Population Map of Indonesia's Most Populous Islands

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
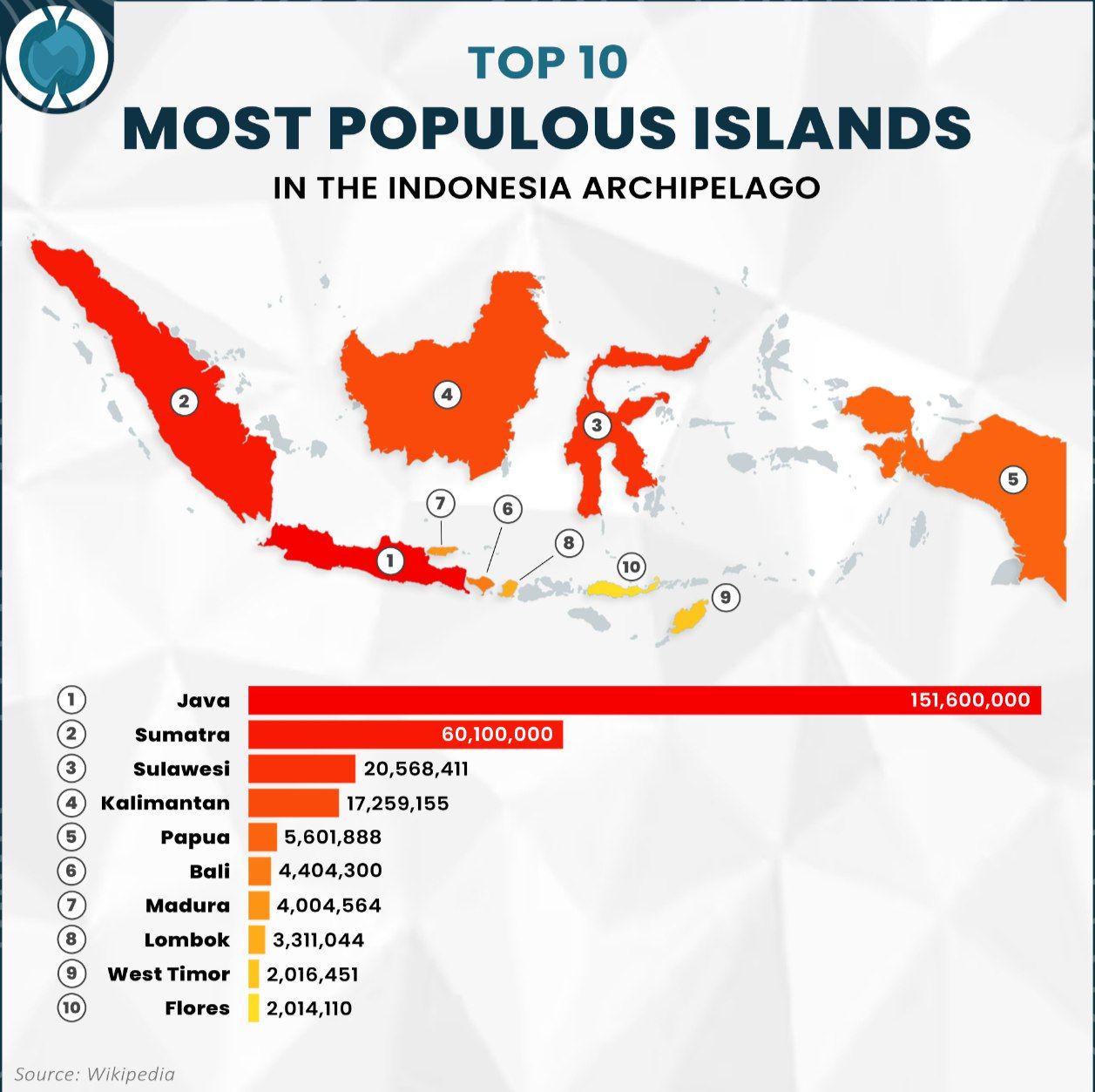
The visualization titled "Top 10 Most Populous Islands in the Indonesia Archipelago" provides a clear representation of the islands in Indonesia ranked by their population size. Indonesia, as the world's largest archipelago, consists of over 17,000 islands, making it a fascinating study in terms of human geography and population distribution. This map highlights the ten islands with the highest population, detailing how Indonesia's inhabitants are spread across its vast maritime expanse.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution in Indonesia
Let's delve into the fascinating topic of population distribution in Indonesia. The country is not only known for its stunning landscapes and rich culture but also for its significant demographic diversity. As of the latest estimates, Indonesia's population is around 270 million, making it the fourth most populous country in the world. The population density varies dramatically across the archipelago, with some islands hosting millions of residents while others remain sparsely populated.
