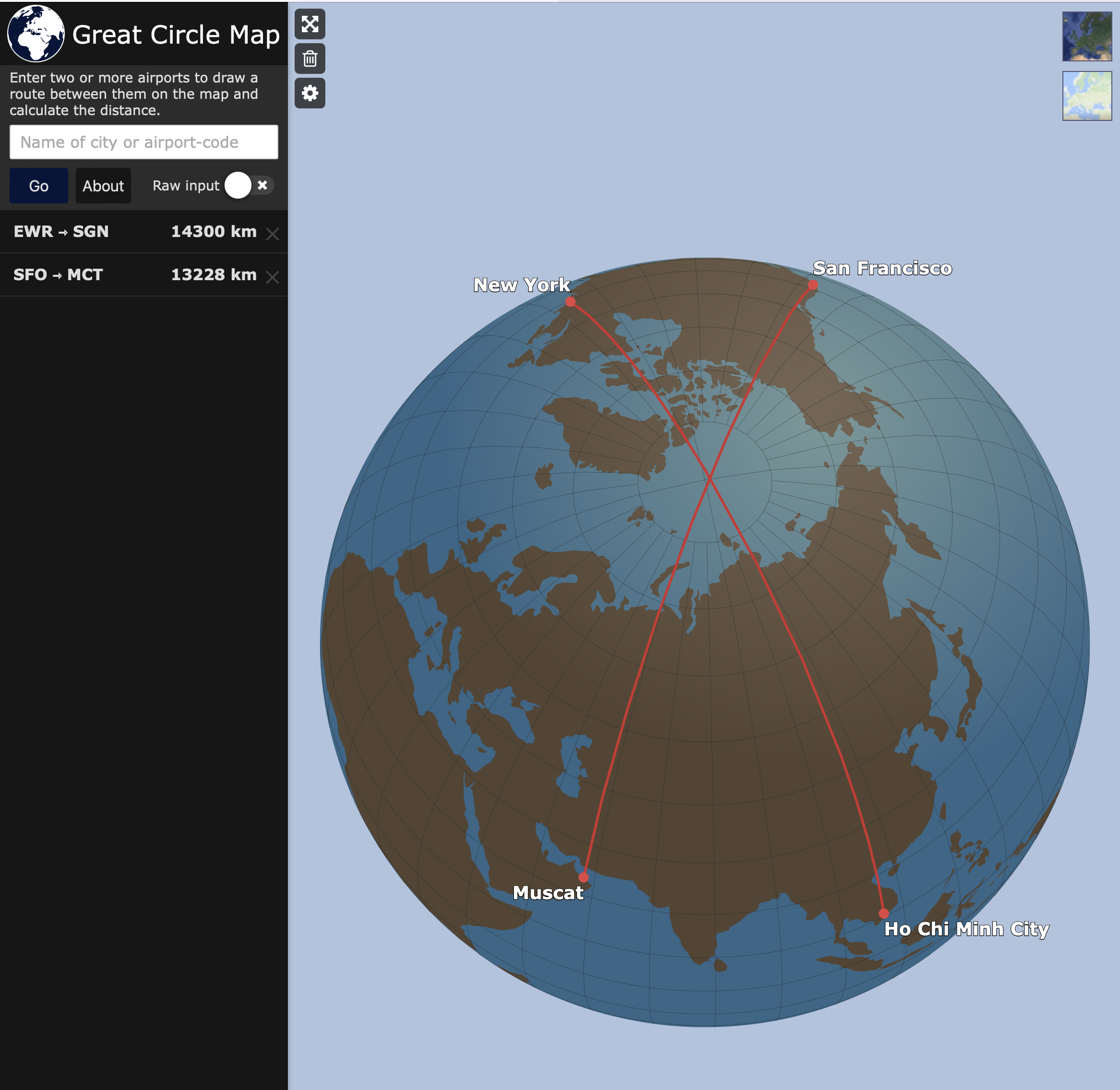
Map of City Pairs Flying Over North Pole

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map visualizes the city pairs that, for the shortest flying route, require aircraft to traverse the North Pole. It highlights a unique aspect of air travel where certain destinations, particularly those located at high latitudes, necessitate paths that arc over the polar region. With the Earth's curvature taken into account, what may seem like a longer distance on a flat map can actually be a more efficient route when plotted on a globe. This phenomenon is known as the great circle route, and it significantly influences flight planning for airlines and travelers alike.
Deep Dive into Polar Flight Paths
Ever wondered why some flights take such seemingly odd routes? The answer often lies in geography, specifically the spherical nature of our planet. The great circle path is the shortest distance between two points on the Earth, which can lead to flights that cross over the North Pole when traveling between cities in the Northern Hemisphere. For instance, flights from cities like New York to cities in Asia, such as Tokyo or Beijing, often take this polar route.
Interestingly, these polar routes not only save time but can also reduce fuel consumption, making them economically advantageous for airlines. However, flying over such extreme latitudes presents unique challenges. Weather conditions at the poles can be unpredictable, and air traffic control must account for potential turbulence and varying wind patterns.
Another key factor to consider is the impact of magnetic fields at high latitudes. Pilots must adjust their navigation systems due to the magnetic anomalies encountered, which can affect flight paths. Additionally, the visibility of landmarks for navigation diminishes as aircraft fly over vast, featureless ice, making reliance on technology for navigation even more critical.
For example, a flight from Los Angeles to London generally takes a more direct route across the Atlantic, while a flight from Toronto to Moscow may take a sharp turn upwards toward the Arctic Circle. The strategic planning around these routes is essential, resulting in a fascinating blend of geography, meteorology, and aeronautics.
Regional Analysis
Let’s explore how this phenomenon varies by region. In North America, cities like Anchorage, Alaska, are prime examples of locations that can create efficient polar routes. Flights from Anchorage to cities in the eastern parts of Asia, like Tokyo or Seoul, can often utilize a direct path over the North Pole, effectively cutting down travel time and distance.
In Europe, cities such as Oslo or Stockholm can similarly benefit from polar routes when flying to destinations in North America or Asia. However, the distances traveled can vary significantly depending on the starting point and destination. For instance, while a flight from London to San Francisco may take a more southerly route, one from London to Anchorage might utilize a polar flight path, taking advantage of its geographical position.
In the Southern Hemisphere, however, the dynamics change drastically. There are fewer city pairs that necessitate polar routes since most major cities are located much further south. Notable exceptions do exist, such as flights from Auckland to Buenos Aires, but these are less common compared to their Northern counterparts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the implications of these North Pole flight paths is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it has a direct impact on travel efficiency and environmental sustainability. Shorter flight paths result in reduced fuel consumption, which translates to lower carbon emissions—an essential consideration in today's climate-conscious world.
Moreover, as air travel continues to grow, optimizing routes over the North Pole could become increasingly important for airlines looking to save costs while adhering to environmental regulations. As technology advances, we may see improvements in navigation systems that better accommodate these unique routes, potentially opening up even more direct flights between far-reaching destinations.
In conclusion, the city pairs that require flying over the North Pole for the shortest path highlight an intriguing intersection of geography and aviation, showcasing how our planet's shape and geography influence travel in profound ways. As we continue to explore the skies, understanding these dynamics will be crucial in shaping the future of global air travel.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 8, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...