Ethnoreligious Diversity Map of Lebanon

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
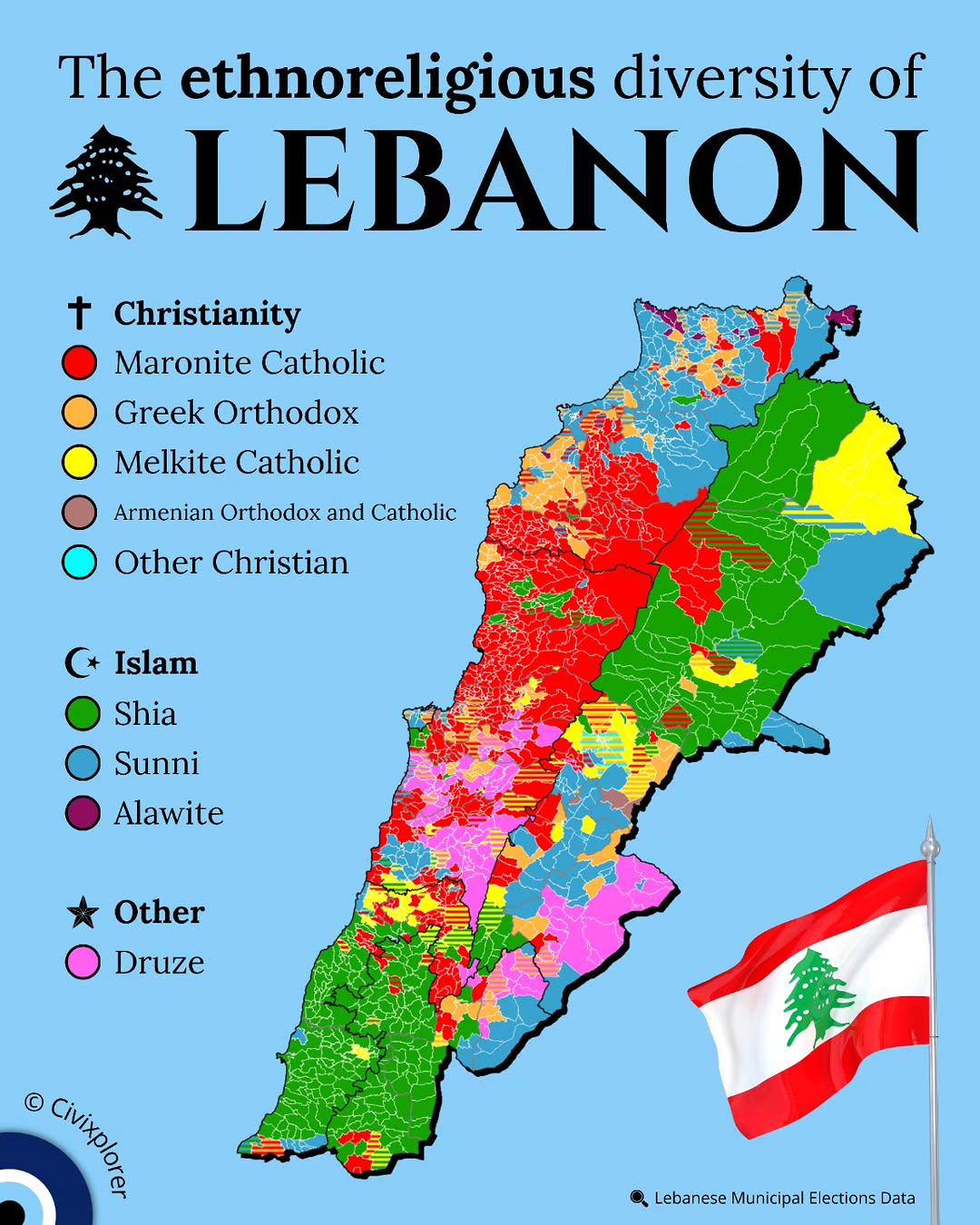
This map illustrates the ethnoreligious diversity of Lebanon, highlighting the various religious sects and ethnic groups that coexist within the country's borders. Lebanon is known for its complex demographic structure, where multiple religious communities contribute to the rich tapestry of its society. By visualizing this diversity, the map provides insight into the distribution of major groups, including Christians, Muslims, and Druze, alongside smaller communities, each with its own unique cultural heritage.
Deep Dive into Ethnoreligious Diversity in Lebanon
Lebanon's ethnoreligious composition is one of the most intricate in the world, with approximately 18 recognized religious sects. The country is primarily divided between Christian and Muslim populations, with significant representation of both groups. The largest Christian denominations include the Maronites, Greek Orthodox, and Armenian Orthodox, while the Muslim community is predominantly divided between Sunni and Shia Muslims, with the Druze representing a distinct religious sect.
Interestingly, the Maronite Christians are predominantly located in the northern and central regions of Lebanon, particularly in areas like Mount Lebanon and the Akkar district. In contrast, the Shia Muslims are primarily concentrated in the southern regions and parts of Beirut, while Sunni Muslims are more prevalent in the northern coastal cities and parts of the capital. This distribution is not merely geographical but deeply rooted in historical, socio-political, and economic factors.
The Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990) dramatically affected the demographic landscape, exacerbating sectarian divisions and leading to significant population displacements. The aftermath of the war resulted in a unique power-sharing arrangement among the different religious groups, a system known as confessionalism, where political power is distributed based on religious affiliation. This has shaped Lebanon’s governance and societal relationships, creating both a sense of identity and ongoing tensions.
Furthermore, Lebanon's diversity is also influenced by the waves of migration and the presence of Palestinian refugees, Syrian migrants, and other expatriates. As of recent estimates, about 1.5 million Syrian refugees reside in Lebanon, significantly impacting the social fabric and presenting challenges to service provision and community relations.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map in detail, it becomes evident that different regions in Lebanon showcase distinct ethnoreligious identities. For instance, the Beqaa Valley is predominantly Shia Muslim, while the northern city of Tripoli is known for its Sunni Arab population. The capital, Beirut, is a microcosm of Lebanon's diversity, home to a mix of religions and sects. The demographics of the suburbs often reflect the historical and socio-economic trends that have influenced migration patterns.
By contrast, the southern region, particularly around Tyre and Sidon, is predominantly Shia, influenced by historical ties to Iran and the presence of Hezbollah. This has implications for political allegiance and social organization, often leading to a stronger communal identity. The Mount Lebanon region, with its Maronite Christian majority, contrasts sharply with the predominantly Muslim areas, showcasing the regional disparities in terms of culture and religion.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Lebanon's ethnoreligious diversity is crucial, not only for grasping the country's identity but also for comprehending the broader regional dynamics in the Middle East. Lebanon serves as a case study for the complexities of multiculturalism, where coexistence and conflict often coexist. The unique demographic profile has implications for social cohesion, governance, and international relations.
Current trends indicate a growing concern over sectarianism, particularly in light of regional conflicts and the impact of external influences, such as Iranian and Saudi Arabian involvement in Lebanese politics. As Lebanon navigates its path forward, the significance of this diversity will continue to shape its political landscape, economic development, and social harmony. The map serves as a reminder of both the rich cultural heritage and the challenges that arise from such a multifaceted society.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 16, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...