Lake Eyre Basin Map Australia

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
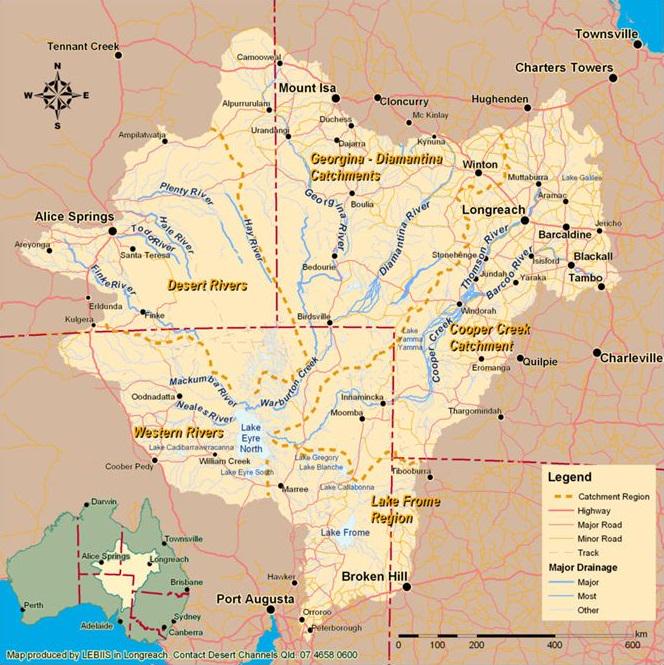
What This Map Shows
This visualization focuses on the Lake Eyre Basin, the largest endorheic lake system in Australia. Covering an expansive area of over 9,000 km² (3,500 sq mi), Lake Eyre typically presents itself as a vast, dry salt lake. However, the map highlights a significant transition; in 2025, following extreme rainfall events in Queensland, floodwaters began to flow into the basin, creating a dynamic and changing landscape. The map illustrates the pathways of these rivers and floodwaters, showcasing how they interact with the arid environment before eventually reaching Lake Eyre. The anticipated peak of these waters in October 2025 adds another layer of interest to this geographical phenomenon.
Deep Dive into Lake Eyre Basin
The Lake Eyre Basin is more than just a dry lake; it is a complex hydrological system that plays a critical role in the ecology and geography of Australia. An endorheic basin, Lake Eyre does not drain into the sea. Instead, its waters evaporate, leaving behind salt and minerals that create the distinctive salt flats seen today. Interestingly, this basin is fed by several rivers, including the Georgina, Diamantina, and Cooper Creek, which originate from the wetter regions of Queensland.
The hydrology of the Lake Eyre Basin is fascinating. The rivers that flow into the basin are often ephemeral, only carrying water during periods of significant rainfall. In 2025, a remarkable weather pattern brought extreme autumn rainfall to Queensland, leading to the flooding of these rivers. The flat terrain allows water to flow at a leisurely pace, sometimes just a walking speed, which means it takes time for the water to travel hundreds of kilometers across the desert landscape to reach Lake Eyre. This phenomenon underscores the unique climatic and geological features of the region.
As the floodwaters make their way to Lake Eyre, they create a temporary wetland environment that supports a variety of wildlife. The arrival of water can transform the usually stark landscape into a vibrant habitat, attracting migratory birds and other species that rely on these rare conditions. The ecological significance of this basin is immense, as it serves as a critical refuge for wildlife in an otherwise harsh environment.
The current situation in 2025 is particularly noteworthy. As the floodwaters begin to fill Lake Eyre, we anticipate that the lake will reach its peak in October 2025. This event will not only reshape the local ecology but will also have broader implications for the region's climate and water management practices. With rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns, understanding the dynamics of the Lake Eyre Basin is crucial for future conservation and sustainable use of its resources.
Regional Analysis
The Lake Eyre Basin spans multiple regions, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. The northern sections, primarily characterized by the Georgina and Diamantina rivers, often experience more rainfall and support a different type of vegetation compared to the southern parts, which are more arid. For example, the Cooper Creek area can experience significant flooding, leading to temporary lakes known as 'bodies of water' that can linger for months.
In contrast, the southern areas of the basin, particularly around Lake Eyre itself, are typically dry and sparsely vegetated. These regions often see much less rainfall, making them more susceptible to extreme drought conditions. The contrast in water availability across the basin has profound implications for land use, agriculture, and conservation efforts.
Interestingly, communities surrounding the Lake Eyre Basin have adapted their livelihoods to these conditions. Some areas utilize the seasonal flooding for irrigation, while others focus on tourism, particularly during peak water events. These activities highlight the basin's versatility and the varied ways in which different regions respond to its unique hydrological patterns.
Significance and Impact
The Lake Eyre Basin is significant not only for its ecological richness but also for its cultural and economic importance. The cyclical nature of flooding and drying has shaped the lifestyles of Indigenous communities for thousands of years. Understanding this basin is essential for appreciating the delicate balance between human activity and natural processes.
As we look towards the future, the impacts of climate change on the Lake Eyre Basin are becoming increasingly relevant. Predictions indicate that rainfall patterns may become more unpredictable, leading to either excessive flooding or prolonged droughts. This variability could affect everything from local agriculture to water resources management.
Moreover, the upcoming peak of water levels in October 2025 will serve as a critical indicator of how the basin responds to changing environmental conditions. Monitoring these changes will be essential for developing effective strategies to manage the basin sustainably, ensuring that it continues to support both its unique ecosystems and the communities that depend on it.
In summary, the Lake Eyre Basin is a remarkable geographical feature that encapsulates the interplay between water, land, and life in one of Australia's most extreme environments. Its future will depend on our understanding and management of this complex system as we navigate the challenges posed by climate change and human activity.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 9, 2025
- Views
- 86
Comments
Loading comments...