Greenland Overlay Map of India and Nepal

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
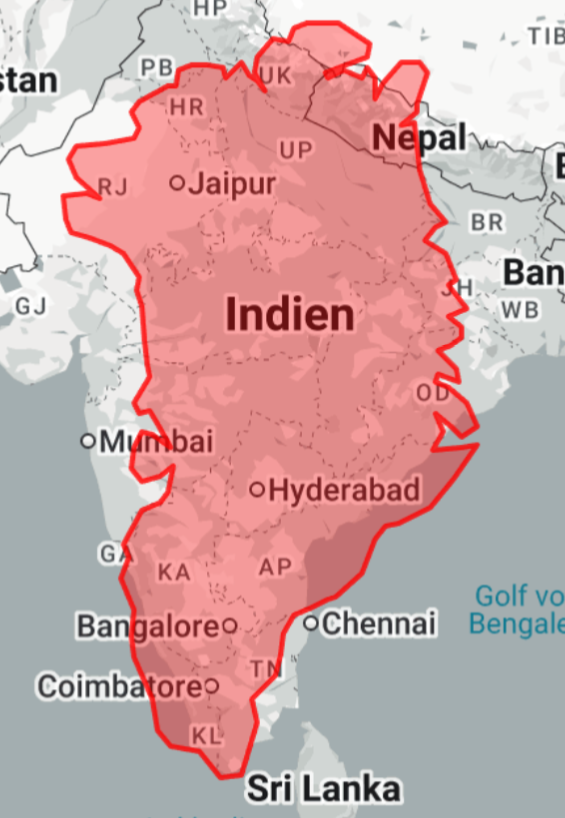
The visualization titled "Greenland on top of India (and Nepal)" demonstrates a unique perspective by overlaying the vast landmass of Greenland over the geographical expanse of India and Nepal. This intriguing mapping technique allows viewers to grasp the relative size of Greenland in comparison to these densely populated regions, offering a tangible sense of scale that is often lost in standard map representations.
However, this exercise is not merely about showcasing size; it opens the door to a deeper understanding of geographical features, climate differences, and regional dynamics present in these areas.
Deep Dive into Size and Scale
Greenland is the largest island in the world, covering an area of approximately 2.166 million square kilometers. In contrast, India spans about 3.287 million square kilometers, and Nepal is much smaller at around 147,516 square kilometers. Interestingly, when plotted on top of India and Nepal, Greenland's vastness becomes strikingly apparent. Not only does this map highlight the sheer scale of Greenland, but it also invites questions about land use, population density, and environmental conditions across these regions.
In the context of population, Greenland's population is a mere 56,000 people, concentrated mostly along the southwestern coast in towns like Nuuk. When overlayed on India, which is home to over 1.4 billion people, it becomes evident how sparsely populated Greenland is in comparison. The population density of India is one of the highest in the world, with urban areas like Mumbai and Delhi showcasing millions living in a relatively small area.
What’s fascinating is the contrast in land use; while Greenland is predominantly covered in ice and tundra, with limited agricultural activity, India is a hub of diverse agricultural practices, ranging from rice and wheat cultivation in the plains to tea plantations in the hilly regions. This stark difference illustrates not only how land is utilized but also how climate and geography influence human activities.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map more closely, we can analyze how different regions of India and Nepal would interact if Greenland's topography were to overlay them. For instance, if Greenland were placed over the northeastern states of India, such as Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya, the rugged terrain and mountainous landscape would align more closely with Greenland's own ice-covered topography, characterized by its glaciers and fjords.
Conversely, placing Greenland over the plains of northern India would reveal how the icy expanses of Greenland contrast sharply with India's extensive agricultural fields and urban sprawls. In Nepal, the overlay over the Himalayas would provoke thought about the climatic and ecological contrasts, as Greenland's frigid environment starkly contrasts with the temperate and tropical climate zones found at lower elevations in Nepal.
Significance and Impact
Why does this map matter? It serves as a powerful reminder of the scale of our planet and the diverse environments that exist within it. Understanding these geographical differences is crucial in our discussions about climate change, land management, and resource distribution. For instance, as global temperatures rise, the melting ice of Greenland poses significant implications for sea-level rise, which could substantially affect densely populated countries like India and coastal regions worldwide.
Moreover, this visualization encourages critical thinking about human adaptation to geography. While Greenland's sparse population might lead to a lifestyle heavily reliant on fishing and hunting, India and Nepal's varied climates foster rich agricultural traditions and urban development, showing how geography shapes cultural and social dynamics.
As we look towards the future, understanding these geographical relationships will become increasingly vital. With climate change causing shifts across the globe, the contrasting environments of Greenland and the Indian subcontinent will likely influence migration patterns, economic opportunities, and ecological challenges. Have you noticed how often geographical contexts are overlooked in discussions about climate policies? It's essential to integrate these perspectives as we navigate the complexities of our changing world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 18, 2025
- Views
- 174
Comments
Loading comments...