Map of Roman Hispania Circa 400

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
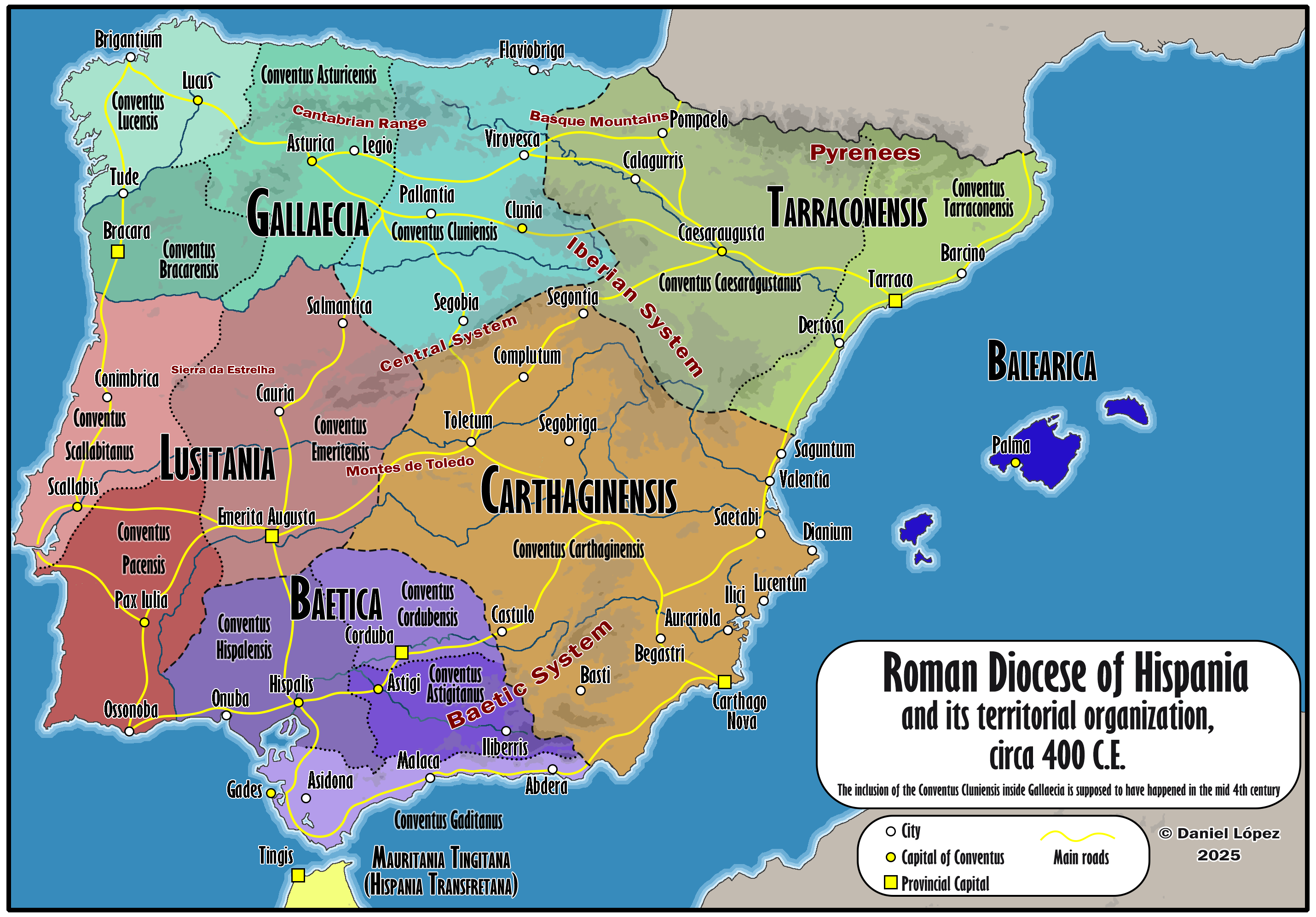
What This Map Shows
The 'Detailed Map of Roman Hispania (c. 400)' provides a rich visual representation of the Iberian Peninsula during a critical period in its history. The map delineates the various provinces of Hispania, showcasing important cities, trade routes, and geographical features that influenced the Roman Empire's administration and cultural diffusion. This visualization helps us understand not just the political landscape of the time but also the socio-economic interactions within the provinces and their connections to the broader Roman world.
