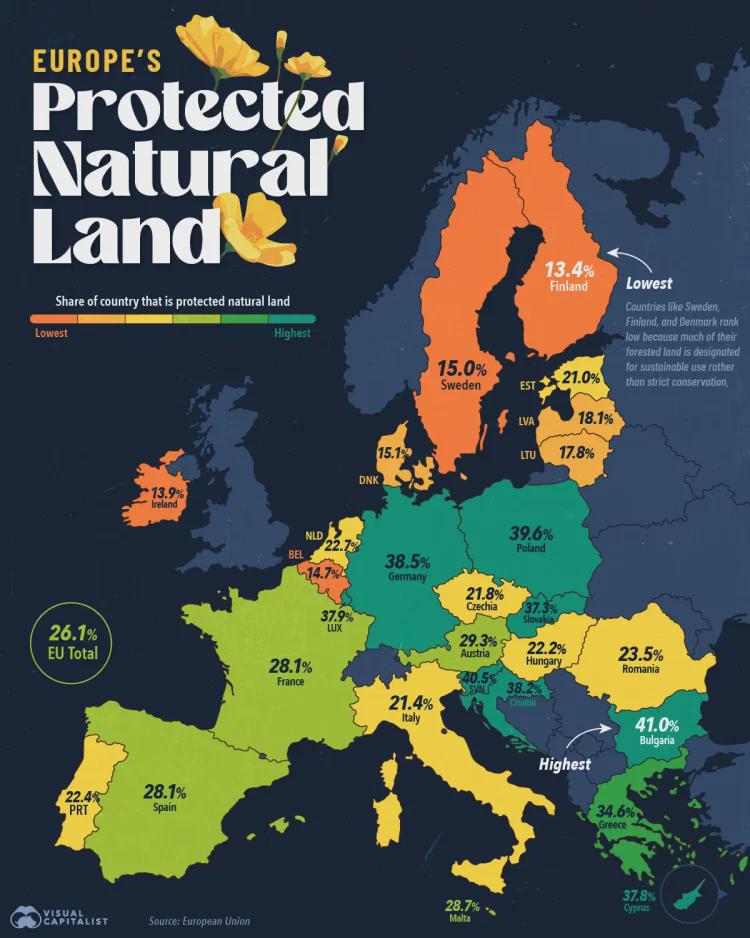
Map of European Union's Protected Natural Land

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This visualization illustrates the extent of protected natural land across the European Union. It highlights regions designated for conservation, showcasing a commitment to preserving biodiversity and natural habitats. As you navigate through the map, you’ll notice varying degrees of protection across different member states, revealing not just the commitment level but also the ecological richness of these regions.
Deep Dive into Protected Natural Land
Protected natural land refers to areas that are safeguarded from development and exploitation, allowing ecosystems to thrive and biodiversity to flourish. The European Union has established a network of protected areas known as Natura 2000, which aims to preserve many of Europe’s most precious species and habitats. Covering over 18% of the EU’s total land area, this initiative is a cornerstone of the EU's environmental policy.
Interestingly, the diversity of protected areas ranges from national parks and nature reserves to marine protected areas. These zones are crucial not only for wildlife but also for the ecosystem services they provide, such as clean air, water filtration, and climate regulation. For instance, forests in Central and Eastern Europe are often designated as protected lands due to their rich biodiversity, housing species like the European bison and various bird species unique to the region.
Have you ever wondered why some areas are more protected than others? The answer often lies in the ecological significance of the land and the pressure from human activities. Countries with extensive agricultural practices or urban development may have less protected land compared to those with a strong emphasis on conservation. In fact, according to recent statistics, countries like Sweden and Finland boast over 30% of their land as protected, while other nations, like Malta, have less than 10%.
The significance of protecting natural land cannot be overstated. Biodiversity loss remains one of the most pressing environmental issues globally. The EU's commitment to protecting its natural heritage is not just about conserving landscapes; it’s an essential strategy for combating climate change and ensuring sustainable development. Healthy ecosystems can better absorb carbon emissions, making conservation efforts an integral part of climate action plans.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes clear that the distribution of protected natural land varies significantly across Europe. Northern European countries, such as Sweden, Finland, and Estonia, lead the charge with extensive protected areas. For example, Finland alone has over 10% of its territory designated as national parks or wilderness areas, which are critical for maintaining biodiversity and ecological integrity.
Conversely, Southern European countries like Spain and Italy also have significant protected areas, but they often face challenges due to tourism and urban expansion. The Balearic Islands, for instance, feature several protected marine areas, yet they are under constant pressure from the tourism industry. This juxtaposition highlights the delicate balance between conservation and economic development.
Central Europe presents another interesting case. Countries like Austria and Germany have robust conservation strategies, with numerous nature reserves that support diverse habitats. However, they also deal with the impact of industrialization and urban sprawl, requiring ongoing efforts to protect these vital ecosystems.
Significance and Impact
The importance of the EU's protected natural land extends beyond mere conservation; it carries profound implications for climate change, public health, and sustainable development. As natural habitats are preserved, they play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change effects, promoting resilience against extreme weather events, and enhancing the quality of life for local communities.
Current trends indicate a growing awareness and urgency surrounding biodiversity conservation, with more EU initiatives aimed at enhancing the effectiveness of protected areas. Recent studies suggest that expanding the network of protected regions could further bolster ecosystem services, which are indispensable for human survival. Furthermore, integrating local communities into conservation efforts can foster sustainable economic opportunities while ensuring the protection of natural resources.
In conclusion, the map of the European Union's protected natural land is more than just a geographical representation; it is a testament to the ongoing commitment to safeguarding the environment for future generations. The varying levels of protection across different regions reflect not only ecological priorities but also socio-economic realities that must be navigated carefully. As we move forward, the challenge remains to protect these vital landscapes while balancing human needs, ensuring that nature continues to thrive alongside society's development.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 7, 2025
- Views
- 98
Comments
Loading comments...