Phytoclimatic Map of Europe

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
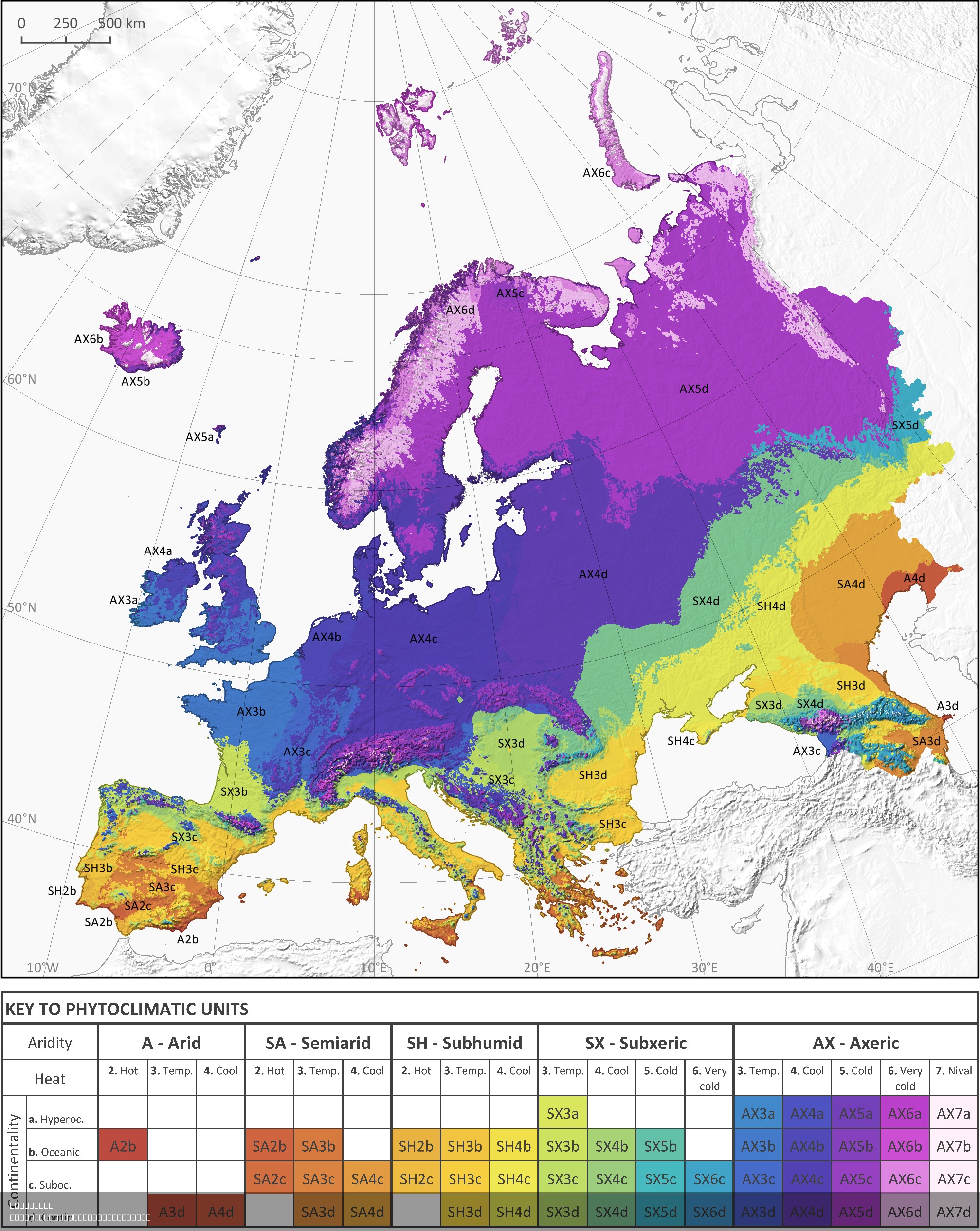
What This Map Shows
The phytoclimatic map of Europe is a detailed visualization that illustrates the distribution of different plant communities across various climatic zones within the continent. This map categorizes regions based on their climatic conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations, which significantly influence the types of vegetation that thrive in those areas. Understanding these phytoclimatic zones is crucial for comprehending biodiversity, agriculture, and ecosystem management in Europe.
