Land Cover Map of Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
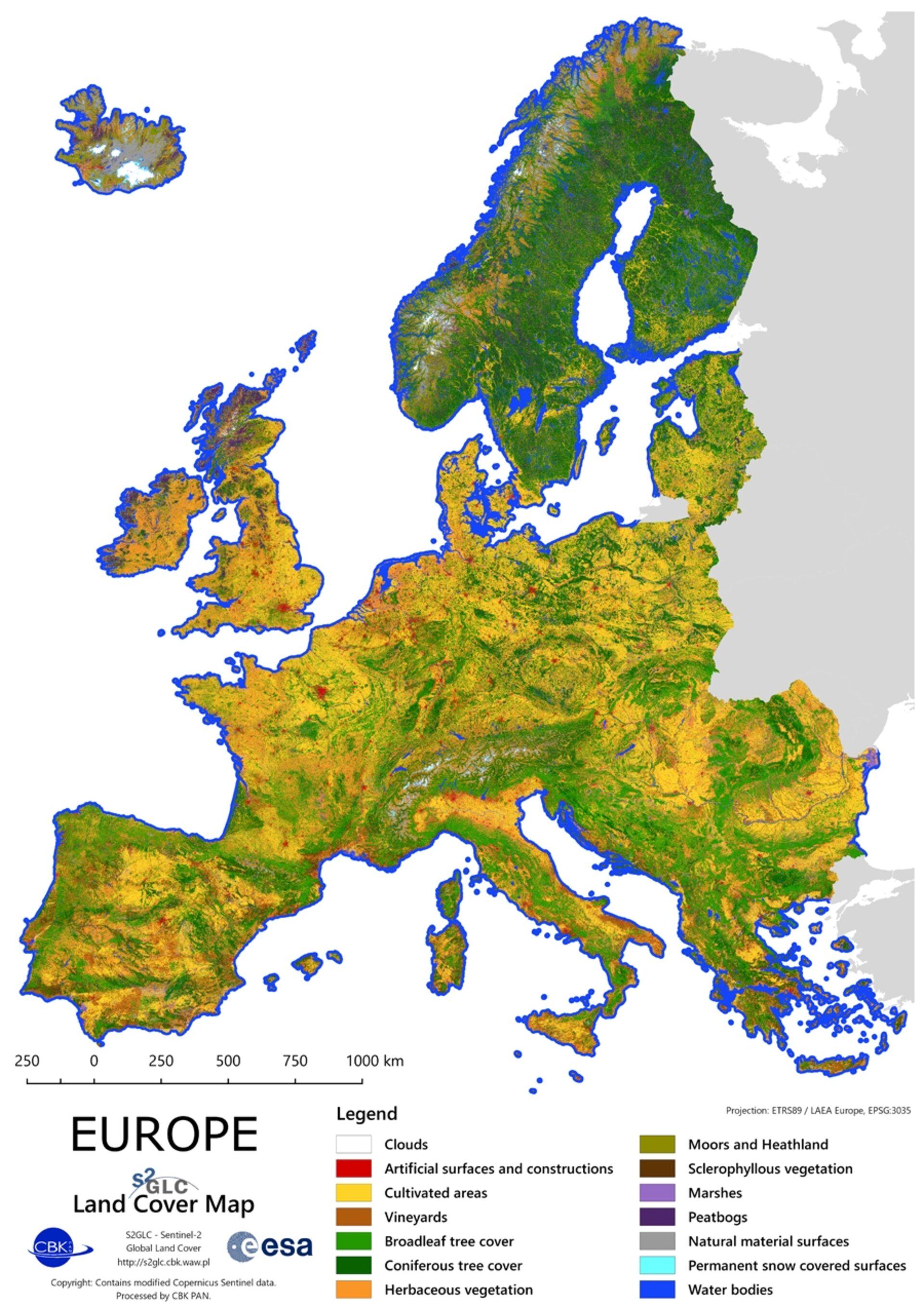
What This Map Shows
The Land Cover Map of Europe provides a comprehensive visual representation of the various types of land cover across the continent. It categorizes areas into distinct classifications such as forests, agricultural lands, urban environments, wetlands, and other natural landscapes. Understanding this map is crucial as it allows us to grasp how land is utilized and conserved, revealing intricate relationships between human activity and the environment.
Deep Dive into Land Cover
Land cover refers to the physical material at the surface of the earth, encompassing everything from vegetation to built environments. In Europe, the diversity of land cover is particularly striking due to its varied climate, geography, and historical land use practices. For example, over 40% of Europe is covered by forests, making them one of the continent's most significant land types. The boreal forests of Scandinavia contrast sharply with the Mediterranean woodlands found in southern Europe. Have you ever wondered why certain areas are more forested than others? Climate plays a pivotal role here—regions with ample rainfall and mild temperatures support denser forests, while drier zones, like those in parts of Spain and Italy, are more likely to be dominated by shrublands or agricultural land.
Agricultural land is another major category, covering about 30% of the continent. Countries like France, Germany, and the Netherlands are famous for their intensive farming practices, producing vast quantities of grains, fruits, and dairy products. Interestingly, the agricultural landscape is continually evolving due to factors such as climate change, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. For instance, the rise in organic farming has led to more diverse crop rotations and a decrease in monoculture practices in some regions.
Urban areas, which encompass cities and towns, are increasingly prominent on the land cover map, reflecting significant trends in urbanization. The urban population in Europe has surged, with more than 75% of people now living in cities. This shift not only highlights the need for sustainable urban planning but also emphasizes the impact of impervious surfaces on local ecosystems. Urban heat islands, for example, are a growing concern as cities expand and natural areas are replaced by concrete and asphalt.
Wetlands, though they cover a smaller portion of the map, are incredibly vital for biodiversity and ecosystem services. They act as natural water filters and provide crucial habitats for various species. The degradation of wetlands, due to urban development and agriculture, poses significant threats to these ecosystems, showcasing the delicate balance between land use and environmental health.
Regional Analysis
When examining land cover across Europe, distinct patterns emerge based on regional characteristics. Scandinavia is dominated by vast coniferous forests, while the Mediterranean region showcases a mix of agricultural land and urban development. For example, Italy’s agricultural landscape is often characterized by terraced vineyards and olive groves, reflecting centuries of land cultivation practices.
In Eastern Europe, countries like Poland and Hungary feature a mix of agricultural fields and natural landscapes, with significant efforts underway to restore forests and wetlands. On the other hand, Western Europe, particularly the Benelux countries, demonstrates high levels of urbanization, with extensive urban sprawl impacting the surrounding natural habitats. Interestingly, the land cover map indicates that despite urban pressures, some countries have successfully implemented policies to preserve green spaces within cities, balancing development with ecological sustainability.
Significance and Impact
Understanding land cover is not merely an academic exercise—it has profound implications for environmental policy, urban planning, and agriculture. As climate change accelerates, the need to monitor and adapt land use practices becomes increasingly urgent. For instance, the ongoing loss of biodiversity linked to land cover change is alarming and requires immediate attention from policymakers and conservationists alike.
Moreover, land cover data can inform strategies for carbon sequestration. Forests, in particular, play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change effects. As Europe strives to meet its climate goals, the importance of preserving and expanding forested areas cannot be overstated.
In conclusion, the Land Cover Map of Europe offers a window into the complex interplay between human activities and the environment. By recognizing the diverse land types and their significance, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in achieving a sustainable future for the continent.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 14, 2025
- Views
- 102
Comments
Loading comments...