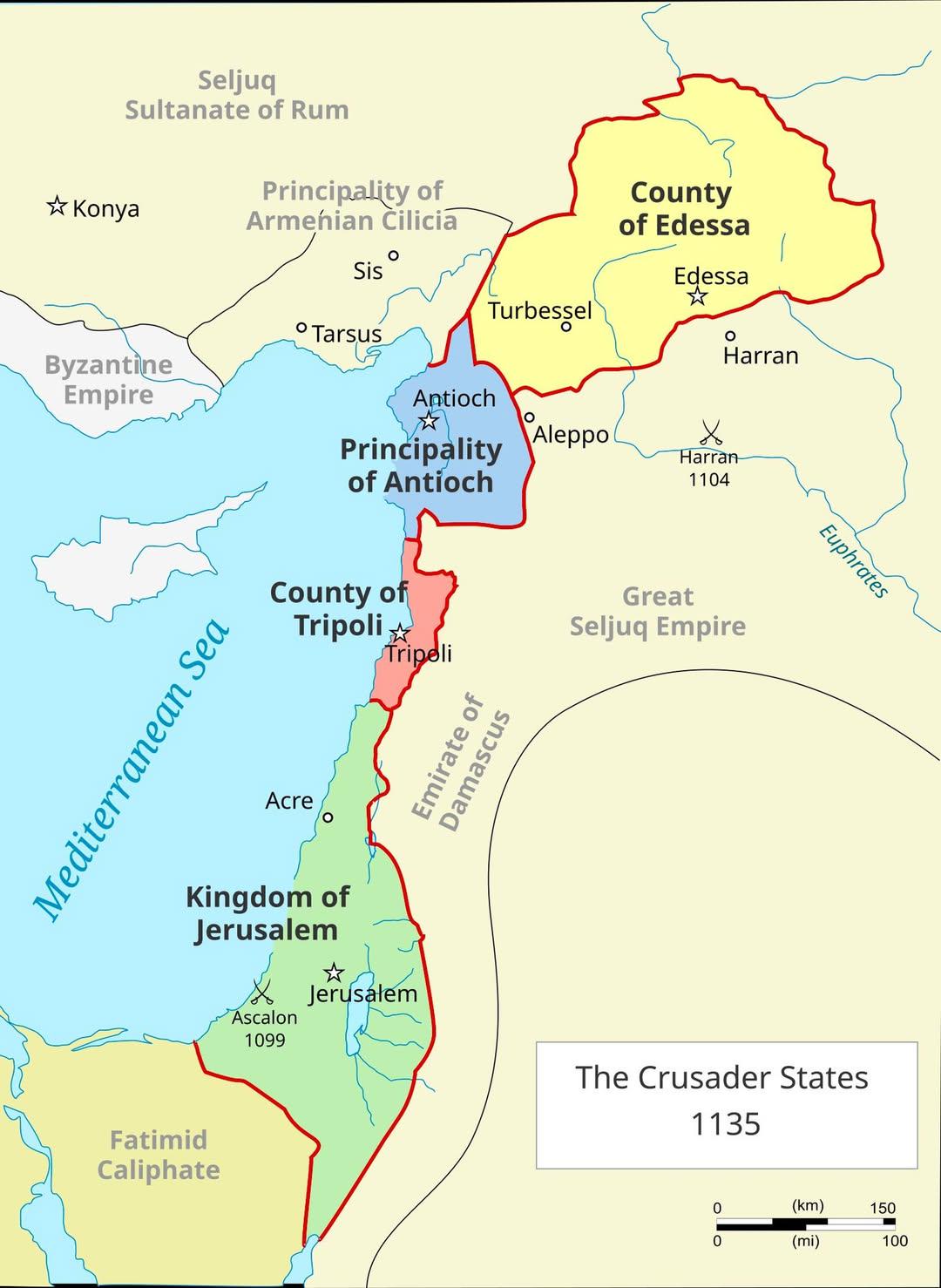
Crusader States in 1135 Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "The Crusader States in 1135 Map" displays the territorial boundaries of the Crusader states established during the early years of the Crusades. These states were established following the First Crusade, which began in 1096, and were pivotal in shaping the political landscape of the Eastern Mediterranean during the medieval period. The map indicates key regions such as the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa, illustrating their geographical extent and the strategic positioning of these territories in relation to surrounding Muslim states.
Deep Dive into the Crusader States
The establishment of the Crusader states marked a significant moment in both Christian and Islamic histories. Following the successful siege of Jerusalem in 1099, European crusaders founded several states in the Levant, which served not only as military outposts but also as centers for Christian influence in the region. The Kingdom of Jerusalem emerged as the most prominent among these, encompassing not just the holy city itself but also surrounding territories.
Interestingly, the Kingdom of Jerusalem was characterized by its diverse population, which included not only Crusaders and local Christians but also a significant Muslim population. This blend of cultures led to a unique societal structure where commerce, trade, and diplomacy thrived, albeit amidst ongoing conflict. The Crusader states relied heavily on trade routes that connected Europe with Asia, facilitating the exchange of goods such as spices, textiles, and precious metals.
The County of Edessa, established in northern Mesopotamia, was the first of the Crusader states but fell to Muslim forces in 1144. Its loss was a significant blow to the Crusader presence, highlighting the vulnerability of these territories. The Principality of Antioch and the County of Tripoli also faced threats from Muslim leaders who sought to reassert control over the region. This constant state of conflict underscored the precariousness of the Crusader states, as they struggled to maintain their hold against formidable enemies.
The political landscape of the Crusader states was heavily influenced by European powers. Kings and nobles from various regions of Europe frequently sent aid and reinforcements, often motivated by a mixture of religious fervor and the promise of wealth. This international dimension added a layer of complexity to the dynamics of the Crusader states, as local leaders had to navigate both their European backers and the local Muslim powers.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes evident that geographic features played a crucial role in the defense and administration of these states. The Kingdom of Jerusalem, for instance, was strategically located along key trade routes that connected the East and West. Its capital, Jerusalem, served as a religious focal point for Christians, which bolstered its importance. However, the mountainous terrain of the region also posed challenges for defense, making it vulnerable to attacks from surrounding territories.
In contrast, the County of Tripoli, situated along the coast, benefited from maritime trade. Its port facilitated economic growth and allowed for the importation of goods and reinforcements from Europe. The Principality of Antioch, on the other hand, served as a critical buffer against Muslim territories to the north, acting as a frontline defense for the Crusader states.
Each of these regions exhibited unique characteristics and challenges. For example, while the Kingdom of Jerusalem enjoyed significant religious significance, the County of Edessa faced geographic isolation, making it difficult to receive support from its European allies. This variance highlights the importance of geography in determining the success and longevity of the Crusader states.
Significance and Impact
The Crusader states of 1135 are significant not only for their historical context but also for the lasting impact they had on the region. They represent a complex interplay of religion, politics, and culture during a time of significant upheaval. The establishment of these states altered the demographic makeup of the Levant, leading to interactions and exchanges that would influence subsequent generations.
Moreover, the Crusader states serve as a reminder of the enduring conflicts in the region, the echoes of which can still be felt today. The dynamics established during this era laid the groundwork for future relations between Christian and Muslim communities, shaping the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East.
In contemporary discussions about the Middle East, understanding the historical context of the Crusader states can provide insights into ongoing conflicts and cultural tensions. With the rise of modern geopolitical issues in the region, the lessons from the Crusader period remain relevant, prompting questions about identity, territorial claims, and the legacy of historical grievances. As we look ahead, it’s crucial to recognize how the past continues to inform the present and future of this historically rich and complex area.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 26, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...