Byzantium and the Levant Map Before the Fourth Crusade

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
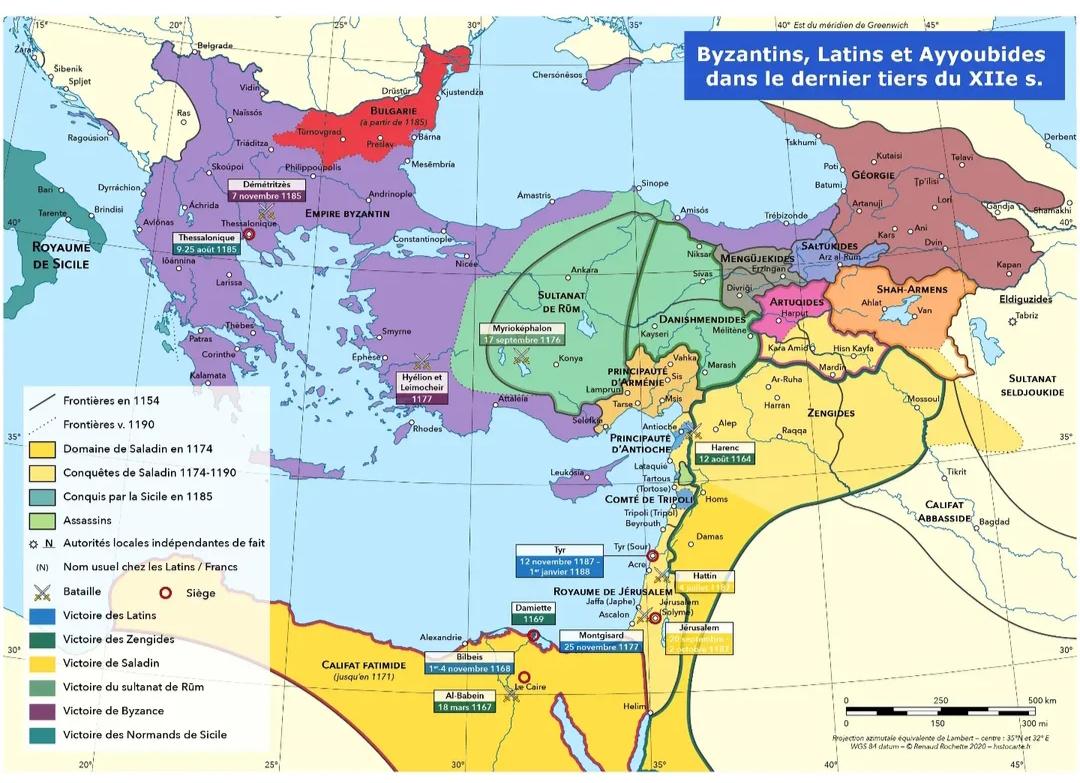
What This Map Shows
This map provides a detailed representation of the Byzantine Empire and the Levant region prior to the onset of the Fourth Crusade in 1202. It highlights key geographical features, including major cities, trade routes, and territorial divisions of the Byzantine Empire, alongside the various political entities within the Levant. This visualization helps us understand the intricate socio-political landscape of the time, which was characterized by a mix of Christian and Muslim territories, and the complex relationships that defined them.
Deep Dive into Byzantine Influence and the Levant
The Byzantine Empire, with its capital in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), was a continuation of the Roman Empire in the East and played a crucial role in the history of Europe and the Mediterranean. By the late 11th century, it was a formidable power, boasting a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and religions. The Empire's influence extended into the Levant, a region that was not only significant for its strategic location but also for its diverse populations and trade routes.
The Levant, encompassing modern-day countries like Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, and parts of Turkey, was a melting pot of various civilizations. The map illustrates key cities such as Antioch, Tyre, and Jerusalem, which were vital centers of trade and pilgrimage. Interestingly, Jerusalem held profound religious significance for both Christians and Muslims, which contributed to the tensions in the region.
During this period, trade flourished across the Mediterranean, facilitated by the Byzantine control of maritime routes. Goods such as silk, spices, and precious metals journeyed between the East and West, often passing through key ports like Alexandria and Acre. However, this economic prosperity was not without challenges. The rise of Seljuk Turks and their incursions into Byzantine territory prompted a response from the Byzantine leadership, which ultimately led to the call for the First Crusade.
The Fourth Crusade, which was initially intended to reclaim Jerusalem, ended up diverting to Constantinople, leading to significant consequences for both the Byzantine Empire and the Levant. The complex interplay of religion, trade, and warfare in this era set the stage for future conflicts and alliances.
Regional Analysis
When examining the regions depicted on the map, we can see stark contrasts. For instance, the coastal cities of the Levant, such as Tyre and Sidon, were heavily influenced by trade and commerce, thriving due to their access to the Mediterranean Sea. In contrast, the inland areas, including regions controlled by various Muslim dynasties, were often more rural and agrarian, relying on agriculture and local craftsmanship.
The map also highlights the division of territories, with the Byzantine Empire to the north and various Muslim states to the south. The boundaries were often fluid, with cities changing hands due to military campaigns and shifting alliances. For example, the city of Antioch changed hands several times during the Crusades, reflecting the volatile nature of power dynamics in the region.
What's fascinating is the impact of these territorial divisions on cultural exchanges. The Byzantine Empire was a center of learning and scholarship, which influenced the Levant in numerous ways. Artistic styles, architectural techniques, and religious practices often blended, leading to a unique cultural synthesis that still resonates in the region today.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geographical and political landscape of Byzantium and the Levant before the Fourth Crusade is crucial for several reasons. This period was marked by significant interactions between different cultures, religions, and economic systems, shaping the course of history in both Europe and the Middle East.
Today, the legacies of these interactions can still be felt. The conflicts that arose from the Crusades set the stage for centuries of tension between Christian and Muslim communities. Interestingly, the geopolitical complexities that emerged during this period continue to influence modern-day international relations in the region.
Moreover, as we examine current trends, such as the resurgence of interest in historical narratives and the impact of cultural heritage on identity, it's clear that maps like this serve as vital tools for understanding the past. They remind us of the intricate tapestry of human history and the importance of geography in shaping our world.
In conclusion, this map serves not just as a historical record but also as a reminder of the interconnectedness of human experiences across time and space. By studying the geographical context of Byzantium and the Levant before the Fourth Crusade, we gain valuable insights into the enduring legacies that continue to influence our global society today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 15, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...