Hours of Daylight on the Summer Solstice Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
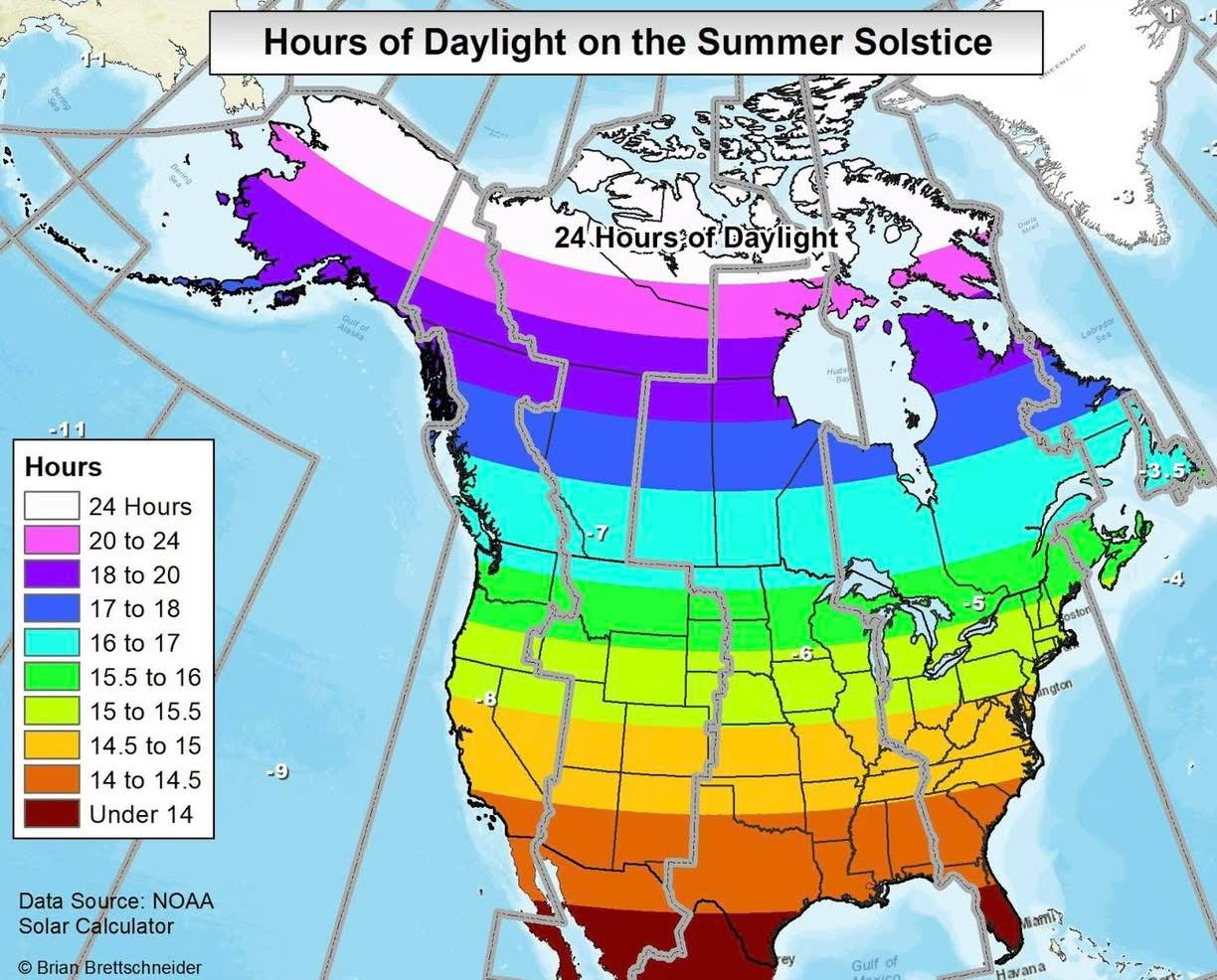
What This Map Shows
The "Hours of Daylight on the Summer Solstice" map provides a visual representation of the varying amounts of daylight experienced around the world on the longest day of the year. This phenomenon occurs annually around June 21st in the Northern Hemisphere, marking the peak of summer when the sun reaches its highest position in the sky. The map displays hours of sunlight across different latitudes, highlighting regions that bask in extended daylight versus those that experience shorter days.
As we transition from the map to the topic at hand, it’s intriguing to consider how daylight hours not only affect our daily lives but also influence ecological systems, agricultural practices, and even cultural traditions.
Deep Dive into Daylight and Its Effects
Daylight, especially during the summer solstice, is a critical factor in various natural and human activities. The amount of sunlight received at different times of the year greatly influences climate, weather patterns, and ecosystems. For instance, regions closer to the poles experience extreme variations in daylight throughout the year, leading to phenomena such as the Midnight Sun, where the sun remains visible at midnight during the summer months.
Interestingly, the amount of daylight affects not just human activities but also plant growth. Plants depend on sunlight for photosynthesis, and longer days provide more energy for growth. Crops such as corn and soybeans thrive in regions with extended daylight during the growing season, boosting agricultural output. Conversely, areas with less daylight might struggle with shorter growing seasons, impacting food production.
Moreover, daylight duration plays a crucial role in human behavior and health. Studies have shown that increased exposure to daylight can improve mood and productivity, while insufficient sunlight can lead to Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD). Ever wondered why some cultures celebrate the solstice? Many societies have festivals and traditions rooted in the significance of the summer solstice, viewing it as a time of renewal and abundance.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the map, it’s clear that there are significant regional variations in daylight hours on the summer solstice. For example, areas within the Arctic Circle experience 24 hours of sunlight, while regions near the equator might see about 12 hours of daylight consistently throughout the year.
In North America, places like Anchorage, Alaska, enjoy nearly 19 hours of daylight, making it an ideal time for outdoor activities and tourism. In contrast, southern states like Florida, while enjoying long days, do not experience the same extremes as their northern counterparts. This leads to different cultural practices, with northern communities often celebrating the solstice with festivals that embrace the long days.
In Europe, locations such as Reykjavik, Iceland, also experience the phenomenon of nearly continuous daylight. This unique situation has led to a vibrant culture that celebrates the solstice with events centered around nature and community. On the other hand, Mediterranean countries like Spain have a more moderate increase in daylight, which influences their agricultural calendar and lifestyle.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the hours of daylight on the summer solstice has profound implications for various sectors of society. It affects everything from energy consumption patterns to tourism and agriculture. For example, longer daylight hours can lead to reduced energy costs in the summer months as natural light minimizes the need for artificial lighting.
Moreover, as we face climate change, understanding daylight patterns becomes increasingly important. Shifts in seasonal sunlight can alter agricultural seasons, affecting food security. Farmers may need to adapt to these changes, adopting new cropping strategies that align with the evolving daylight patterns. Additionally, as urban areas expand and the demand for green spaces grows, cities might look to incorporate more outdoor areas that capitalize on extended daylight for public enjoyment.
In conclusion, the hours of daylight on the summer solstice not only shape our environmental landscape but also our societal structures and practices. They remind us of the interconnectedness of nature, culture, and human activity. As we look ahead, understanding these patterns will be essential in navigating the challenges posed by a changing climate and the ongoing need for sustainable practices.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 4, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...