World Population Distribution Map by Zones

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
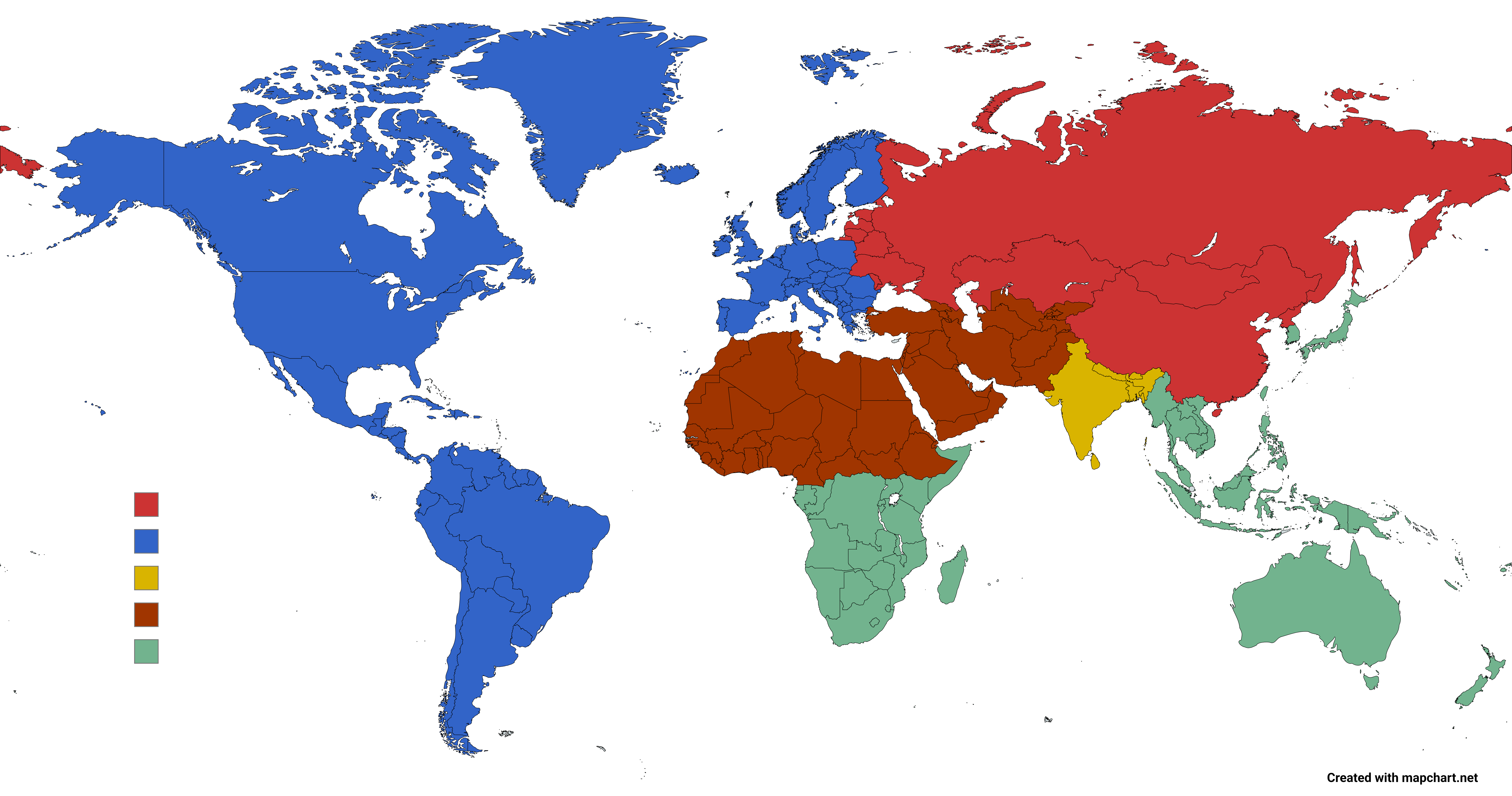
What This Map Shows
This visualization presents an intriguing division of the world into five distinct zones, each containing approximately equal populations. While the exact numbers may fluctuate due to demographic changes and migration patterns, the map serves as a powerful tool to visualize how human populations are distributed across the globe. This segmentation allows us to look beyond borders and see the world through the lens of population density, opening a dialogue about resource allocation, urbanization, and socio-economic development.
