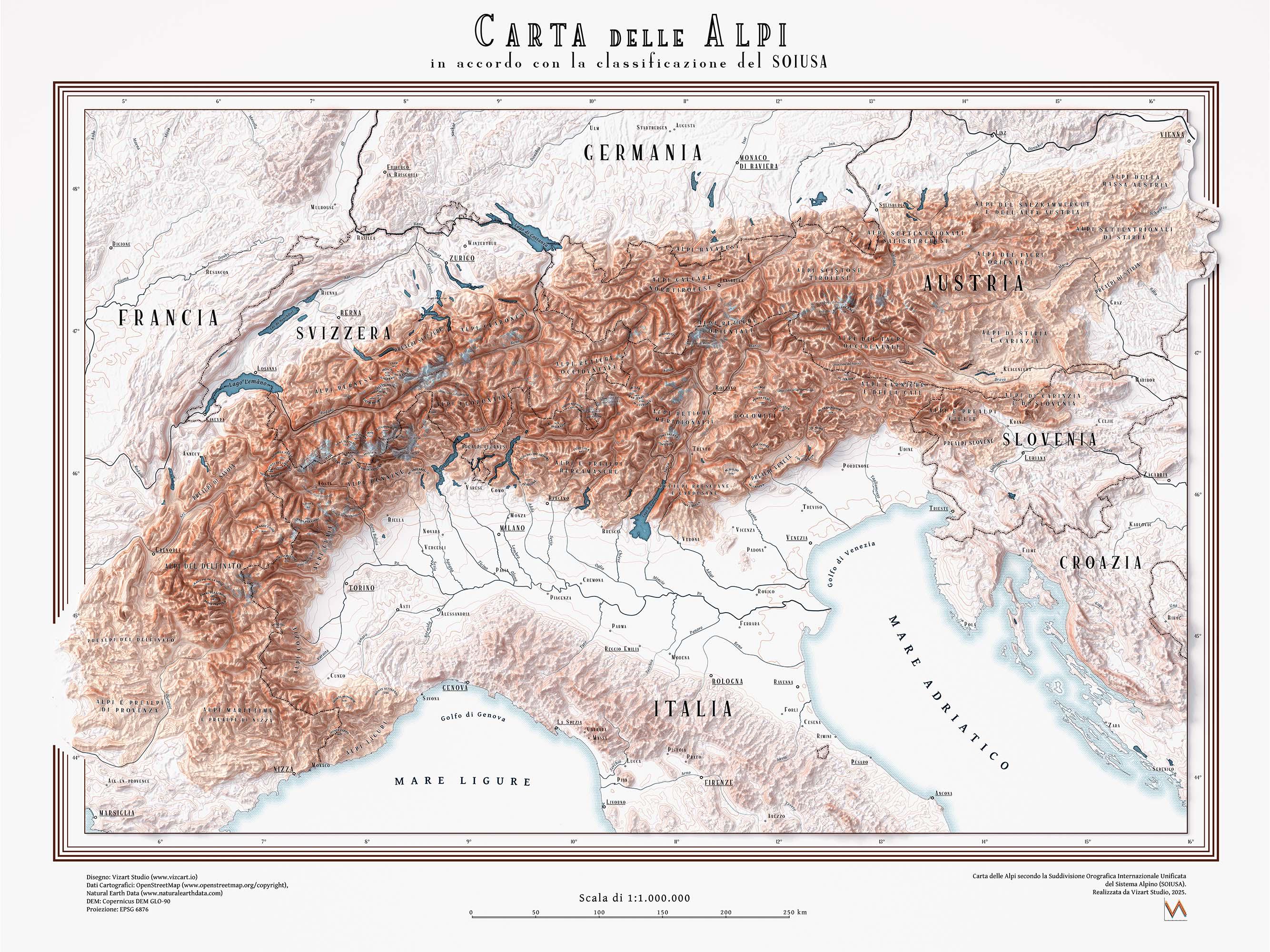
Map of Alps According to SOIUSA Classification

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Map of Alps according to the SOIUSA classification" visualizes the Alpine mountain range and its subdivisions based on the SOIUSA (Sistema delle Orografia Unita del Sistema Alpino) classification system. This unique classification divides the Alps into various sections, providing a structured way to understand their geographical and geological complexity. The map is not just a representation of peaks and valleys; it offers insights into the diverse environments that shape the Alpine region.
