
David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
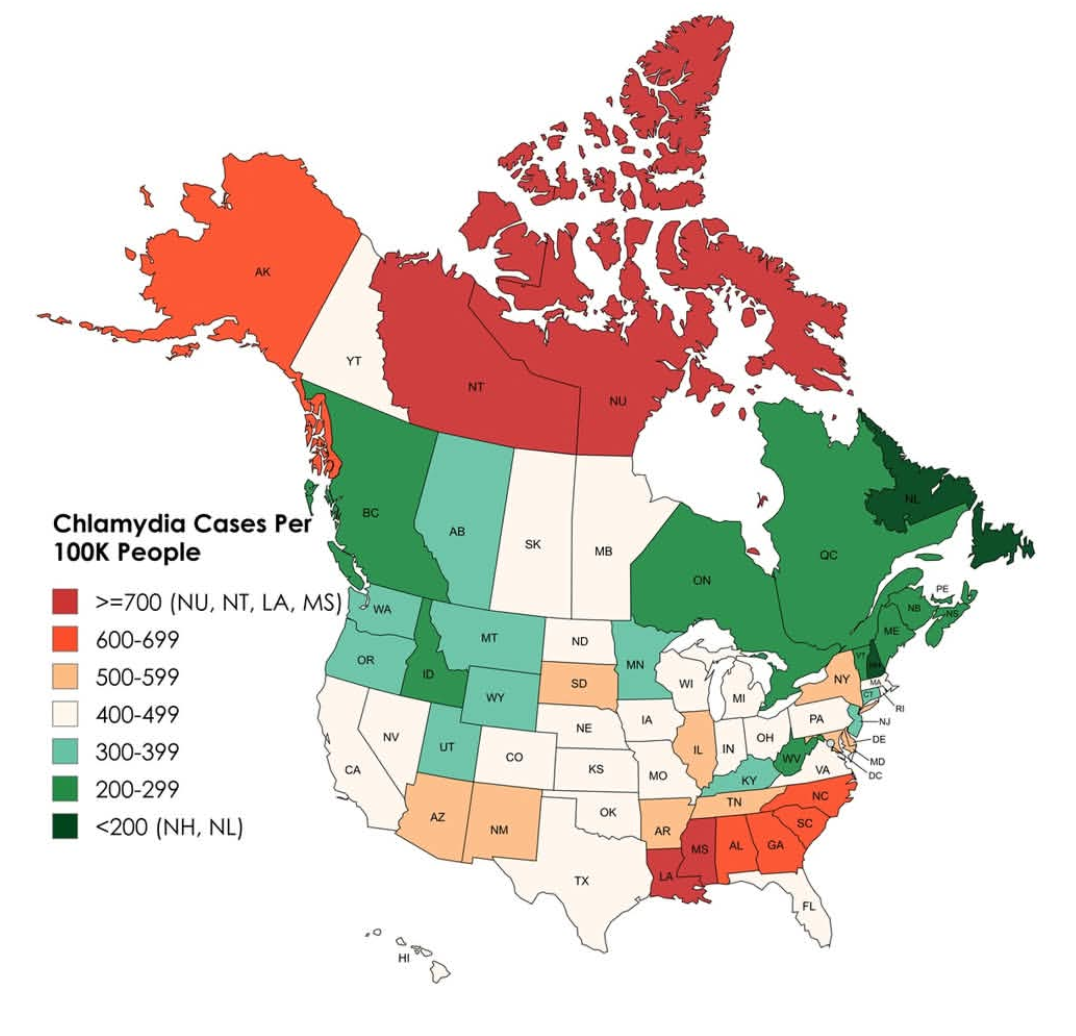
This map illustrates the incidence of chlamydia cases per 100,000 people across the United States and Canada, providing a detailed overview of how this sexually transmitted infection (STI) affects different regions. It’s a stark reminder of the public health challenges that both countries face. The visualization captures the intensity of chlamydia infections, allowing us to see which areas are most affected and prompting deeper discussions about sexual health education and access to healthcare services.
Deep Dive into Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the most common STIs globally, often affecting younger populations, particularly those aged 15 to 24 years. The bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis causes this infection, and many individuals are asymptomatic, meaning they don't experience any noticeable symptoms. This silent nature contributes significantly to its spread, as undiagnosed cases can lead to severe health complications, including infertility in women and increased risk of HIV transmission.
Interestingly, the rates of chlamydia can vary significantly depending on various factors such as demographics, availability of healthcare, public awareness, and social stigma surrounding sexual health. In the U.S., the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that the national chlamydia rate reached an all-time high in recent years, indicating a growing public health concern. In Canada, similar trends have been observed, with certain provinces reporting higher rates than others.
What’s fascinating is that regions with higher rates often correlate with areas that have less access to healthcare services or lower rates of sexual health education. For example, urban areas might show different statistics compared to rural regions due to varying healthcare infrastructures and educational outreach programs.
Moreover, the availability of testing and treatment options plays a crucial role in the reported rates. Areas with robust public health initiatives and easy access to testing typically show lower rates of undiagnosed cases, while regions lacking these resources may report higher rates due to the undiagnosed population.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it’s clear that certain regions in both the U.S. and Canada are more affected than others. In the United States, the Southeast often reports the highest rates of chlamydia infections. States such as Mississippi and Louisiana have consistently high incidence rates, often exceeding 700 cases per 100,000 people. This trend can be attributed to several factors, including socioeconomic challenges, limited access to healthcare, and less emphasis on sexual health education in schools.
Conversely, states like Massachusetts and New Hampshire show significantly lower rates, often below 300 cases per 100,000. These states benefit from comprehensive sexual health programs and better access to medical resources. Interestingly, Canada displays a similar pattern, with provinces like British Columbia and Alberta reporting higher rates of chlamydia compared to the Prairie provinces. The urban centers often have a higher incidence due to the population density and greater awareness of sexual health issues, while rural areas may struggle with lower testing rates and healthcare access.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of chlamydia cases is crucial for public health initiatives. High rates of infection can lead to increased healthcare costs, both for individuals and the healthcare system as a whole. Moreover, untreated chlamydia can result in more severe health complications, making it imperative for healthcare providers to implement effective screening and treatment programs.
The implications extend beyond individual health; they affect community health as well. High rates of STIs can lead to increased stigma and fear surrounding testing and treatment, further exacerbating the issue. Public health campaigns aimed at reducing chlamydia incidence must focus not only on education but also on creating a supportive environment that encourages individuals to seek testing and treatment without fear of judgment.
Looking ahead, it’s essential to continue monitoring these trends and to invest in preventive measures. Increased funding for sexual health education, particularly in high-incidence areas, can significantly impact future rates of chlamydia. Moreover, incorporating comprehensive sexual health programs into school curricula can help change the narrative around STIs and promote healthier behaviors among young people. As we continue to navigate the complexities of public health, understanding the geographical disparities in chlamydia cases will be critical in crafting effective interventions.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 20, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...