Java, the most populous island, is home to over 150 million people, accounting for approximately 56% of the country's total population. This island is where the capital city, Jakarta, is located, which itself is one of the most densely populated urban areas globally. Interestingly, the concentration of people in Java can be attributed to historical factors, including its role as the political and economic center of Indonesia. Urbanization has surged in recent decades, with people flocking to cities for better job opportunities and living conditions.
Following Java, Sumatra is the second-most populous island, hosting around 58 million residents. Unlike Java, Sumatra is rich in natural resources, which have historically attracted industries and workers. The island's demographic composition is diverse, with various ethnic groups, including the Acehnese, Batak, and Minangkabau. This diversity contributes to a vibrant cultural landscape, evident in the island's languages, traditions, and festivals.
Then we have Borneo (Kalimantan), which is shared with Malaysia and Brunei. Although its population is lower at about 16 million, it plays a crucial role in Indonesia's economic landscape due to its vast rainforests and rich biodiversity. However, deforestation and land conversion for palm oil plantations are critical issues here, which could affect future population trends as indigenous communities struggle with environmental changes.
Other notable islands include Sulawesi, with a population of roughly 19 million, and Bali, a smaller island with around 4.3 million residents. Bali is particularly interesting as it's a major tourist destination, and its demographic structure has been influenced significantly by tourism, which brings in an influx of both domestic and international migrants.
Regional Analysis
Now, let’s break down the population dynamics by regions as illustrated on the map. The western part of Indonesia, primarily Java and Sumatra, shows a high concentration of people. This part of the country is characterized by urban centers that attract a large workforce. For example, Jakarta alone has a population density of about 14,000 people per square kilometer, highlighting the pressures on infrastructure and housing.
In contrast, the eastern regions, such as Papua and the smaller islands, have a much lower population density, which can be as low as 10 people per square kilometer. These areas tend to be less developed, with challenges related to access, infrastructure, and economic opportunities. The stark contrast between these regions raises intriguing questions about resource allocation and development strategies.
Interestingly, while Java is bursting at the seams with people, the government is actively promoting migration to less populated islands to balance demographic pressures. Programs aimed at developing infrastructure and economic opportunities in regions like Sulawesi and Sumatra are gaining traction, potentially reshaping the demographic landscape in the years to come.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution in Indonesia is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. High population density in urban areas can lead to significant challenges, including traffic congestion, pollution, and inadequate public services. Conversely, underpopulated regions may not receive the investment they need to thrive.
Moreover, the demographic trends suggest potential shifts in economic focus. As urban areas continue to grow, there may be increased demand for sustainable urban development practices. The Indonesian government is looking into smart city initiatives that could address some of these challenges while promoting economic growth.
Future projections show that Indonesia’s population is expected to continue growing, albeit at a slower rate. By 2050, it’s estimated that the population could reach around 320 million. This growth will require careful planning and investment in infrastructure, education, and health services to ensure a sustainable future for all Indonesians. Have you ever considered how the population distribution could affect Indonesia’s role on the global stage? As the nation grows, its influence in regional and international affairs will likely expand, making it essential to understand the demographic landscape.
This map serves not only as a snapshot of where people live but also as a tool to engage with the broader narrative of Indonesia's development, culture, and future potential.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 166
Comments
Loading comments...