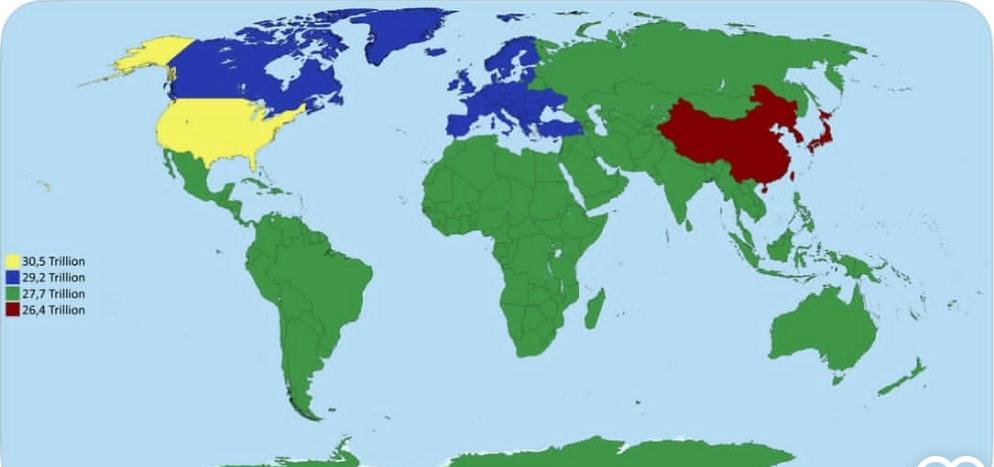
Equal GDP Distribution Map by Region

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Dividing the World into 4 Regions with Equal GDP" presents a unique perspective on the global economy by segmenting the world into four distinct areas, each contributing equally to the world's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This approach not only highlights economic disparities but also underscores how wealth is distributed across geographic boundaries. Understanding this distribution is crucial, as it connects to broader themes of development, inequality, and economic policy across different regions.
Deep Dive into Global GDP Distribution
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, serves as a vital economic indicator, representing the total monetary value of all goods and services produced in a country over a specified period. It provides insights into the economic performance and health of nations. But have you ever wondered how these numbers translate into real-world impacts? The division of the world into regions with equal GDP allows us to explore this question.
Interestingly, the GDP distribution can reveal a lot about the economic activities prevalent in different parts of the world. For instance, regions with high GDP often correlate with advanced industrial sectors, services, and technology-driven economies. In contrast, areas with lower GDP may rely more heavily on agriculture or natural resource extraction, affecting their overall economic stability and growth potential.
The implications of GDP distribution are profound. Countries with higher GDP per capita generally enjoy better living standards, access to education, and healthcare. For example, nations like the United States, Germany, and Japan represent regions with significant GDP contributions, showcasing advanced infrastructure and technological innovation. However, these regions may also experience challenges such as income inequality and environmental sustainability concerns.
On the other hand, countries within lower GDP regions, such as parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, often grapple with issues like poverty, lack of access to essential services, and political instability. Understanding these dynamics is crucial, as it not only reflects the current state of global economics but also informs policy decisions aimed at fostering equitable growth.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map into its four regions reveals fascinating contrasts and similarities.
1. **North America and Western Europe**: This region boasts some of the highest GDP figures globally. The economic landscape is characterized by a diverse range of industries, including technology, finance, and healthcare. Cities like New York and London are economic powerhouses, driving innovation and attracting global talent. However, this wealth is not evenly distributed, leading to significant urban-rural divides and socioeconomic disparities.
2. **Asia-Pacific**: Including emerging economies like China and India, this region is rapidly transforming. With a blend of high-tech industries and traditional sectors, it presents a unique case of economic evolution. Interestingly, while China contributes a significant portion to global GDP, the income inequality within the country raises questions about sustainable growth.
3. **Latin America**: This region exhibits a diverse economic landscape, with countries like Brazil and Mexico leading the way. However, many nations face challenges such as political instability and reliance on commodity exports, which can lead to volatility in GDP. The disparity in wealth distribution is evident, with urban centers often overshadowing rural areas in terms of economic activity and development.
4. **Africa and the Middle East**: Characterized by rich natural resources, this region is undergoing significant changes. While countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia contribute substantially to the global GDP, many face challenges in translating natural wealth into economic benefits for their populations. Factors such as governance, infrastructure, and investment play critical roles in determining how effectively these regions can leverage their resources for broader economic growth.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the global GDP distribution is vital for several reasons. It informs policymakers and economists about where resources may be needed most and highlights regions that may require targeted interventions to foster growth. In today's interconnected world, economic disparities can lead to broader social and political tensions, making it essential to address these issues to ensure global stability.
Moreover, as we look towards the future, trends such as globalization, technological advancements, and climate change will continue to reshape economic landscapes. By analyzing GDP distribution, we can better prepare for shifts in economic power and the challenges that may arise from these changes. The implications extend beyond mere numbers; they affect lives, livelihoods, and the overall quality of life across the globe. In conclusion, the map of equal GDP regions serves not just as a statistical representation, but as a call to action for a more equitable world economy.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 14
Comments
Loading comments...