Map of the True Size of the Pacific Ocean

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
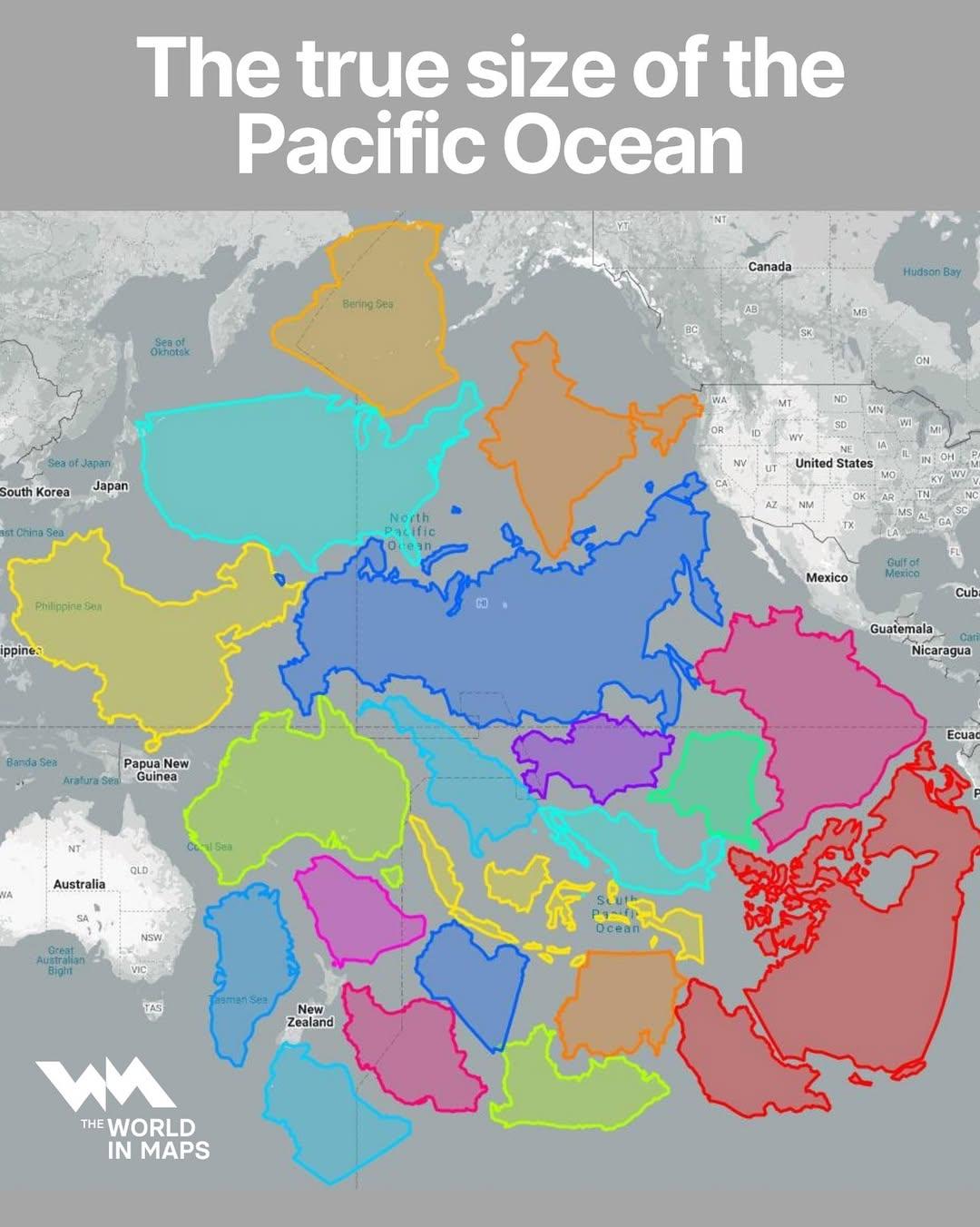
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "The True Size of the Pacific Ocean" illustrates the vastness of the Pacific Ocean by accurately representing its dimensions relative to landmasses around the globe. Unlike many traditional maps that distort the size of oceans and continents due to projection methods, this map provides a more realistic view of the Pacific, emphasizing its monumental scale compared to other geographical features.
The Pacific Ocean is not just the largest ocean on Earth; it is a crucial component of our planet's climate, ecosystems, and human interaction. Covering about 63 million square miles (165 million square kilometers), it spans from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south and is bordered by Asia and Australia to the west and the Americas to the east. This is a staggering expanse, but its significance goes beyond mere size.
Deep Dive into the Pacific Ocean
Ever wondered why the Pacific Ocean is so integral to global weather patterns? This ocean plays a pivotal role in the Earth’s climate system. The warm waters of the Pacific influence weather across the globe, driving phenomena like El Niño and La Niña, which can lead to extreme weather events such as droughts and floods in various regions. Interestingly, the Pacific's vastness allows it to act as a heat sink, absorbing significant amounts of solar energy and redistributing it through ocean currents.
The Pacific Ocean is also home to some of the most diverse marine ecosystems on the planet. The Great Barrier Reef, located off the coast of Australia, is one of the most famous coral reef systems and a UNESCO World Heritage site. This biodiversity is not only important for ecological balance but also for the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on fishing and tourism.
Furthermore, the Pacific is dotted with numerous islands, many of which are volcanic in origin. Islands such as Hawaii and those in the Polynesian region offer unique habitats and cultural significance. The ocean's depth reaches an astounding 36,000 feet (over 10,900 meters) at the Mariana Trench, the deepest known point on Earth. This trench is a site of scientific interest, harboring unique organisms and geological features yet to be fully explored.
Culturally, the Pacific Ocean has been a crucial conduit for trade and exploration. Historically, the ocean has seen the movement of peoples, ideas, and goods, shaping the cultures of societies from Polynesia to the Americas. Its vastness has also made it a site of conflict, with territorial disputes arising over maritime boundaries and fishing rights.
Regional Analysis
The Pacific Ocean encompasses a wide variety of regions, each with its unique characteristics. For example, the Western Pacific includes nations like Japan, the Philippines, and Indonesia, where the ocean's warm waters contribute to typhoon formation, impacting millions. In contrast, the Eastern Pacific, which borders the Americas, experiences different environmental conditions, where cold currents like the Humboldt Current are crucial for nutrient cycling and marine life support.
One notable area is the Coral Triangle, located in the Western Pacific, renowned for its marine biodiversity — it contains more species of coral than the entire Caribbean Sea. This area is crucial for conservation efforts, as it supports not just marine life but also the livelihoods of over 120 million people.
In the South Pacific, islands like Fiji and Samoa are affected by rising sea levels due to climate change, posing a threat to their existence and the cultures tied to these lands. The impact of climate change is felt differently across the Pacific, with some areas experiencing increased typhoon activity while others face droughts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the true size of the Pacific Ocean is essential, not just for geographical knowledge but for addressing global challenges. Climate change, overfishing, and pollution are pressing issues that directly impact this vast body of water. The Pacific holds significant resources, including fish stocks and mineral deposits, which are increasingly being contested.
Moreover, with the ongoing challenges of climate change, the Pacific Ocean serves as a frontline for understanding how rising temperatures and sea levels affect island nations and coastal communities. As we look to the future, the health of the Pacific Ocean will be critical in determining ecological stability and human resilience.
In conclusion, the map of the true size of the Pacific Ocean is a powerful reminder of its vastness and the myriad of factors influenced by this monumental body of water. Understanding its significance is vital for fostering sustainable interactions with our planet's largest ocean, ensuring that it continues to support life — both human and ecological — for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 21, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...