Fire Danger Map of Current Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
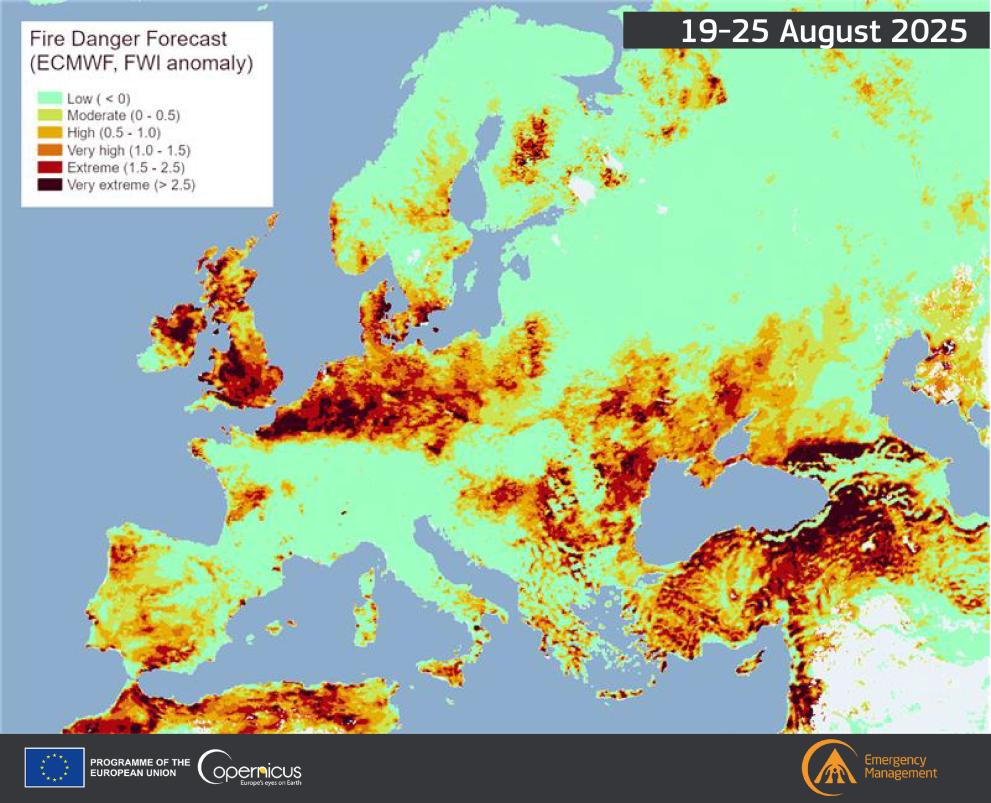
What This Map Shows
The "Fire Danger Map of Current Europe" provides a crucial snapshot of fire risk levels across various regions in Europe. Utilizing a color-coded system, it highlights areas facing heightened fire danger based on current weather conditions, vegetation types, and other environmental factors. This data is vital for understanding fire susceptibility, aiding both authorities and citizens in preparing for and mitigating the risks associated with wildfires.
Deep Dive into Fire Risks in Europe
Fire risks in Europe are influenced by a complex interplay of climatic, geographical, and human factors. Wildfires can occur in any environment where dry vegetation exists, but they are particularly prevalent in regions with hot, dry summers. For instance, the Mediterranean climate, characterized by long, hot, and dry summers, presents an ideal condition for fire outbreaks. Countries such as Spain, Portugal, and Italy experience severe wildfires during these months, often exacerbated by drought conditions and strong winds.
Interestingly, the vegetation types across Europe also play a significant role in fire danger. Forests, grasslands, and shrublands vary in their capacity to ignite and spread fires. For example, coniferous forests, common in Scandinavia and parts of Central Europe, can become highly flammable when there is a lack of moisture. Conversely, deciduous forests may be less susceptible due to their moisture-retaining properties.
Moreover, climate change is intensifying these risks. As global temperatures rise, Europe has experienced more extreme weather events, including prolonged droughts and heatwaves. According to the European Environmental Agency, the number of wildfires in Europe has increased by approximately 50% since the 1980s, with an alarming upward trend forecasted for the coming decades.
Statistically, the European Commission has reported that countries like Greece and Italy suffer some of the highest costs due to wildfires, not only in terms of economic loss but also in social and environmental impacts. In 2021, wildfires in Greece resulted in the evacuation of thousands of residents and destroyed vast tracts of land. This highlights the urgent need for effective fire management strategies and community awareness.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the fire danger levels across Europe, distinct regional differences emerge. Southern European countries, particularly those bordering the Mediterranean, consistently show higher fire risk levels. Spain and Italy often report elevated danger during summer months, with regions like Andalusia and Sicily facing critical threats. Interestingly, Portugal has adopted a proactive approach, implementing extensive fire prevention programs in response to previous catastrophic fires in 2017.
Moving north, countries like France and Croatia exhibit a mixed fire risk profile. While coastal areas experience high fire danger similar to their southern neighbors, inland regions may have lower risks due to increased humidity and vegetation diversity. Northern European countries, including Sweden and Finland, experience lower fire danger overall, but recent years have shown that even these regions are not immune to wildfires, particularly during heatwaves.
In the Balkan region, countries like Bulgaria and Romania have seen increasing fire risks due to changes in land use and increased temperatures. In these areas, abandoned agricultural lands can become fuel for wildfires, demonstrating how human activity—or inactivity—can shape fire dynamics.
Significance and Impact
Understanding fire danger is critical not just for environmental reasons but also for public safety and economic stability. The implications of wildfires extend far beyond the immediate destruction of land and property. They can lead to air quality issues, affecting health, tourism, and agriculture. Interestingly, many European countries are now investing more heavily in wildfire management, including early warning systems, community education, and improved firefighting resources.
Looking ahead, the trends in fire danger are alarming. With climate change continuing to affect weather patterns, we can expect a rise in the frequency and intensity of wildfires across Europe. Recent studies predict that by 2050, the area burned by wildfires in Europe could increase by 50%, impacting not just natural landscapes but also human lives.
In conclusion, the "Fire Danger Map of Current Europe" serves as an essential tool for understanding and responding to the increasing threat of wildfires. By recognizing the underlying factors contributing to fire risk and the regional variations, we can better prepare for and mitigate the impacts of these devastating events. Awareness and proactive measures are crucial in ensuring the safety of both people and the environment in the face of rising fire dangers.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 22, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...