World Population Distribution Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
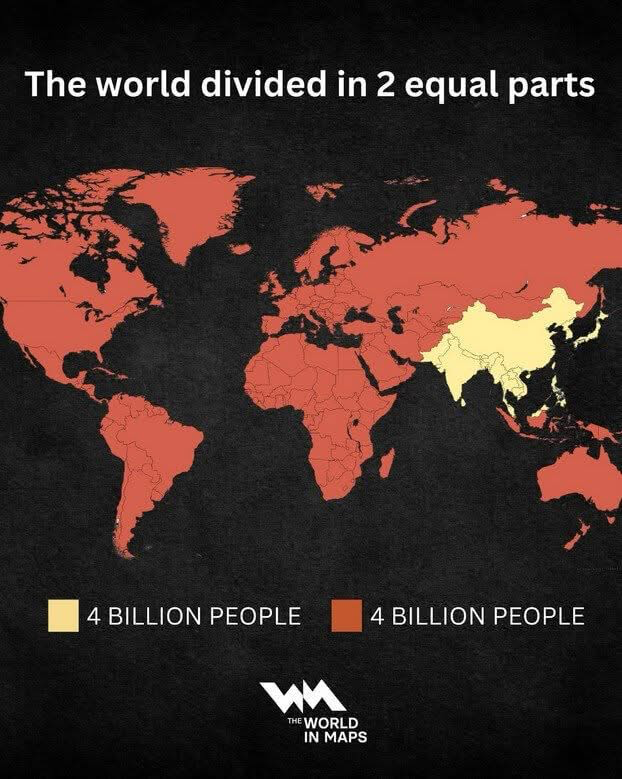
What This Map Shows
The 'World Population Distribution Map' effectively visualizes how the global population is divided into two equal parts. This intriguing map allows us to see how densely populated areas contrast with sparsely inhabited regions. Essentially, half of the world's population resides in a relatively small portion of the Earth's land. This stark division highlights not just where people live, but also raises questions about urbanization, resource allocation, and social dynamics across different regions.
Deep Dive into Global Population Distribution
Population distribution is a fascinating aspect of geography that reflects human settlement patterns, economic opportunities, and environmental factors. As of 2023, approximately 7.9 billion people inhabit our planet, with significant concentrations in urban areas. The two-thirds of the world's population lives in just 10 countries, with China and India alone accounting for around 37% of the total population.
One of the key factors influencing population distribution is geography itself. For instance, fertile plains, river valleys, and coastal regions tend to attract larger populations due to their agricultural potential and access to trade routes. In contrast, harsh terrains like deserts and high mountain ranges are often sparsely populated. Interestingly, this means that many urban centers are located along coastlines or near major rivers, where they can thrive economically.
Urbanization also plays a critical role in how populations are distributed. Rapid urban growth has transformed cities into sprawling metropolises. For example, Tokyo, Japan, is one of the most populous cities in the world, with over 37 million residents. This urban explosion is not exclusive to developed nations; cities in developing countries like Lagos, Nigeria, and Dhaka, Bangladesh, are experiencing unprecedented growth due to rural-to-urban migration.
Demographics further complicate this picture. Age distribution, cultural factors, and economic conditions all influence how populations are arranged. For instance, countries with higher birth rates may experience youthful populations, while those with aging demographics face different challenges. The implications of these factors are profound, affecting everything from education and healthcare to employment and social services.
Regional Analysis
Let's break down population distribution by regions, as shown on the map. In Asia, for instance, the concentration of people in countries like China and India is staggering. Notably, Northern India and Eastern China are among the most densely populated areas globally, with significant urban hubs like Delhi and Shanghai.
Conversely, regions like Sub-Saharan Africa are experiencing rapid population growth, yet they still have vast areas that remain underpopulated. Countries such as Namibia and Botswana have low population densities due to their arid climates. In contrast, Nigeria's population density is high despite the presence of less hospitable environments, demonstrating how economic opportunities can drive population density despite geographic challenges.
In Europe, population distribution is more evenly balanced, although urban areas, particularly in Western Europe, such as London, Paris, and Berlin, see high densities. Interestingly, Eastern Europe has seen population declines in some areas due to emigration and lower birth rates, leading to significant demographic shifts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding global population distribution is crucial for several reasons. It helps policymakers address infrastructure needs, healthcare access, and education. For example, with urban areas experiencing rapid population growth, cities must adapt to provide adequate housing, transportation, and social services. Failure to do so can lead to overcrowding, increased poverty rates, and heightened social tensions.
Moreover, the implications of population distribution extend to global challenges like climate change. As populations grow in coastal cities, the risks associated with rising sea levels and extreme weather become increasingly pronounced. This makes it essential for governments and organizations to develop strategies that accommodate growth while mitigating environmental impact.
In summary, the 'World Population Distribution Map' not only illustrates where people live but also prompts deeper considerations about resource management, urban planning, and social equity. As we move forward, understanding these patterns will be integral to addressing the complex challenges of our increasingly interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 14, 2025
- Views
- 62
Comments
Loading comments...