Austria Neighboring Countries Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
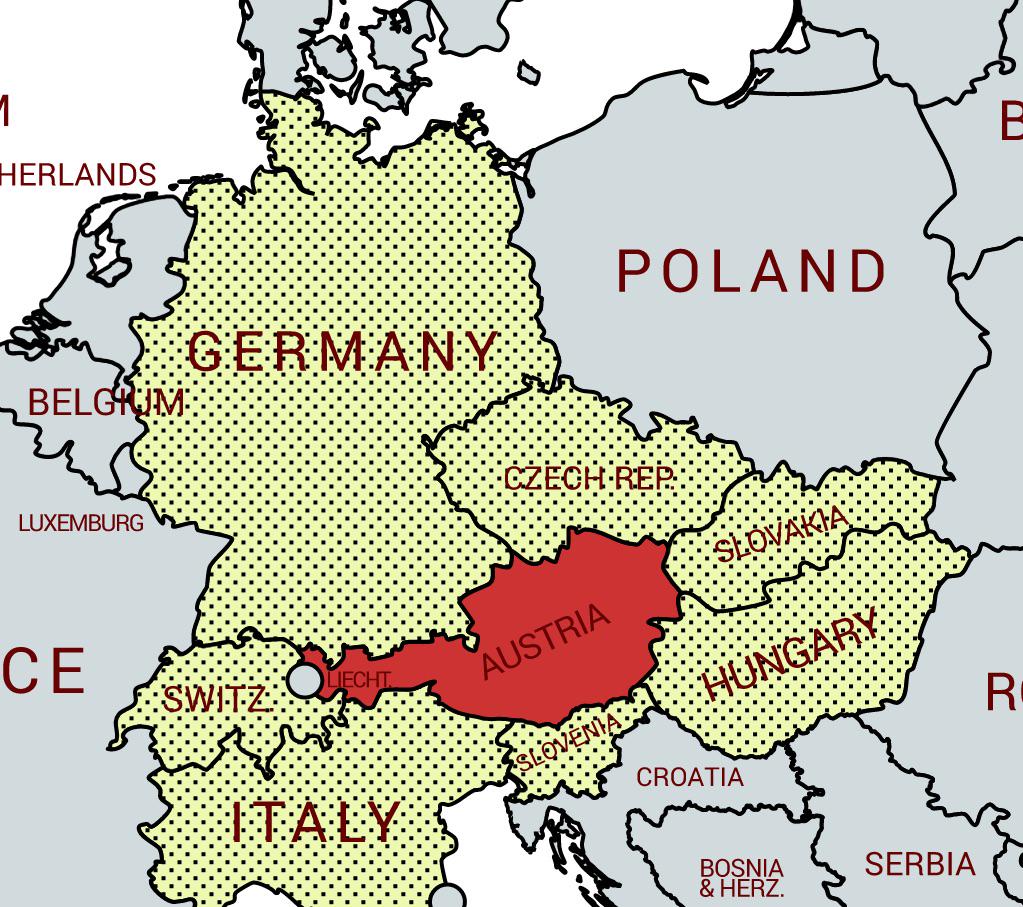
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the unique geographical position of Austria as a landlocked country that shares borders with eight neighboring nations. Austria is surrounded by Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. Interestingly, the map also highlights that Serbia has the same number of neighboring countries, but its border with Kosovo complicates its classification since Kosovo is not universally recognized as a UN member state.
Deep Dive into Austria's Position
Austria’s geographical significance is remarkable, given its central location in Europe. The country is not only landlocked but also serves as a crucial connector between Western and Eastern Europe. With a total of eight neighbors, Austria showcases a rich tapestry of cultural and historical interactions. Each of these neighboring countries brings its own unique influences and characteristics that shape Austria’s identity.
For instance, Germany to the north shares a language and many cultural similarities with Austria, while Slovakia to the east has a distinct Slavic heritage that adds to the cultural diversity of the region. This blend of cultures is not merely an academic curiosity; it has real-world implications in areas such as trade, tourism, and international relations.
Interestingly, Austria’s borders have shifted over the centuries, influenced by historical events such as the Austro-Hungarian Empire's expansion and subsequent dissolution after World War I. The current borders reflect a complex history and ongoing geopolitical dynamics. Austria's role within the European Union further enhances its connectivity, allowing for extensive economic ties with its neighbors. In 2020, Austria's trade with Germany alone accounted for nearly 30% of its total exports, showcasing the interdependence fostered by these borders.
Moreover, Austria’s landlocked status has implications for its transport and trade. While it does not have direct access to the sea, Austria has developed a robust network of railways and highways that facilitate the movement of goods and people across its borders. The Alpine region, while presenting natural barriers, also offers stunning landscapes and outdoor tourism opportunities, drawing visitors from neighboring countries.
Regional Analysis
When examining the neighboring countries of Austria, it’s essential to consider regional variations. The northern border with Germany is characterized by a strong economic relationship, given the historical and linguistic ties. Bavarian culture influences parts of Austria, especially in regions like Salzburg and Upper Austria. Conversely, the eastern border with Hungary represents a different historical narrative, with influences from both the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburgs shaping cultural exchanges.
Travelers often notice unique architectural styles and culinary differences as they cross these borders. For instance, the traditional Hungarian dish gulyás is a staple in both Hungary and Austria, albeit with regional variations. Furthermore, the Austrian-Slovenian border showcases a blend of Alpine and Mediterranean influences, providing a fascinating contrast in lifestyle and geography.
In the south, Austria shares borders with Italy and Slovenia, two countries known for their picturesque landscapes and outdoor activities. The interplay between the Alpine mountains and the Mediterranean climate creates diverse ecosystems and biodiversity, making this region a hotspot for environmental studies.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Austria’s geographical position and its neighboring countries holds significant relevance in today’s global context. The interconnectedness of these nations emphasizes the importance of diplomacy and collaboration in addressing regional challenges, such as environmental issues and economic disparities.
Additionally, with the rise of global trade and travel post-COVID-19, Austria’s central location offers strategic advantages for businesses looking to expand into Eastern Europe. The emphasis on sustainable tourism in the region also highlights the need for cooperation among neighboring countries to protect natural landscapes while promoting economic growth.
As Europe continues to navigate political, social, and environmental changes, Austria’s role as a bridge between east and west remains crucial. The dynamics of its borders not only shape its national identity but also influence broader European integration and cooperation in the 21st century. What’s fascinating is how these geographical relationships can evolve, reflecting the changing tides of history and culture. Will Austria continue to be a central player in shaping European relations? Only time will tell, but its unique geographical position ensures that it will remain an essential part of the story.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 6, 2025
- Views
- 72
Comments
Loading comments...