Fertility Rate Per Woman Map of Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
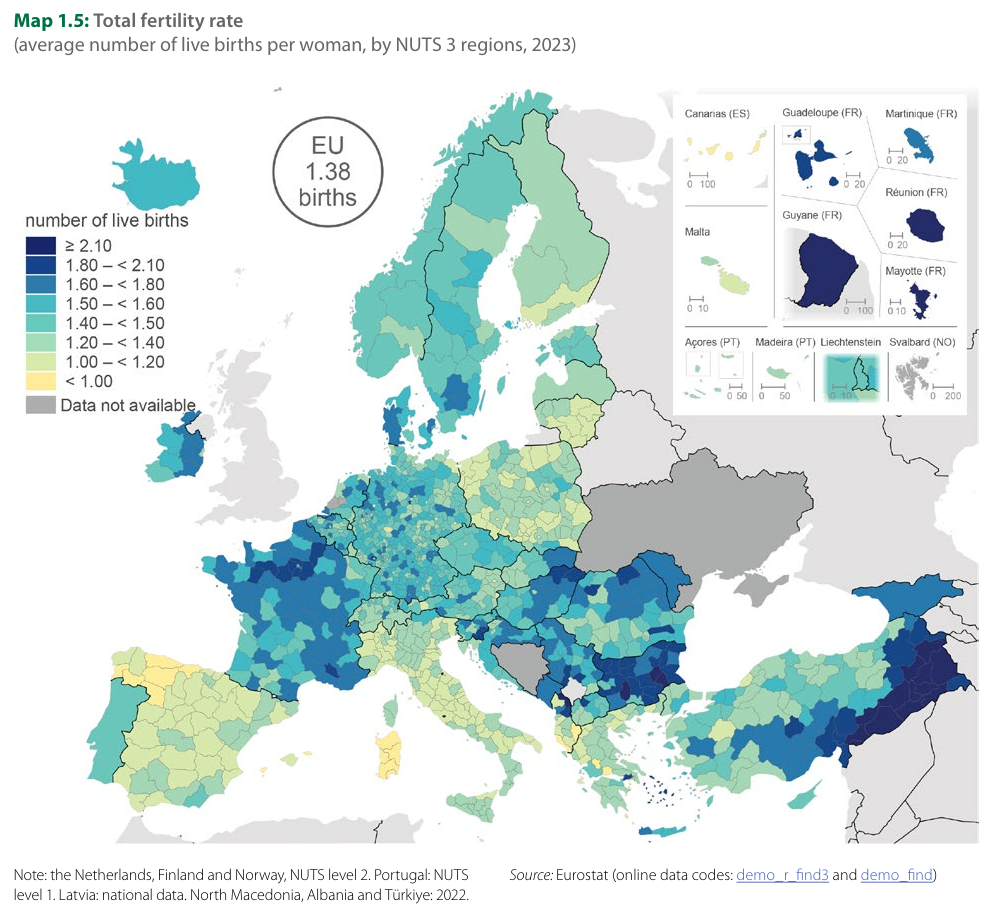
The visualization titled "Europe's Fertility Rate Per Woman via EuroStats through NUTS-3 Level Regional Data" provides a comprehensive look at the fertility rates across various regions in Europe. This map highlights the average number of children born per woman in different areas, revealing significant demographic trends that can have profound implications on society, economy, and culture.
Understanding fertility rates is crucial for policymakers, sociologists, and economists alike. These figures not only indicate population growth or decline but also reflect societal values, economic conditions, and even healthcare accessibility.
Deep Dive into Fertility Rates
Fertility rates are a key demographic indicator that reflect the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime. In Europe, these rates vary widely due to a multitude of factors, including cultural norms, economic conditions, and government policies. Interestingly, the European average fertility rate is around 1.5 children per woman, which is below the replacement level of 2.1 required to maintain population size.
High fertility rates are typically observed in regions with ample social support for families, such as generous parental leave policies, affordable childcare, and healthcare availability. In contrast, lower rates often correlate with higher urbanization levels, where the cost of living may deter family growth. For example, the regions of Mayotte (6.11), French Guiana (5.88), Reunion Island (3.59), and Guadeloupe (3.52) exhibit notably high fertility rates, likely due to a combination of cultural factors and social policies that support larger families.
On the other end of the spectrum, countries like the UK have seen a fertility rate of 1.40, which is reflective of urban lifestyles and economic pressures. The impact of socio-economic factors cannot be overstated here; as women gain more access to education and career opportunities, many choose to delay childbirth or have fewer children.
Similarly, in Ukraine, the ongoing war and subsequent emigration have made it challenging to track current fertility rates, with the last recorded figure in 2021 being a mere 1.20. This situation underscores how conflict and instability can dramatically influence population dynamics. Belarus, with a fertility rate of 1.22, faces its unique challenges, while Bosnia and Herzegovina's rate of 1.49 suggests a slightly healthier demographic trend, potentially influenced by a mix of cultural and economic factors.
Regional Analysis
Taking a closer look at specific regions, we see stark contrasts that highlight the impact of local conditions. For instance, the high fertility rates in the overseas territories of France, such as Mayotte and French Guiana, can be attributed to cultural norms that favor larger families, coupled with support systems that encourage childbirth. These regions often have young populations and include significant immigrant communities, which can also bolster higher birth rates.
In contrast, many Western European countries, including the UK and Belarus, are grappling with low fertility rates. The UK’s figures reflect urban pressures, high living costs, and changing family structures. Interestingly, this trend is not isolated to the UK; many European nations have seen similar patterns, leading to concerns about future workforce sustainability and economic growth.
Bosnia and Herzegovina's fertility rate of 1.49 is noteworthy. While it remains below the replacement level, it indicates a relatively more favorable demographic trend compared to its neighbors. This could be a reflection of a cultural preference for larger families, despite economic challenges faced by the nation in the post-war era.
Significance and Impact
Understanding fertility rates is essential for grasping the demographic shifts that affect economic and social landscapes in Europe. High fertility rates can indicate a youthful population, which can be beneficial for workforce growth and economic vitality. Conversely, countries facing declining birth rates may confront aging populations, leading to increased healthcare and pension costs.
Current trends suggest that many European countries will need to reevaluate their immigration policies and family support systems to address the demographic challenges posed by low fertility rates. As societies evolve, so too must the policies that govern them. This is not merely an academic exercise; the implications are real and pressing, affecting everything from labor markets to social services.
In conclusion, the fertility rate map of Europe reveals a complex tapestry of demographics that speak to the cultural, social, and economic realities of each region. By understanding these patterns, we can better navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in shaping the future of European society.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 25, 2025
- Views
- 10
Comments
Loading comments...