significantly shape the climates and ecosystems of both regions, influencing everything from biodiversity to human settlement patterns.
Moreover, Africa's geographical diversity leads to a variety of climate zones. From the arid conditions of the Sahara in the north to the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin in the central region, the continent experiences a wide range of weather patterns. Greenland, on the other hand, is largely categorized under Arctic climate conditions with cold temperatures and limited vegetation.
Have you ever considered how these geographical differences affect human activities? In Africa, the variety of climates allows for agriculture, mining, and tourism, contributing to the livelihoods of millions. Conversely, Greenland's harsh conditions lead to a reliance on fishing, hunting, and, increasingly, tourism that focuses on its unique landscapes and the effects of climate change.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, it's clear that Africa's size encompasses a multitude of regional variations. For example, North Africa, which includes countries like Egypt and Libya, is predominantly desert, leading to a sparse population density compared to Sub-Saharan Africa, which is home to bustling cities and diverse cultures. Countries like Nigeria and Kenya showcase rapid urbanization and population growth, a stark contrast to Greenland, where most of the population is concentrated along the western coast, primarily in the town of Nuuk.
In Southern Africa, nations like South Africa and Namibia illustrate how geography can influence economic development. With a mix of rich mineral resources and agricultural land, these regions are economically vibrant. This is quite different from Greenland, where the economy is heavily dependent on fishing, with limited agricultural opportunities due to the icy terrain.
Interestingly, the disparities in land area also reflect historical and socio-economic factors. Africa's vastness has allowed for a larger array of different cultures, languages, and traditions to flourish. In contrast, Greenland's small population and geographic isolation have led to a more homogenous culture centered around its Indigenous peoples, primarily the Inuit.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the real scale of Greenland versus Africa is more than just a cartographic lesson; it holds significant implications in various spheres, including environmental studies, geopolitics, and economics. As climate change continues to reshape our planet, the Arctic, where Greenland is located, is experiencing some of the most rapid changes. Melting ice sheets are not only altering global sea levels but also affecting global weather patterns.
On the flip side, Africa faces unique challenges and opportunities that arise from its geographical size and diversity. Issues such as climate change, resource management, and urbanization are critical as populations grow and economies develop. The continent is projected to have a population exceeding 2 billion by 2050, making it essential to address sustainable development that respects its varied environments while fostering growth.
In conclusion, the map comparison of Greenland and Africa serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of accurate representations in geography. It encourages us to rethink our perspectives about size, land use, and the intricate relationships between geography and human life. As we continue to face global challenges, understanding our planet's geography becomes ever more crucial for informed decision-making and effective policy development.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 7, 2025
- Views
- 54
Comments
Loading comments...