Deep Dive into Global Population Distribution
Population distribution is a key concept in geography that seeks to understand where people live and why they choose to inhabit certain areas over others. Globally, the population is not evenly spread out; instead, it tends to cluster in urban areas, along coastlines, and in fertile plains. As of 2023, the world population is estimated to be over 8 billion, with significant concentrations in Asia, especially in countries like China and India, which are home to over a third of the global populace.
Interestingly, urbanization plays a critical role in shaping population distribution. Cities are beacons of opportunity, drawing individuals from rural areas in search of jobs, education, and a better quality of life. For instance, megacities like Tokyo, Delhi, and São Paulo have populations exceeding 10 million, yet they represent just a fraction of their respective countries' total populations.
Moreover, the geographic features of a region heavily influence where populations can thrive. Mountainous areas, deserts, and extreme climates tend to deter large populations, while regions with ample freshwater resources and arable land, such as the Nile Delta or the Great Plains in the United States, see higher population densities. According to the World Bank, urban areas are expected to house nearly 68% of the world's population by 2050, which raises compelling questions about infrastructure, environmental sustainability, and resource management.
Regional Analysis
In analyzing the five zones depicted in the map, we can draw significant contrasts between regions:
1. **Zone 1: Asia-Pacific** - This zone encompasses countries like India, Indonesia, and Australia. It is characterized by high population density, with urban hubs such as Mumbai and Jakarta leading the charge. Interestingly, this zone also faces challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and resource scarcity, prompting governments to rethink urban planning strategies.
2. **Zone 2: Europe and Russia** - Home to a mix of densely populated cities like London and Paris, this zone experiences an aging population alongside immigration trends. Urbanization here has led to a rich cultural tapestry, but also to challenges like housing shortages and climate change impacts.
3. **Zone 3: North America** - The United States and Canada dominate this zone, showcasing a higher standard of living and diverse economic opportunities. However, it also exhibits stark contrasts between urban centers and rural areas, with cities like New York City and Los Angeles housing millions while vast expanses of the Midwest remain sparsely populated.
4. **Zone 4: Latin America** - Stretching from Mexico to Argentina, this zone has vibrant urban centers such as Mexico City and São Paulo. However, it grapples with issues like inequality, informal housing, and social unrest, which are often exacerbated by rapid population growth in urban areas.
5. **Zone 5: Africa** - This zone is witnessing the fastest population growth in the world, with cities like Lagos and Nairobi expanding rapidly. While this growth presents opportunities, it also brings challenges related to infrastructure, healthcare, and education. Interestingly, as African nations develop, we may see shifts in global economic power.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution is vital for a multitude of reasons. It informs governmental policies on resource allocation, urban planning, and environmental conservation. For example, countries with high population densities must prioritize sustainable development to ensure that their cities can support growing populations without depleting resources.
Moreover, as the global population continues to rise, projections indicate that regions like Africa will play an increasingly significant role in the future global economy. This shift could lead to new geopolitical dynamics as countries adapt to changing demographics.
In conclusion, the map showcasing the world divided into five zones by population reveals much more than just numbers; it highlights the intricate relationships between geography, culture, and economics. Understanding these dynamics is crucial as we navigate the challenges and opportunities of a rapidly changing world. Have you ever thought about how your own region fits into this global picture? It’s a fascinating puzzle that continues to evolve.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 21, 2025
- Views
- 30
Comments
Loading comments...