Deep Dive into Phytoclimatology
Phytoclimatology is the study of the relationship between climate and the distribution of plant species. The European continent exhibits a rich tapestry of climates—from the Mediterranean warmth in the south to the subarctic conditions in the north. Each climate zone fosters unique plant life, which can be grouped into distinct phytoclimatic regions.
For instance, regions with temperate maritime climates, such as those found in parts of the British Isles and western France, support lush forests dominated by broadleaf trees like oaks and beeches. In contrast, the Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, is home to drought-resistant species such as olive trees and various herbs.
Interestingly, the continental climate found in Central Europe leads to a different kind of vegetation. Here, we see expansive grasslands and mixed forests that include both coniferous and deciduous trees. The presence of these species is a direct response to the temperature fluctuations and precipitation patterns typical of this region.
Moreover, the alpine regions, such as the Alps and the Pyrenees, host unique flora adapted to cold temperatures and high altitudes. These areas are dotted with endemic species that have evolved over thousands of years to survive in harsh conditions, showcasing the diversity of plant life across Europe.
Statistics reveal that Europe's biodiversity hotspots are often located in areas where different climatic influences converge. For instance, the Mediterranean Basin is recognized as one of the world's biodiversity hotspots, boasting a high percentage of endemic species that cannot be found anywhere else on the planet. This region is vital for conservation efforts, especially in the face of climate change, which poses significant risks to these ecosystems.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the phytoclimatic zones of Europe, we can see distinct regions that provide a clearer understanding of how climate shapes plant life.
1. **Northern Europe**: This area includes countries like Norway, Sweden, and Finland, where the boreal forests dominate. Coniferous trees such as spruces and pines thrive in these cooler temperatures, which are critical for maintaining the region's biodiversity.
2. **Central Europe**: Stretching across Germany, Poland, and the Czech Republic, this region features a mix of deciduous and coniferous forests. Interestingly, urban expansion in cities like Berlin and Prague has started to alter natural habitats, leading to discussions around sustainable development and conservation efforts.
3. **Southern Europe**: Countries such as Spain, Italy, and Greece are characterized by a Mediterranean climate. Here, the vegetation includes evergreen shrubs and drought-resistant plants. However, the increasing frequency of wildfires due to climate change is raising alarms about the future of these ecosystems.
4. **Eastern Europe**: This region, including Ukraine and Belarus, experiences a continental climate that supports steppe vegetation. The grasslands here are vital for agriculture, but they are also increasingly threatened by industrial development and urbanization.
What’s fascinating is the contrast between these regions. For example, while the Mediterranean regions flourish with unique plant species, the boreal forests of Northern Europe are essential for carbon sequestration, playing a crucial role in combating climate change.
Significance and Impact
Understanding phytoclimatic zones is more than just an academic exercise; it has profound real-world implications. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the delicate balance of these ecosystems is at risk. Changes in temperature and precipitation can lead to shifts in vegetation zones, threatening both biodiversity and food security.
Farmers and policymakers must pay attention to these shifts, as they can influence crop yields and land management practices. For instance, if the Mediterranean climate becomes more arid, it could drastically affect the cultivation of traditional crops like grapes and olives.
Moreover, with the rise of urbanization, preserving these phytoclimatic zones becomes essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring that future generations can enjoy biodiversity. Conservation efforts are increasingly focused on identifying and protecting key areas where plant species thrive, ensuring that these ecosystems can withstand the pressures of climate change.
In conclusion, the phytoclimatic map of Europe not only serves as a guide to understanding plant distributions but also highlights the intricate relationship between climate and vegetation. As we navigate the challenges posed by environmental changes, this knowledge will be crucial in shaping sustainable practices and preserving Europe’s rich natural heritage.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 7, 2025
- Views
- 112
Comments
Loading comments...