Political Map of Europe in 972

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
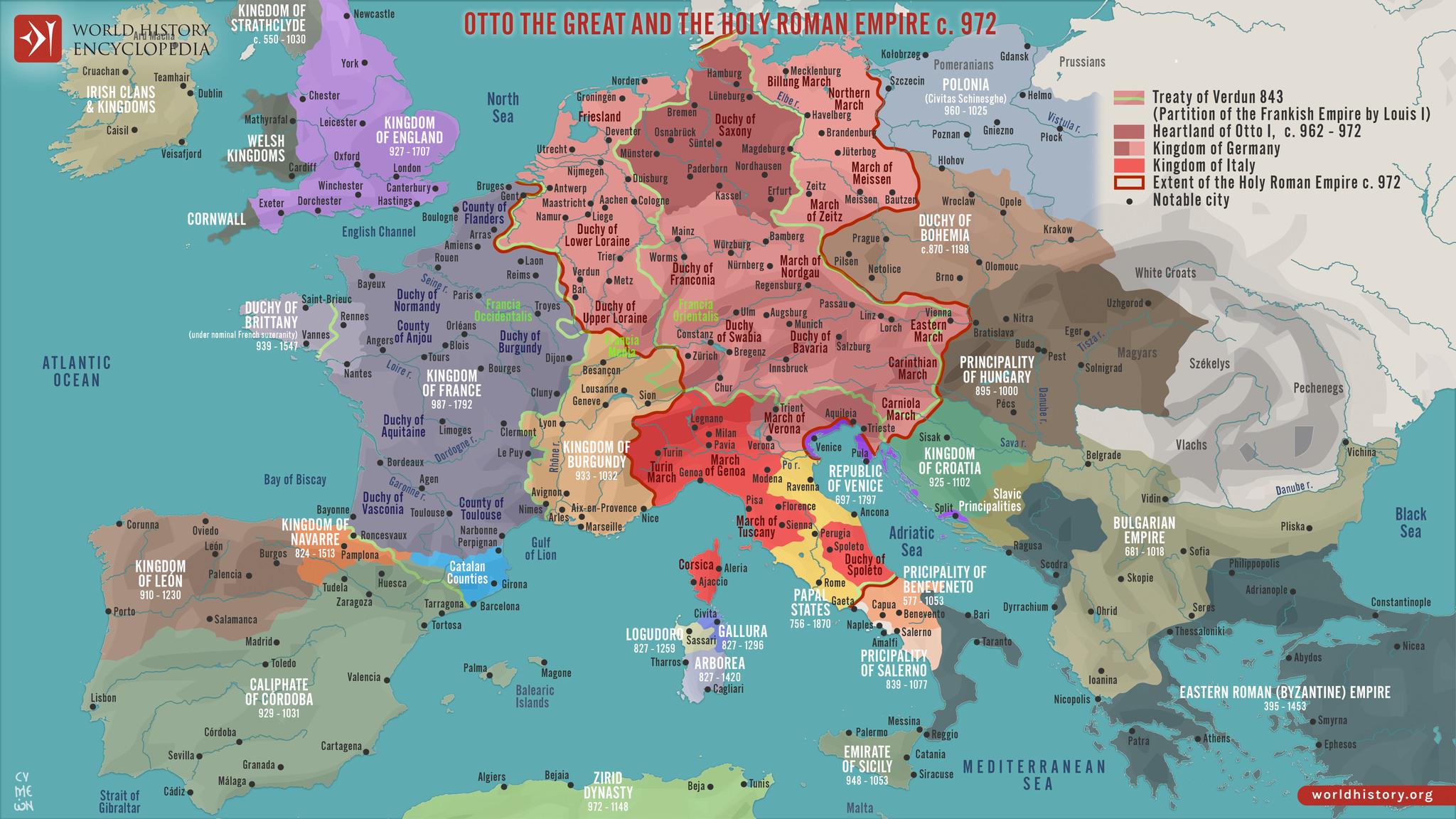
The "Map of Europe in 972" provides a fascinating glimpse into the political landscape of medieval Europe, depicting the various kingdoms, territories, and tribal regions that existed during this period. This map illustrates the complex relationships and borders that defined the continent at a time when Europe was undergoing significant transformation due to various socio-political factors, including feudalism, the rise of the Holy Roman Empire, and the spread of Christianity.
Deep Dive into Political Structures of 972
In 972, Europe was a patchwork of kingdoms and principalities, each with its own rulers and systems of governance. The concept of nation-states as we understand it today was still in its infancy. Instead, the continent was characterized by a feudal system where local lords held power over smaller regions in exchange for military support to a higher authority, often a king or emperor. The Holy Roman Empire, for instance, dominated much of Central Europe, uniting various Germanic tribes and regions under a single crown.
Interestingly, the map indicates the presence of several notable kingdoms, such as the Kingdom of France, which was beginning to solidify its identity under the Capetian dynasty. The map also shows the extensive reach of the Byzantine Empire, which, despite being predominantly situated in the east, had influences and territories that spanned parts of Italy and the Balkans. At the same time, the Kingdom of England was still in a formative stage, struggling with internal divisions and external threats, particularly from Viking invasions.
Have you noticed how the borders drawn on the map reflect not only political power but also cultural and linguistic divisions? The Slavic tribes in Eastern Europe were gradually establishing their presence, with territories that would later evolve into modern nations such as Poland and Russia. The map serves as a historical document that highlights these evolving identities, showcasing both the conflicts and cooperation that shaped the continent.
The map also reflects the significant influence of the church during this period. The spread of Christianity played a crucial role in unifying various tribes and regions, as many rulers sought the church's endorsement to legitimize their rule. This is particularly evident in regions such as Northern Italy and modern-day France, where ecclesiastical powers held considerable sway in political matters.
Regional Analysis
Now, let’s break down the political landscape by regions as shown on the map. In Western Europe, the Kingdom of France was a rising power, characterized by a network of feudal relationships that gave rise to strong local lords. Contrast this with the fragmented political scenario in the British Isles, where the Kingdom of England was still grappling with Viking raids and internal strife. The presence of the Danelaw—territories under Viking control—further complicated governance in the region.
In Central Europe, the Holy Roman Empire dominated, with Emperor Otto I at the forefront. His reign marked a significant consolidation of power, but various duchies and principalities maintained a degree of autonomy, leading to a complex political tapestry. The map shows the division between the empire and the emerging Polish territories, which were beginning to coalesce under the Piast dynasty.
Turning our gaze to Eastern Europe, we see the rise of Slavic principalities. The map indicates the nascent states of Kievan Rus', which would eventually lay the groundwork for modern Russia and Ukraine. This area was a melting pot of cultures and political entities, making it one of the most dynamic regions in Europe at that time.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the political landscape of Europe in 972 is crucial for grasping how historical events shaped the modern world. The divisions and alliances forged during this time laid the foundation for centuries of conflict, cooperation, and cultural exchange. The feudal system, while often seen as a backward approach to governance, was a necessary step towards the more centralized forms of government that would emerge in the following centuries.
From a contemporary perspective, the map serves as a reminder of how borders are often fluid and politically charged. The ongoing debates over territory and national identity in regions like Eastern Europe can trace their roots back to these early medieval dynamics. As we analyze the past, it’s essential to recognize how history informs current geopolitical landscapes, shedding light on the complexities that define our world today.
In conclusion, the "Map of Europe in 972" is not merely a representation of territorial lines; it is a window into a transformative period in European history. It invites us to reflect on the intricate interplay between politics, culture, and identity that continues to shape our societies.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 2, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...