Deep Dive into Roman Hispania
Hispania, an expansive region that corresponds to modern-day Spain and Portugal, was integral to the Roman Empire. By 400 AD, the Roman Empire was at a pivotal juncture, facing internal strife and external threats. Hispania was a vital part of the empire due to its resources, strategic location, and economic importance.
One of the most significant aspects of Roman Hispania was its diverse geography. The land was characterized by mountains, rivers, and plains, each influencing local cultures and economies. The Pyrenees mountains acted as a natural barrier to the north, while the Mediterranean coastline facilitated trade and cultural exchange. Rivers such as the Ebro and the Guadalquivir were crucial for irrigation, transportation, and trade. These waterways allowed for the movement of goods and people, linking provinces like Baetica and Tarraconensis with the rest of the empire.
The provinces of Hispania were not monolithic; they each had unique characteristics shaped by local tribes and Roman administration. For instance, Baetica, known for its agricultural wealth, was famous for producing olive oil and wine, which were major exports to Rome. On the other hand, Lusitania, encompassing a large part of modern Portugal, was less urbanized but rich in mineral resources, particularly gold and silver.
Interestingly, the Romanization of Hispania was a gradual process. While urban centers like Emerita Augusta (modern Mérida) and Corduba (Córdoba) flourished, rural areas maintained many of their native traditions. This blend of cultures enriched the region, leading to a unique identity that combined Roman and indigenous influences. By 400 AD, Hispania was home to a melting pot of cultures, languages, and religions, setting the stage for the complex historical developments that would follow.
Regional Analysis
The map of Roman Hispania allows for a detailed regional analysis of the provinces. For instance, the province of Tarraconensis, located in the northeast, was one of the most populous regions. It included major cities such as Tarraco (Tarragona) and was pivotal for military and economic activities. The presence of Roman roads facilitated trade, which contributed to urban growth.
In contrast, the province of Baetica in the south was known for its agricultural output. The fertile plains and the Mediterranean climate made it ideal for farming, particularly for olive groves and vineyards. The richness of Baetica's agriculture not only supported local populations but also contributed significantly to the economy of the entire Roman Empire.
Moreover, the coastal regions of Hispania had a different demographic and economic profile compared to the interior. Cities like Carthago Nova (Cartagena) served as crucial ports for maritime trade, connecting Hispania with North Africa and the rest of the Mediterranean. The coastal trade routes were vital for the import of goods like grain and luxury items, which were highly sought after in Rome.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the map of Roman Hispania is significant for several reasons. First, it illustrates how geography influenced the development of civilizations. The varied landscapes of the Iberian Peninsula shaped agricultural practices, economic activities, and urbanization patterns that are still relevant today.
Furthermore, the legacy of Roman Hispania is evident in modern Spain and Portugal. The infrastructure, cultural practices, and legal systems established during this period laid the groundwork for contemporary societal structures. For example, many cities founded during Roman rule have remained important urban centers through the centuries.
Looking ahead, the historical significance of Roman Hispania continues to resonate. As Europe grapples with issues of identity, migration, and cultural integration, the lessons learned from the Roman period can provide insights into the dynamics of contemporary society. The blending of cultures in Hispania serves as a reminder of the richness that comes from diversity and interaction.
In conclusion, the 'Detailed Map of Roman Hispania (c. 400)' is not just a representation of geographical territories; it is a window into a dynamic historical landscape that shaped the future of Europe. As we study this map, we gain valuable perspectives on how geography and history intertwine, influencing the cultures and economies that define our world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 18, 2025
- Views
- 218
Comments
Loading comments...