Population Distribution Map of Germany

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
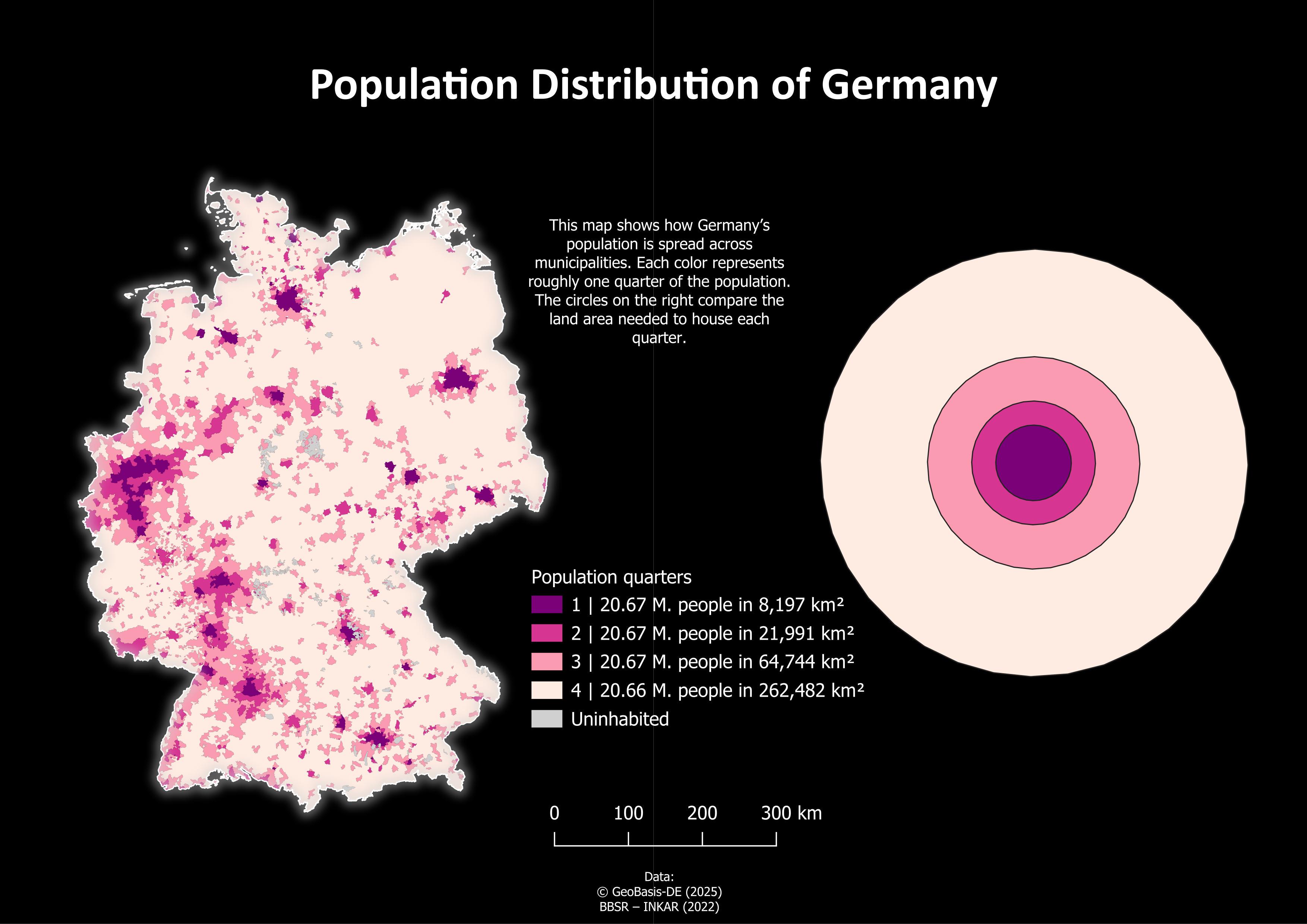
What This Map Shows
The "Population Distribution of Germany" map provides a visual representation of how the population is spread across various regions of the country. It highlights population density, indicating which areas are characterized by high concentrations of people versus those that are more sparsely populated. This visualization is crucial for understanding demographic trends and urbanization patterns in Germany, as it illustrates not just where people live, but also hints at the economic, social, and cultural dynamics at play.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution
Population distribution refers to the way in which people are spread across a given area. In Germany, this distribution is heavily influenced by historical, geographical, and economic factors. The country has a total population of approximately 83 million people, making it the most populous nation in the European Union. The distribution is anything but uniform; rather, it reveals a fascinating mosaic of urban and rural living.
Interestingly, around 75% of Germany's population resides in urban areas, indicating a significant trend towards urbanization. Cities like Berlin, Hamburg, and Munich are not only the largest in terms of population but also act as economic hubs, attracting individuals seeking employment and a higher standard of living. For instance, Berlin, the capital, is home to over 3.7 million people and is known for its vibrant culture and diverse economy.
Conversely, rural areas, particularly in the eastern states, show much lower population densities. Regions like Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia have seen population declines in recent years, primarily due to younger generations moving to urban centers for better opportunities. This phenomenon often leads to what is termed as 'counter-urbanization,' where the population shifts from rural to urban settings, leaving behind aging populations in many small towns.
The demographic composition also plays a role in population distribution. Germany is known for its multicultural society, with significant immigrant populations contributing to the diversity of urban centers. The migration trends, especially following the 2015 refugee crisis, have further impacted the population dynamics, leading to increased numbers in cities that offer more resources and support systems.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the population distribution by regions as shown on the map, a clear picture emerges. The North German Plain, encompassing cities like Hamburg and Bremen, exhibits high population density due to its economic advantages and proximity to trade routes. The metropolitan area of Rhine-Ruhr, which includes cities such as Düsseldorf and Cologne, is one of the most densely populated areas in Europe, showcasing a mix of industrial and service-oriented economies.
In contrast, southern Germany, particularly Bavaria, has a balanced population distribution due to its strong economic base in sectors such as automotive and technology. The capital city, Munich, attracts a large population, while the surrounding rural areas maintain a lower population density but are characterized by beautiful landscapes and a high quality of life.
The eastern regions, including Saxony and Brandenburg, present a stark contrast to the west. Here, the population density is significantly lower, and towns often struggle with depopulation as younger residents migrate to larger cities. The map clearly indicates these disparities, revealing the socio-economic challenges faced by these areas, including declining infrastructure and services.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution in Germany is critical for various reasons. From urban planning to resource allocation, policymakers must consider demographic trends to make informed decisions. For instance, the concentration of populations in urban areas puts pressure on housing, transportation, and public services, leading to potential challenges in sustainability and quality of life.
Moreover, the demographic shifts have significant implications for the labor market. With an aging population in rural areas, there are concerns about workforce shortages in certain sectors, while urban areas face the challenge of accommodating an influx of new residents. This dynamic creates a need for strategic planning in housing, infrastructure, and social services.
Looking ahead, projections indicate that Germany will continue to experience demographic changes. As urbanization trends persist, it will be essential to consider the balance between urban growth and rural revitalization. Policymakers must address these challenges to ensure that all regions can thrive, fostering a sense of community and belonging for every citizen.
In conclusion, the Population Distribution Map of Germany is more than just a snapshot of where people live; it encapsulates the country's demographic narrative, guiding us through its historical influences, economic structures, and future challenges. Understanding these patterns is vital for creating sustainable and equitable communities across Germany.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 20, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...