Deep Dive into the Alps
The Alps are one of the most significant mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately 1,200 kilometers across eight countries, including France, Switzerland, Italy, and Austria. What’s fascinating is that the Alps not only serve as a natural barrier but also play a crucial role in the climatology and hydrology of the region. The SOIUSA classification divides the Alps into several major sectors—such as the Western Alps, Central Alps, and Eastern Alps—each with its own distinct geographical characteristics.
One interesting aspect of the Alps is their formation. These mountains were formed approximately 30 million years ago due to the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. This geological process led to the uplift of the mountains, creating a stunning landscape filled with rugged peaks, deep valleys, and numerous glacial formations. The highest peak in the Alps, Mont Blanc, rises to 4,808 meters and is a popular destination for climbers and tourists alike.
The SOIUSA classification also highlights the unique ecosystems present in the Alps. The varied altitudes and climates across the range give rise to diverse flora and fauna, from lush green valleys at lower elevations to barren, rocky peaks where only the hardiest of species can survive. Interestingly, the Alps are home to approximately 30,000 plant species and a plethora of wildlife, including ibex, chamois, and the elusive snow leopard.
Moreover, the climate in the Alps is highly variable. The western side—exposed to prevailing westerly winds—receives significantly more rainfall than the eastern side. This phenomenon not only affects the vegetation but also the agriculture in the region. Many Alpine communities engage in traditional farming practices, cultivating crops like barley and potatoes, which are well-suited to the cooler, alpine climate.
Regional Analysis
Breaking the Alps down by their SOIUSA classifications reveals fascinating regional differences. For example, the Western Alps, primarily located in France and parts of Italy, are characterized by steep, dramatic landscapes with numerous high peaks. The Mont Blanc massif, located here, attracts climbers and hikers from around the world. In contrast, the Central Alps, which include parts of Switzerland, exhibit a different geological composition, with a mix of granite and limestone that contributes to their unique beauty.
The Eastern Alps, stretching across Austria and Slovenia, are known for their rolling hills and alpine lakes. This region is particularly famous for its picturesque landscapes, including Lake Bled and the Salzkammergut area. Interestingly, each of these regions has developed distinct cultural identities influenced by their geographical features. For instance, the Tyrolean region in the Eastern Alps is known for its traditional mountain culture, including distinctive architecture and culinary specialties.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the SOIUSA classification of the Alps is essential for various reasons. Firstly, it aids in environmental conservation efforts, as different regions require tailored approaches to preserve their unique ecosystems. The Alps face significant threats from climate change, including glacial retreat and biodiversity loss. By recognizing the specific characteristics of each sector, policymakers can develop more effective conservation strategies.
Moreover, the Alps are crucial for water resources in Europe. Many of the continent's major rivers, including the Rhine and Po, originate in the Alpine region. This makes the mountains vital for hydrological systems that support agriculture, industry, and drinking water supplies in surrounding areas. The ongoing changes in climate patterns are raising concerns about water availability, making the study of the Alps ever more significant.
In conclusion, the "Map of Alps according to SOIUSA classification" is not just a geographical tool; it encapsulates the rich tapestry of geology, ecology, and culture that defines this iconic mountain range. As we move forward, understanding the intricacies of the Alps through such classifications will be crucial for sustainable development and environmental stewardship in this breathtaking part of the world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 21, 2025
- Views
- 92
Comments
Loading comments...