Trump's Gaza Withdrawal Map Analysis

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
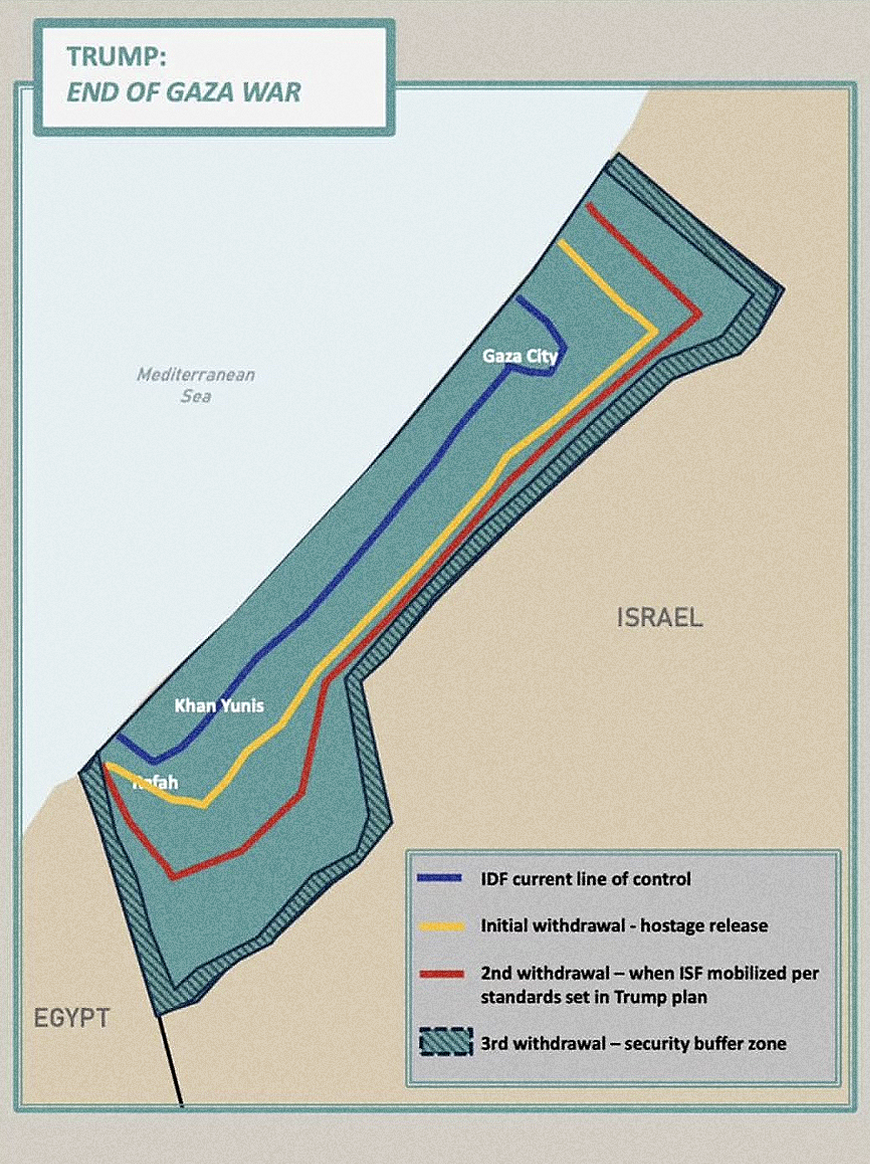
What This Map Shows
The "Trump’s Gaza Withdrawal Map" published by the White House visualizes the proposed territorial changes and withdrawal plans during the Trump administration concerning the Gaza Strip. This map provides a clear outline of the areas affected by the proposed withdrawal, showing both the territories intended for Israeli control and those earmarked for Palestinian governance. With a focus on borders, settlements, and strategic zones, it illustrates a significant political and geographical shift in a region long plagued by conflict.
However, to understand the implications of such a map, we must delve deeper into the geographical and political context of the Gaza Strip itself.
Deep Dive into the Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip is a narrow piece of land along the Mediterranean coast, bordered by Israel to the north and east and Egypt to the southwest. Spanning approximately 365 square kilometers, it is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, home to nearly two million people. The geography of Gaza plays a crucial role in its political situation, with its limited land area intensifying the conflicts over territory and governance.
Interestingly, the Gaza Strip's population is predominantly Palestinian, composed of various demographics that reflect the rich cultural tapestry of the region. The population density reaches about 5,500 people per square kilometer, which contributes to various socio-economic challenges, including access to resources, housing, and basic services. Have you noticed how such density can influence daily life and community interactions?
The Gaza Strip is characterized by a Mediterranean climate, which means it experiences hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate heavily influences agricultural practices in the region, with crops such as citrus fruits, vegetables, and grains being prominent. However, agricultural productivity is often hampered by the geopolitical situation, affecting food security and economic stability for many residents.
Moreover, the map also highlights the significant Israeli settlements in the vicinity. These settlements have been a point of contention, creating a complex overlay of territorial claims. The areas marked for Israeli control on the map raise questions about the future of these settlements and their impact on peace negotiations. The historical context is essential here; since the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel has maintained control over Gaza, leading to various military and civilian tensions.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing the regions depicted in the map reveals stark contrasts within the Gaza Strip itself. For example, the northern part of Gaza, including cities like Jabalia and Beit Hanoun, tends to be more urbanized and densely populated compared to the southern regions, such as Rafah and Khan Younis, which still have agricultural expanses.
This urban-rural divide affects not just the population density but also access to services. Northern Gaza is often more affected by conflicts, such as airstrikes or military incursions, which can lead to significant damage to infrastructure, compared to the relatively quieter southern areas. However, the southern regions are not immune, as they often face blockades and restrictions that impact their economic viability and access to essential goods.
Interestingly, the map also alludes to the demarcation lines that have shifted over time due to various political agreements and conflicts. For instance, the Oslo Accords in the 1990s introduced certain administrative divisions that still influence the current political landscape. Understanding these divisions is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of the proposed withdrawal and its potential outcomes.
Significance and Impact
The implications of the Gaza Withdrawal Map extend far beyond geographical lines; they resonate deeply within the social, economic, and political fabric of the region. The ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict has roots in territorial disputes, and any proposed changes to borders can lead to significant reactions from both sides.
What's fascinating is how this map encapsulates the broader trends in Middle Eastern geopolitics. The shifting dynamics of power, especially with the influence of the United States and its allies, often play a role in shaping the lives of millions in the region. The discussions around this map also highlight the need for sustainable solutions that can lead to lasting peace.
As we look ahead, projections suggest that the demographics of Gaza will continue to evolve, placing even greater pressure on land and resources. The potential for future conflicts remains high if equitable solutions are not pursued. Understanding maps like this one is essential, as they serve as a visual representation of the ongoing struggles and aspirations of people in Gaza, reminding us that geography is not just about lines on paper; it's about the lives intertwined within those boundaries.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 29, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...