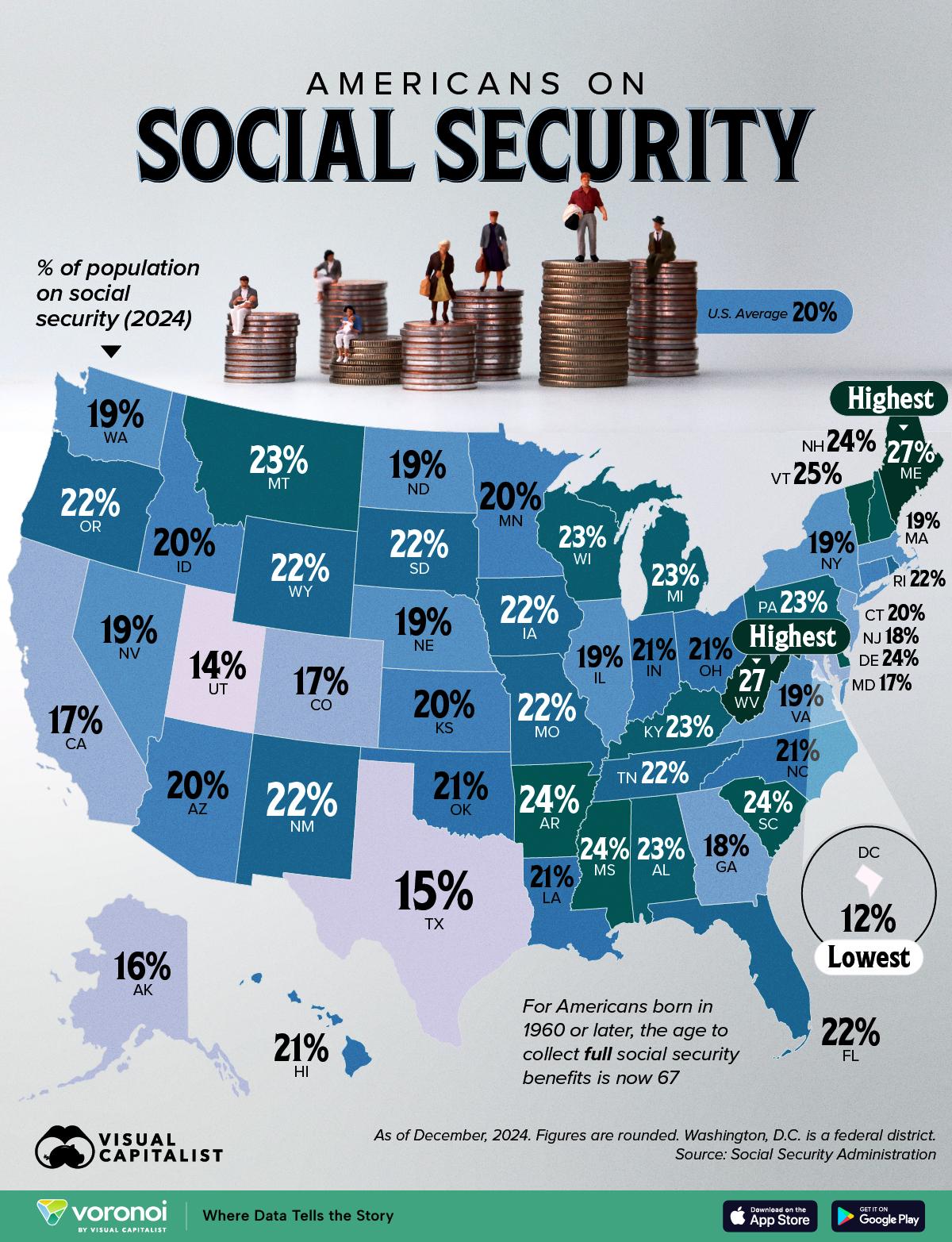
Social Security Recipients by State Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Where Americans Receive Social Security, by State" map provides a visual representation of the distribution of Social Security benefits across the United States. Each state is color-coded to indicate the percentage of its population receiving Social Security, which encompasses retirement, disability, and survivor benefits. This visualization helps us understand not only the demographics of Social Security recipients but also the economic and social landscapes of different states.
Deep Dive into Social Security in America
Social Security is one of the largest social welfare programs in the United States, designed to provide financial support to retirees, disabled individuals, and survivors of deceased workers. Established in 1935, the program has evolved over the decades to meet the changing needs of the American populace. As of 2023, approximately 66 million Americans receive Social Security benefits, representing nearly 20% of the U.S. population.
Interestingly, the percentage of residents receiving Social Security varies significantly from state to state. For instance, states with larger populations of older adults, such as Florida and West Virginia, tend to have higher percentages of Social Security recipients. This is not surprising, considering that the program is primarily designed to assist seniors. In fact, in Florida, over 30% of the population receives some form of Social Security, highlighting the state’s appeal as a retirement destination.
Moreover, Social Security benefits serve as a crucial safety net for individuals who are unable to work due to disability. States such as New Mexico and Mississippi show notable figures in terms of disability beneficiaries, reflecting higher poverty rates and lower employment opportunities in these regions. In these areas, Social Security can comprise a substantial portion of household income, which underscores its importance in providing economic stability.
Another interesting aspect is the relationship between Social Security benefits and economic factors. States with robust economies and high employment rates, like Utah and Colorado, often have lower percentages of Social Security recipients. This correlation suggests that economic opportunity allows individuals to rely less on government assistance, potentially delaying their need for Social Security benefits.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map by region, distinct patterns emerge. The Northeast, for instance, showcases a mix of high and low percentages of Social Security recipients. States like Maine, which has a significant elderly population, have a high percentage of recipients, while Massachusetts, with a robust economy and younger demographic, has a lower percentage. This divergence is a reflection of both the aging population in rural areas versus the younger, more diverse urban centers.
The South is particularly noteworthy. States such as Alabama and Arkansas show higher rates of Social Security recipients, often due to economic challenges and higher rates of disability. In contrast, states like Texas, which has a growing population and economy, have lower rates of dependency on Social Security.
In the West, states like California and Washington illustrate a similar trend, with urban areas having lower percentages of recipients compared to rural counterparts. However, California's vast population means that it still accounts for a significant number of Social Security recipients overall.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of Social Security recipients is crucial for several reasons. First, it informs policymakers about the economic health and demographic trends of each state. As the population continues to age, states with higher percentages of recipients may face increased pressure on their budgets and healthcare systems. This could lead to calls for reform to ensure the sustainability of Social Security in the face of a growing elderly population.
Moreover, the economic implications are profound. Regions with high dependency on Social Security may struggle to attract businesses and investment, perpetuating cycles of poverty and economic stagnation. Conversely, states with lower dependency may enjoy more robust economic growth, leading to better services and opportunities for their residents.
Current trends indicate that as the Baby Boomer generation continues to retire, the number of individuals relying on Social Security will increase. Projections suggest that by 2030, nearly 1 in 5 Americans will be over 65, intensifying the need to address the challenges facing the Social Security system. Have you ever wondered what this could mean for younger generations? The potential burden on future taxpayers and the need for reform are critical conversations that will shape the future of this essential program.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 15, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...