Rainfall Distribution Map of Spain

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
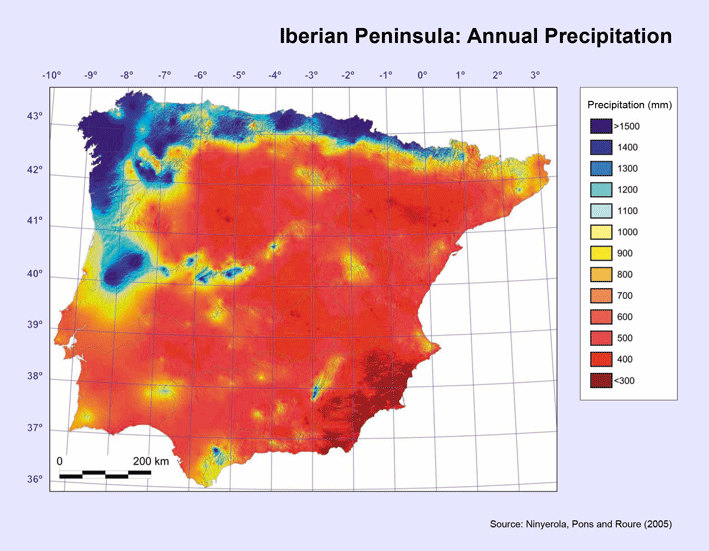
The visualization titled "The rain in Spain falls mainly on the...mountainous north coast" provides a detailed look at the distribution of rainfall across different regions of Spain. It highlights the significant variations in precipitation levels, particularly emphasizing the contrast between the wet northern areas and the drier southern regions. The map serves as a visual representation of how geography influences climate, showcasing not only the amount of rainfall but also patterns that can affect agriculture, urban planning, and even tourism.
Deep Dive into Rainfall Patterns in Spain
Spain's climate is as diverse as its geography, ranging from arid regions to lush, green landscapes. One of the most intriguing aspects of this diversity is the rainfall distribution, which is heavily influenced by the country's topography. The northern coast, particularly the regions of Galicia, Asturias, and the Basque Country, receives the most rainfall due to the influence of the Atlantic Ocean and the presence of the Cantabrian Mountains. In fact, some areas in these regions can receive up to 2,000 millimeters (about 79 inches) of rain annually.
Interestingly, the orographic effect plays a crucial role in this rainfall distribution. As moist air from the ocean rises over the mountains, it cools and condenses, leading to higher precipitation levels on the windward side. Conversely, the leeward side tends to be much drier, exemplified by the stark contrast found in the central and southern parts of Spain, where the rainfall can drop to as low as 300 millimeters (about 12 inches) per year.
Have you ever wondered why some of Spain's most famous vineyards, such as those in Rioja, thrive in the northern regions? It's primarily due to the abundant rainfall that nourishes the vines. Furthermore, the climate in northern Spain tends to be milder, allowing for a longer growing season compared to the hotter and drier south.
In addition to agricultural implications, the rainfall patterns significantly affect Spain's ecosystems. The lush forests of the north, dominated by species such as beech and oak, are thriving due to the ample moisture, while the semi-arid regions of the southeast are characterized by Mediterranean scrubland and drought-resistant vegetation. This contrast in ecosystems is not just a matter of aesthetics; it plays a vital role in biodiversity and habitat conservation efforts across the country.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the rainfall distribution across different regions of Spain, several key differences emerge. The northern coast, including Galicia, is often referred to as "Green Spain" due to its verdant landscapes resulting from consistent rainfall. In contrast, the central plateau, known as La Mancha, experiences significantly less precipitation, leading to a more arid environment. This region is famous for its windmills and vast plains, which are not as lush but have their own unique beauty.
In the south, regions like Andalusia experience a Mediterranean climate, where summers are hot and dry, and winters are mild and wetter. Cities like Seville and Cordoba showcase this pattern, often recording significant rainfall in winter months, yet suffering from drought conditions in the summer. Interestingly, the Sierra Nevada mountain range in the south also receives considerable snowfall, contributing to the region’s water supply through melting in the warmer months.
Comparing these areas reveals how local geography and climate interact. For example, while coastal areas benefit from maritime influences, inland regions are often more susceptible to continental weather patterns, resulting in stark differences in agricultural practices and lifestyle.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the rainfall distribution across Spain is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it directly impacts agricultural practices. Farmers in the north can rely on consistent rainfall for crops, while those in the south must adapt to variable weather conditions, often resorting to irrigation methods. This geographic disparity in rainfall can also influence food supply chains and economic stability in different regions.
Moreover, as climate change continues to affect weather patterns globally, monitoring rainfall distribution becomes even more critical. Predictions of increased drought in southern Spain or altered precipitation patterns in the north could have profound implications for water management and environmental sustainability. Additionally, tourism, a vital part of Spain's economy, can be influenced by these climate factors, with wetter northern areas attracting visitors interested in nature and outdoor activities, while the sun-drenched south appeals to those seeking warmer climates.
In conclusion, the rainfall distribution map of Spain reveals much more than just numbers; it tells a story of how geography shapes the landscapes, economies, and lifestyles of its people. As we continue to explore these patterns, we gain insight into the myriad ways the environment influences human activity and vice versa.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 22, 2025
- Views
- 16
Comments
Loading comments...