Population Distribution Map of the Indian Subcontinent

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
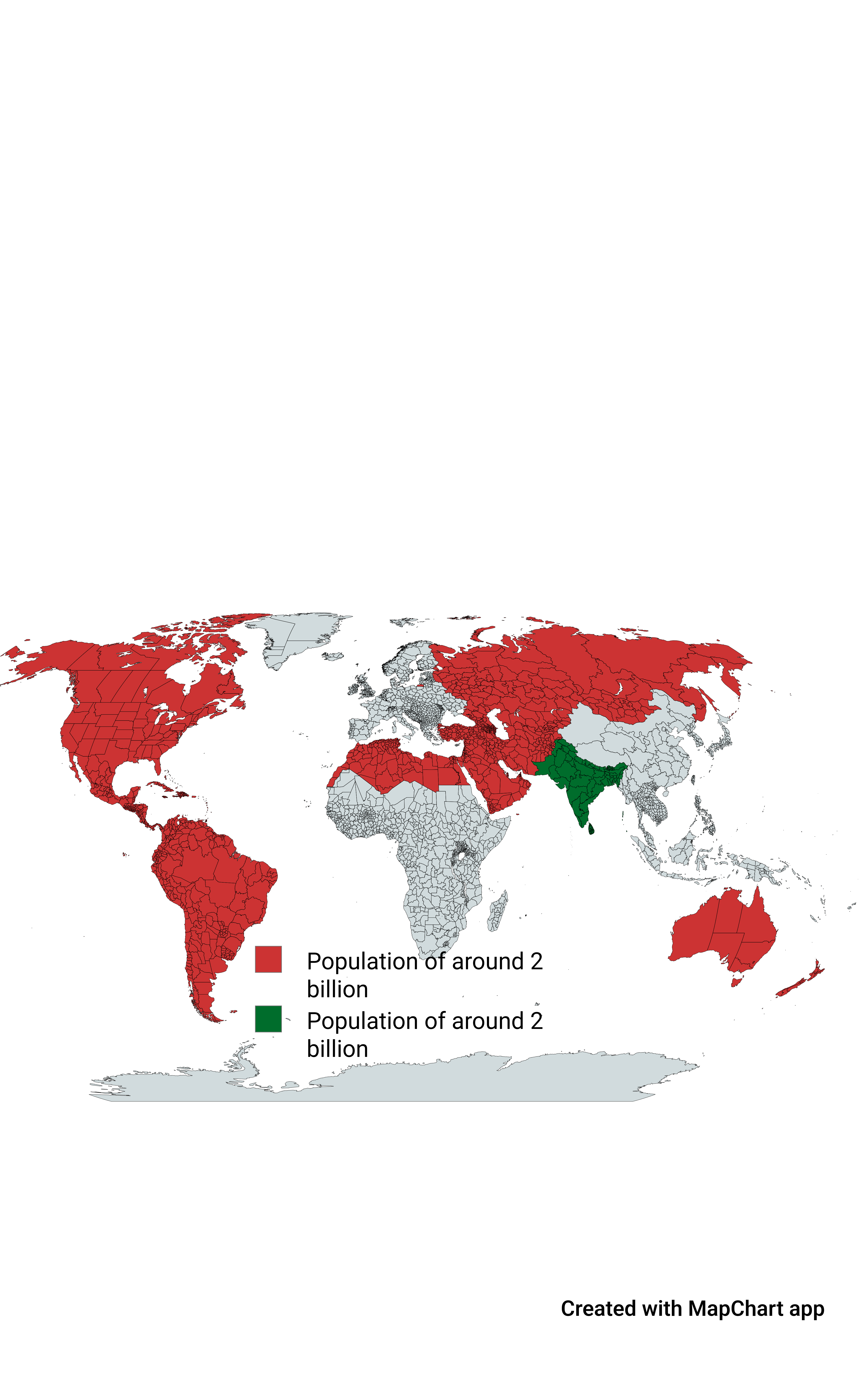
What This Map Shows
The visualization highlights a striking comparison between the population of the Indian subcontinent, depicted in green, and the corresponding red areas, which represent regions with a similar population density. This map serves as a powerful reminder of the immense demographic significance of the Indian subcontinent, which encompasses countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka. With over 1.7 billion people collectively, the population of this region is not only vast but also diverse, influencing global trends in economics, culture, and environment.
Deep Dive into Population Dynamics in the Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is one of the most densely populated regions in the world, characterized by a complex tapestry of cultures, languages, and ethnicities. The sheer scale of its population poses unique challenges and opportunities. For instance, as of 2023, India alone has a population exceeding 1.4 billion, making it the most populous country on the planet, with a growth rate that, while slowing, continues to shape its demographic landscape.
Interestingly, the population distribution is not uniform across the subcontinent. Major urban centers like Mumbai, Delhi, and Dhaka are hotspots of density, each housing millions. What's fascinating is how these cities act as economic engines, attracting people from rural areas in search of better opportunities. This urban migration fuels a range of social and economic phenomena, including the rise of megacities, which are expected to play pivotal roles in the global economy.
However, rural areas also contribute significantly to the overall population. States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in India have some of the highest population figures, often exceeding that of entire countries. This demographic concentration leads to a variety of challenges, including resource allocation, infrastructure development, and public health management.
Additionally, the subcontinent is home to various demographic trends, such as youth bulges in certain regions, aging populations in others, and significant migration patterns both internally and externally. The youth population has the potential to drive innovation and economic growth, but it also necessitates substantial investment in education and job creation. Conversely, dealing with an aging population in some areas requires a reevaluation of healthcare and social services.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the population dynamics by regions shown in the map, distinct patterns emerge. For instance, northern India, which includes states like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, showcases a high population density with significant agricultural output. In contrast, southern regions like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have a different demographic profile, showcasing urbanization and industrial growth, which are crucial to their economic development.
Interestingly, Bangladesh presents a unique case within this context. With a population density that rivals that of India's most crowded states, it struggles under the weight of its demographics. Despite being a smaller country in terms of land area, its population-related challenges—such as poverty and environmental hazards—are profound. On the other hand, Sri Lanka, while also densely populated, benefits from a higher literacy rate and better healthcare outcomes, illustrating how variations in governance and development can impact demographic challenges.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the population distribution of the Indian subcontinent is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it informs policymakers about where to allocate resources effectively. As urban areas continue to swell, the pressure on infrastructure and services will only increase, necessitating strategic planning and investment.
Moreover, this demographic insight is crucial for addressing issues like climate change, where densely populated regions are often more vulnerable to environmental impacts. As countries grapple with rising sea levels, particularly in Bangladesh, the intersection of population and environmental policy will be vital for sustainability.
Looking to the future, projections suggest that the Indian subcontinent's population will continue to grow, albeit at a slower pace. This growth will require a shift in focus—from merely managing numbers to ensuring that people have access to quality education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Ever wondered why some regions seem to thrive while others struggle? The answer often lies in how effectively they manage their population dynamics, balancing growth with sustainability.
In conclusion, the map not only highlights population figures but also serves as a lens through which we can understand the complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors in the Indian subcontinent. It’s a reminder that behind every statistic lies a story waiting to be told.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 13, 2025
- Views
- 184
Comments
Loading comments...