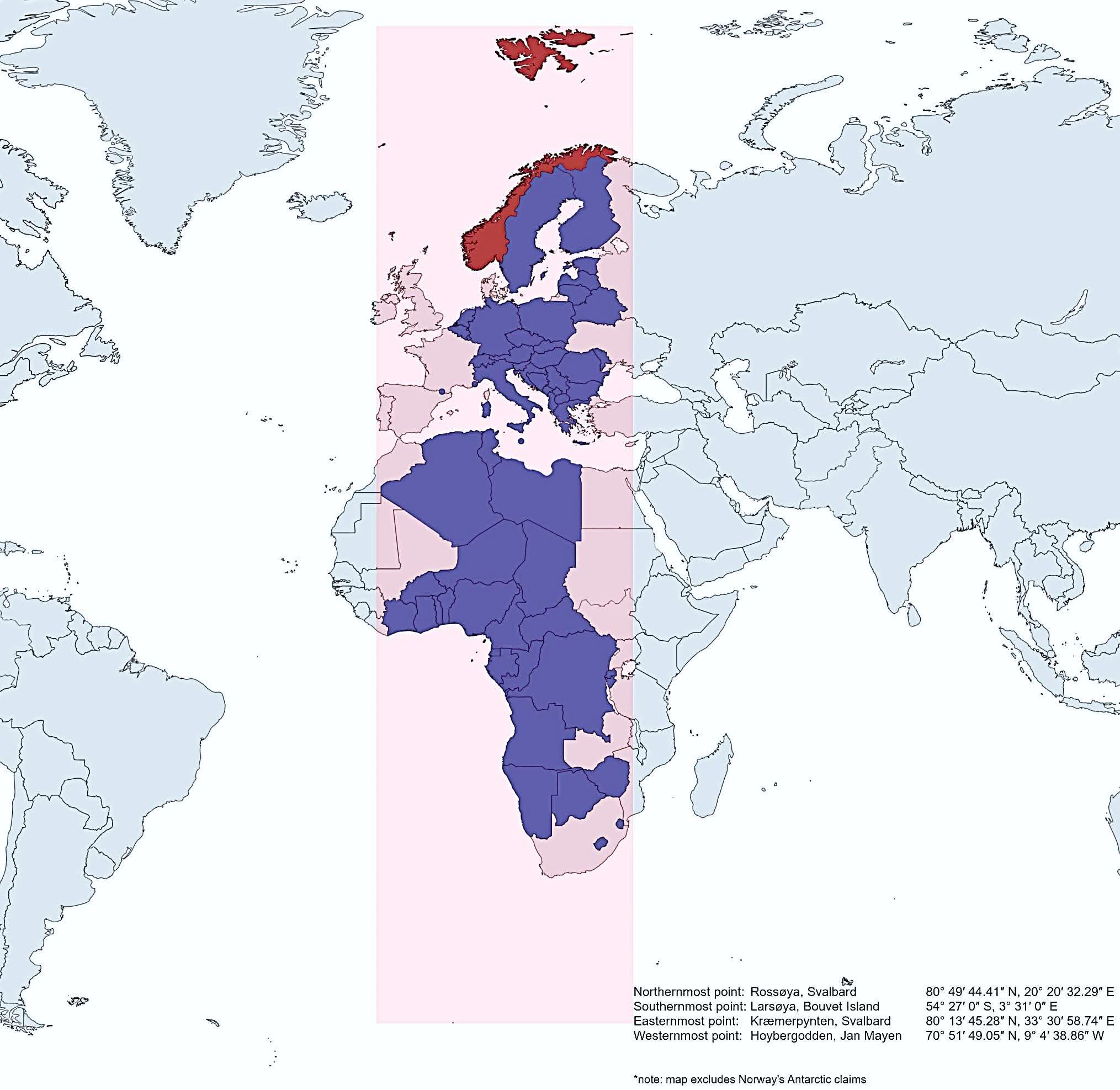
Map of Norway's Geographic Extent Compared to Other Countries

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map vividly illustrates how Norway extends further north, south, east, and west than several other countries, showcasing its unique geographical position and vast territorial reach. It highlights Norway's status as one of the northernmost countries in Europe, while also emphasizing its expansive coastline and mountainous terrain that stretches into the Arctic Circle. The visualization contrasts Norway's geographic boundaries with those of various neighboring and distant countries, allowing us to appreciate the scale and diversity of its landscape.
Deep Dive into Norway's Geographic Extent
Norway, often celebrated for its stunning fjords and rugged mountains, covers an impressive area of approximately 323,802 square kilometers (125,021 square miles). What’s particularly remarkable about Norway is its extreme latitudinal reach. The country stretches from the southern tip at Lindesnes, which is about 58° N, all the way to the northernmost point at Nordkapp, reaching up to 71° N. This stark contrast in latitude allows for a wide range of climatic conditions, from the temperate maritime climate in the south to the stark Arctic climate in the north.
Interestingly, Norway’s longitudinal stretch is also notable. The country extends well into the western part of the Scandinavian Peninsula, bordering Sweden to the east, and includes a number of islands, such as Svalbard, which push its territory even further into the Arctic Ocean. The sheer length of Norway's coastline, which measures about 25,148 kilometers (15,626 miles) when including all its islands and inlets, is among the longest in the world. This extensive coastline not only contributes to Norway’s breathtaking scenery but also plays a significant role in its economy, particularly through fishing and tourism.
Moreover, Norway's rugged terrain is characterized by fjords, mountains, and plateaus, which creates various microclimates and ecosystems. The country's highest point, Galdhøpiggen, rises to 2,469 meters (8,100 feet) above sea level, while the lowest point is at the bottom of the ocean, where the continental shelf drops off. This varied geography has led to a rich biodiversity, with unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing Norway’s geographic extent in relation to other countries, it’s fascinating to compare how its neighboring countries measure up. For instance, Sweden, which is located directly to the east of Norway, is larger in area at approximately 450,295 square kilometers (173,860 square miles), yet Norway’s northern reaches extend further into the Arctic than any point in Sweden. Similarly, while Finland lies to the northeast, its northernmost point, Nuorgam, is located at 70° N, which is still south of Norway’s Nordkapp.
Furthermore, if we shift our focus to countries outside the Nordic region, we can see that areas like Russia extend far north, but again, Norway's unique position along the coast provides it with a distinct maritime influence. Countries such as Canada and Alaska may boast significant northern territories as well, yet Norway’s geographic diversity within a relatively compact area stands out. The interplay of mountains, valleys, and coastlines creates a landscape that is not only beautiful but also rich in resources, making it a unique case study in geography.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Norway’s geographic extent is critical for multiple reasons. Firstly, it underlines the country’s strategic location in terms of geopolitical importance, particularly in relation to Arctic shipping routes and resource exploration. As climate change continues to alter the Arctic landscape, Norway's position may play a pivotal role in international discussions regarding territorial claims and environmental stewardship.
Moreover, the country’s varied geography also impacts its population distribution and urban development. With the majority of Norwegians residing in the southern coastal cities like Oslo and Bergen, the northern regions remain sparsely populated. This demographic trend raises questions about sustainability, infrastructure development, and economic opportunities in the less populated areas.
Ultimately, Norway's geographic extent not only shapes its natural environment but also influences its cultural identity, economic prospects, and international relations. As we look toward future trends, such as the potential for increased Arctic shipping and tourism, Norway’s role on the global stage will likely continue to expand, making its geographic characteristics all the more significant in the years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 12, 2025
- Views
- 120
Comments
Loading comments...