Proposed Boundaries for Guyana Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
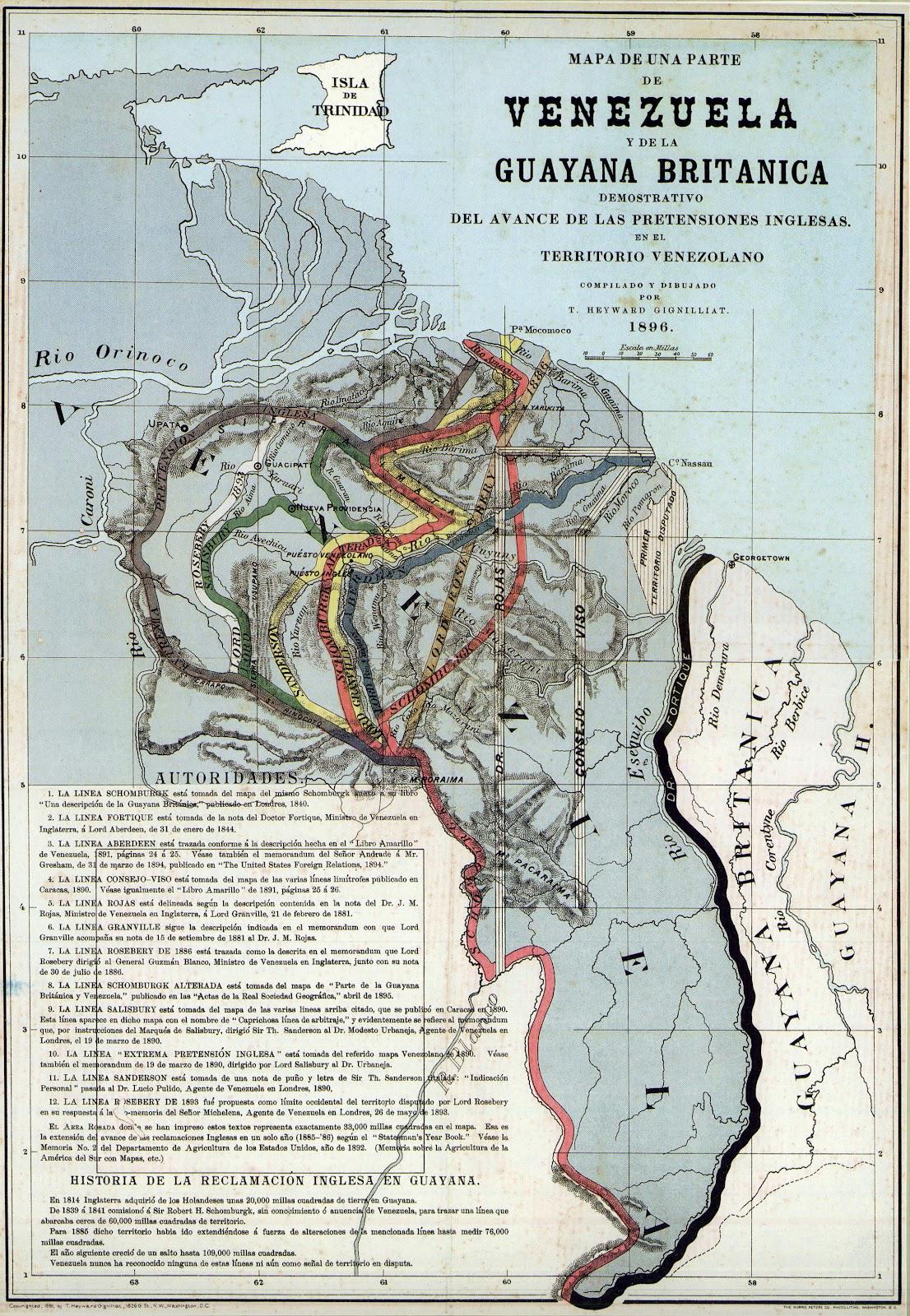
The "Proposed Boundaries for Guyana Map" visualizes the various territorial claims and proposed administrative borders within the country of Guyana. This map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the complex geopolitical landscape of Guyana, particularly in the context of its historical disputes and ongoing negotiations concerning land and maritime boundaries.
Guyana is located on the northeastern coast of South America, bordered by Venezuela to the west, Brazil to the south, and Suriname to the east. The country has a rich tapestry of ethnic diversity and natural resources, yet its territorial claims have led to longstanding disputes, especially with Venezuela. The map provides an overview of the proposed boundaries that have been put forward by different stakeholders, including government proposals, indigenous land claims, and international negotiations.
Deep Dive into Territorial Claims and Boundaries
The issue of proposed boundaries in Guyana is deeply intertwined with its colonial history and the legacy of European powers in South America. The most significant territorial dispute involves the region known as the Essequibo, an area rich in resources that Venezuela claims as part of its own territory. This claim dates back to the 19th century and has led to various confrontations between the two nations.
Interestingly, the Organization of American States (OAS) and the United Nations have been involved in mediating this dispute, emphasizing the importance of international law and diplomacy in resolving such territorial conflicts. The map illustrates not just the proposed borders but also highlights areas of contention, making it clear that the stakes are high for the local populations, including indigenous communities who have their own claims and rights to the land.
The proposed boundaries also reflect the internal political dynamics within Guyana. The country is divided into ten administrative regions, each with its own local government and resource management plans. For instance, the region of Potaro-Siparuni is known for its mining activities, while the coastal regions are more developed and urbanized. This variation in regional development illustrates how proposed boundaries can impact local economies and livelihoods.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the proposed boundaries by region reveals significant variations in land use and resource ownership. In the coastal regions, where most of the population resides, proposed boundaries are often more contested due to higher economic stakes. The areas around Georgetown, the capital, are characterized by urban development and industrial activities, leading to competing interests among various stakeholders.
In contrast, the interior regions like the Rupununi and the Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo are less densely populated but are rich in biodiversity and indigenous cultures. Here, proposed boundaries often involve considerations of indigenous land rights and environmental protection. For example, the proposed boundaries around the Iwokrama Forest Reserve are shaped by both conservation efforts and indigenous claims, showcasing the need for balance between development and sustainability.
Interestingly, the proposed boundaries can also be influenced by external factors, such as foreign investment and environmental policies. With the discovery of significant oil reserves off the coast, there has been a renewed interest in territorial claims and resource management, making the delineation of boundaries even more crucial.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the proposed boundaries in Guyana is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for the people living in these areas. The ongoing disputes can affect everything from economic development to social cohesion among diverse ethnic groups. What's fascinating is how these territorial claims can influence international relations in the region, particularly as new resources are discovered and exploited.
As Guyana continues to develop its oil industry, the dynamics surrounding its proposed boundaries will likely evolve. Future projections suggest that if the territorial disputes are resolved amicably, it could lead to increased foreign investment and economic growth. However, unresolved claims could also lead to tensions and conflict, underscoring the need for constructive dialogue among all parties involved.
In conclusion, the "Proposed Boundaries for Guyana Map" is more than just a representation of geographical lines; it encapsulates the complexities of land rights, resource management, and international diplomacy. As this South American nation navigates its future, the conversations surrounding its boundaries will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping its identity and development for years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 48
Comments
Loading comments...