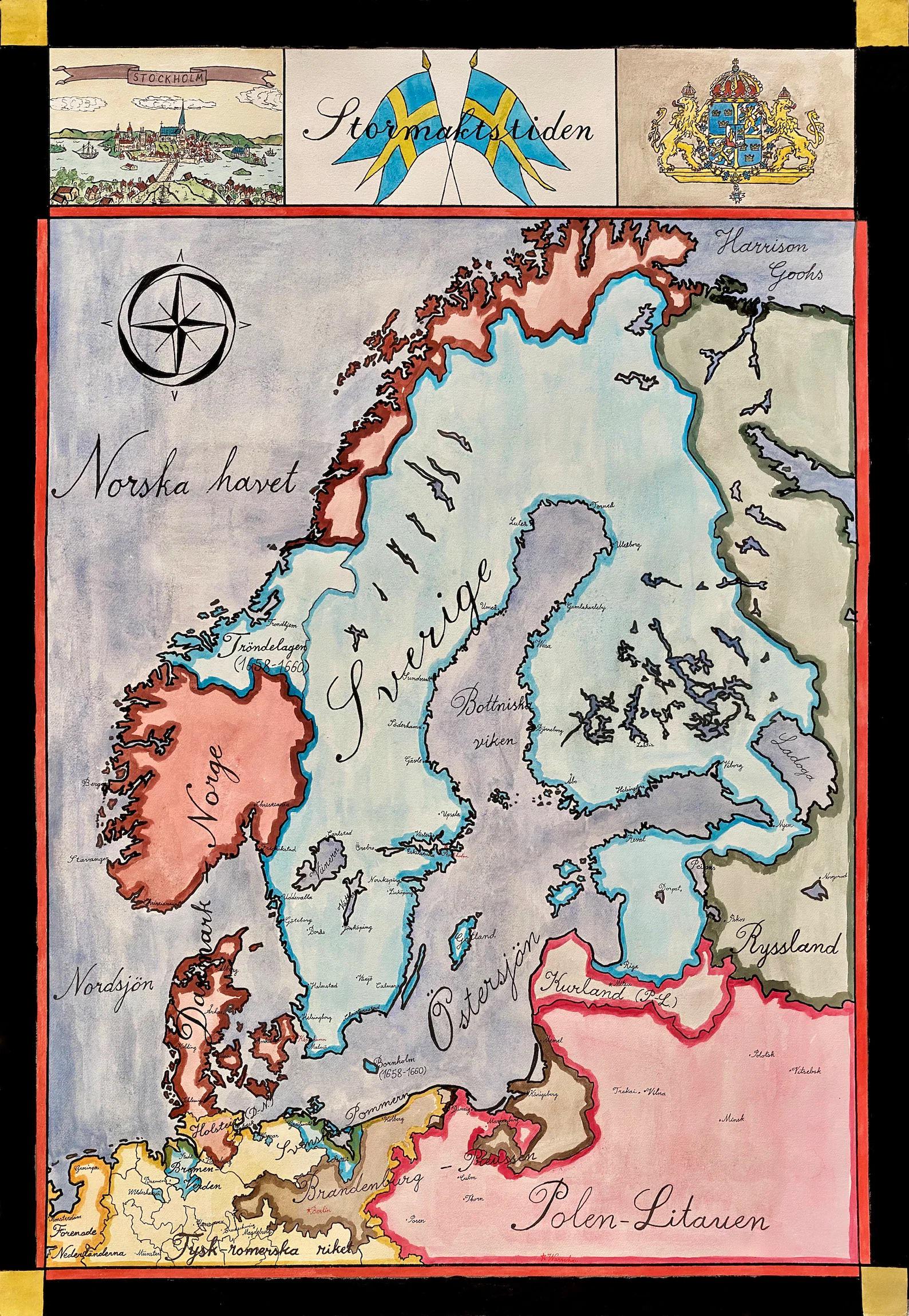
Map of Sweden in 1660

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Map of Sweden in the year 1660" provides a fascinating glimpse into a pivotal time in the country's history. This historical map not only outlines the geographical boundaries of Sweden at that time but also highlights key settlements, trade routes, and territorial disputes. The map showcases Sweden's vast territories, which included parts of modern-day Finland and territories in the Baltic region. This visualization serves as a starting point for understanding the geopolitical landscape of 17th-century Sweden, an era marked by ambition and expansion.
Deep Dive into Sweden's Territorial Expansion
During the 17th century, Sweden was undergoing significant territorial expansion, thanks in large part to its military prowess and strategic alliances. In 1660, Sweden had transformed into a major European power, largely due to the outcomes of the Thirty Years' War and the subsequent Treaty of Westphalia. One of the most striking features of the map is the delineation of Sweden's borders, which extended to encompass Finland, parts of present-day Estonia, Latvia, and even parts of northern Germany.
Interestingly, the geographical layout of Sweden played a crucial role in its expansion. The country’s long coastline along the Baltic Sea provided robust access to trade routes, allowing it to establish a maritime empire that would influence commerce and politics in the region. The waters of the Baltic were not just a means of transportation; they were vital for the fishing industry and naval power.
The map also illustrates the significant urban centers of the time, such as Stockholm, which served as the capital and a hub of trade and governance. Other important cities like Gothenburg and Malmö were instrumental in supporting Sweden's economy through trade with other European nations. It's fascinating to note that the population during this period was heavily concentrated in these urban centers, which were critical for both economic and military activities.
Moreover, the map highlights the strategic importance of mining in Sweden, particularly in the regions rich with iron and copper resources. These resources were crucial for the production of weapons and tools, further bolstering Sweden's military capabilities. By 1660, Sweden was producing large quantities of iron ore, making it one of the primary suppliers for European armies.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map regionally, one can see distinct differences in urbanization and resource distribution. For instance, the coastal areas were more developed compared to the inland regions. Stockholm, located on the eastern coast, was not just the political center but also a bustling trade port. In contrast, the northern territories, which were more rugged and sparsely populated, were primarily used for hunting and agriculture.
In the southern parts of Sweden, particularly around Skåne, the map shows a higher concentration of agricultural land, reflecting its fertile soil and favorable climate. This area was key for food production and supported a growing population. Interestingly, Skåne would later become a focal point of conflict during the Scanian War due to its strategic location and agricultural wealth.
Conversely, the northern regions, particularly Lapland, were largely inhabited by the Sámi people, who traditionally engaged in reindeer herding and fishing. The contrast between the agricultural south and the nomadic lifestyles of the north illustrates the diverse ways of life within Sweden at the time.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geography and territorial dynamics of Sweden in 1660 is crucial for grasping the historical context of Northern Europe. This period set the stage for future conflicts and alliances that shaped the continent. The expansionist policies of Sweden not only affected its immediate neighbors but also had lasting implications for European politics.
Today, historians and geographers alike find relevance in the lessons from Sweden’s past. The balance of power, resource management, and urbanization trends observed in this historical context can provide insights into current geopolitical issues. For instance, as nations grapple with resource allocation and territorial disputes in today's world, reflecting on historical maps like this one can offer valuable perspectives.
The significance of the 1660 map of Sweden transcends mere geographical representation; it embodies the ambitions, conflicts, and transformations of a nation that was once a formidable power in Europe. As we look to the future, understanding these historical dynamics becomes increasingly important in navigating contemporary global relationships.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 25, 2025
- Views
- 10
Comments
Loading comments...