Population Density Map by Country

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
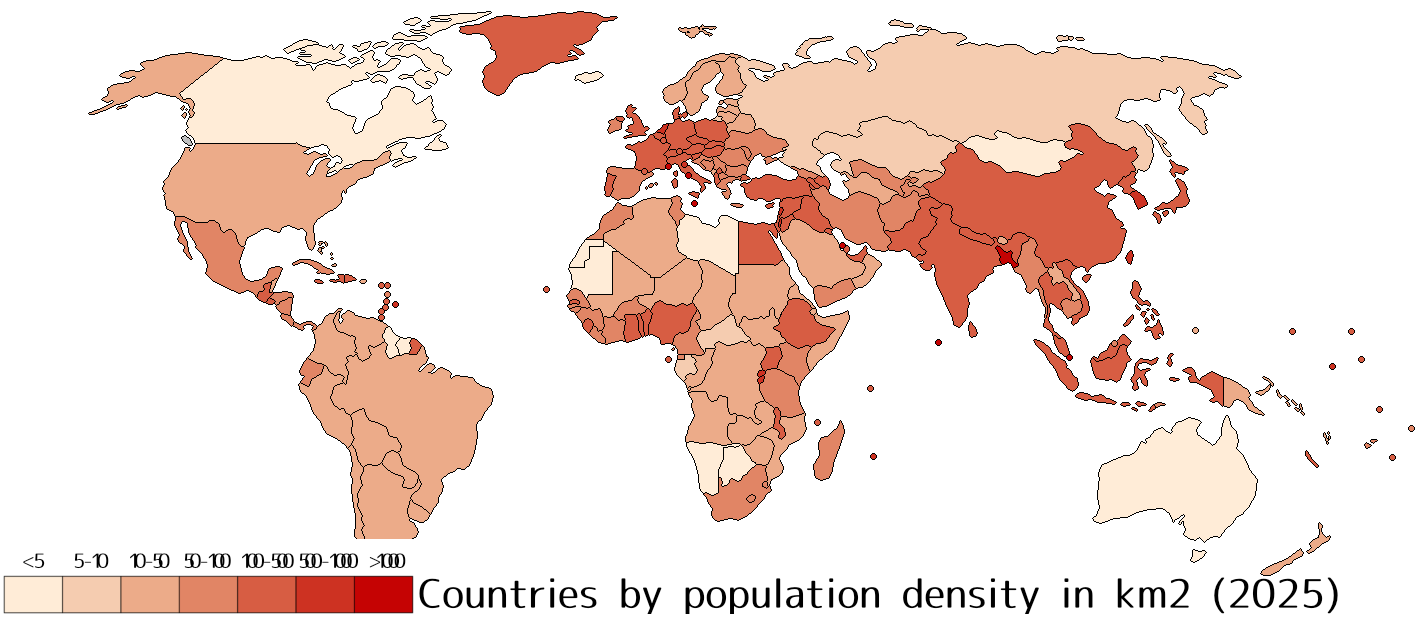
What This Map Shows
This visualization illustrates the population density of countries around the world, providing a clear perspective on how many people live in each area relative to its size. Population density, measured as the number of people per square kilometer, offers insights into the spatial distribution of human populations. In this map, countries are color-coded to reflect their density levels, making it easy to identify regions of high and low population pressure. This kind of data is crucial for understanding urbanization trends, resource allocation, and potential environmental impacts.
Deep Dive into Population Density
Population density serves as a key indicator of demographic trends and urban development. It reveals how human populations are distributed across the globe and can be influenced by a multitude of factors, including geography, economic opportunities, and social structures. For instance, countries like Monaco and Singapore exhibit extremely high population densities, with Monaco boasting over 26,000 people per square kilometer. This density arises from limited land availability and a thriving economy, leading to a concentration of people in urban areas.
Conversely, large countries such as Canada and Russia have vast stretches of land with relatively low population densities—Canada’s density is about 4 people per square kilometer, primarily because much of its territory is uninhabitable or sparsely populated. Interestingly, this contrast often leads to different challenges and opportunities within these countries. In densely populated areas, issues like housing shortages, traffic congestion, and environmental stress are prevalent. On the other hand, sparsely populated regions may face challenges related to service delivery, economic viability, and infrastructure development.
Factors influencing population density include not only geographic and climatic conditions but also historical migration patterns, urbanization rates, and government policies. For example, countries with favorable climates and rich resources tend to attract more settlers, leading to higher population densities. Furthermore, urban areas typically have much higher densities compared to rural regions. Cities like Tokyo and Mumbai exemplify this trend, with population densities of around 6,000 and 12,000 people per square kilometer, respectively. The pull factors such as employment opportunities, education, and healthcare in urban centers often drive rural-to-urban migration, further exacerbating density issues in cities.
Regional Analysis
When examining the population density map, distinct patterns emerge across different regions. In Asia, countries such as Bangladesh and Nepal demonstrate some of the highest population densities, influenced by agricultural practices and urban migration. Bangladesh, for instance, has a staggering density of approximately 1,265 people per square kilometer, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world. The situation is complicated by the ongoing effects of climate change, which threatens agricultural productivity and can intensify migration pressures.
In contrast, Africa presents a diverse picture; while countries like Nigeria are experiencing rapid urban growth and increasing densities, others like Namibia and Botswana maintain low densities due to vast arid lands and lower urbanization rates. In Europe, nations like the Netherlands and Germany show high population densities, attributed to their advanced economies and high levels of urbanization. Interestingly, the demographic distribution in Europe also reflects historical migration patterns and the integration of diverse communities.
The Americas showcase a mix of high and low densities as well. For instance, the United States has a varied landscape, with densely populated states like New York and California juxtaposed against vast, sparsely populated areas in the Midwest and Montana. This variance underscores the importance of regional economic opportunities and cultural factors that influence where people choose to live.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population density is crucial for several reasons. It helps in planning for infrastructure development, healthcare services, and environmental management. High population densities can lead to increased demand for resources such as water, housing, and transportation, which can strain local and national governments. Additionally, it plays a vital role in addressing global challenges such as climate change, urbanization, and sustainability. As more people migrate to urban areas, cities must adapt to growing populations while ensuring the quality of life for residents.
Current trends indicate that urbanization will continue to rise, with projections suggesting that by 2050, nearly 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas. This shift will undoubtedly intensify issues related to population density, including housing shortages and increased pollution. It's essential for policymakers to address these challenges proactively, focusing on sustainable urban planning and resource management.
In conclusion, the population density map not only highlights where people live but also serves as a vital tool for understanding the dynamics of human settlement and its implications for the future. As we continue to navigate the complexities of our growing world, this data will be instrumental in shaping policies and strategies that promote balanced and sustainable development.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 29, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...