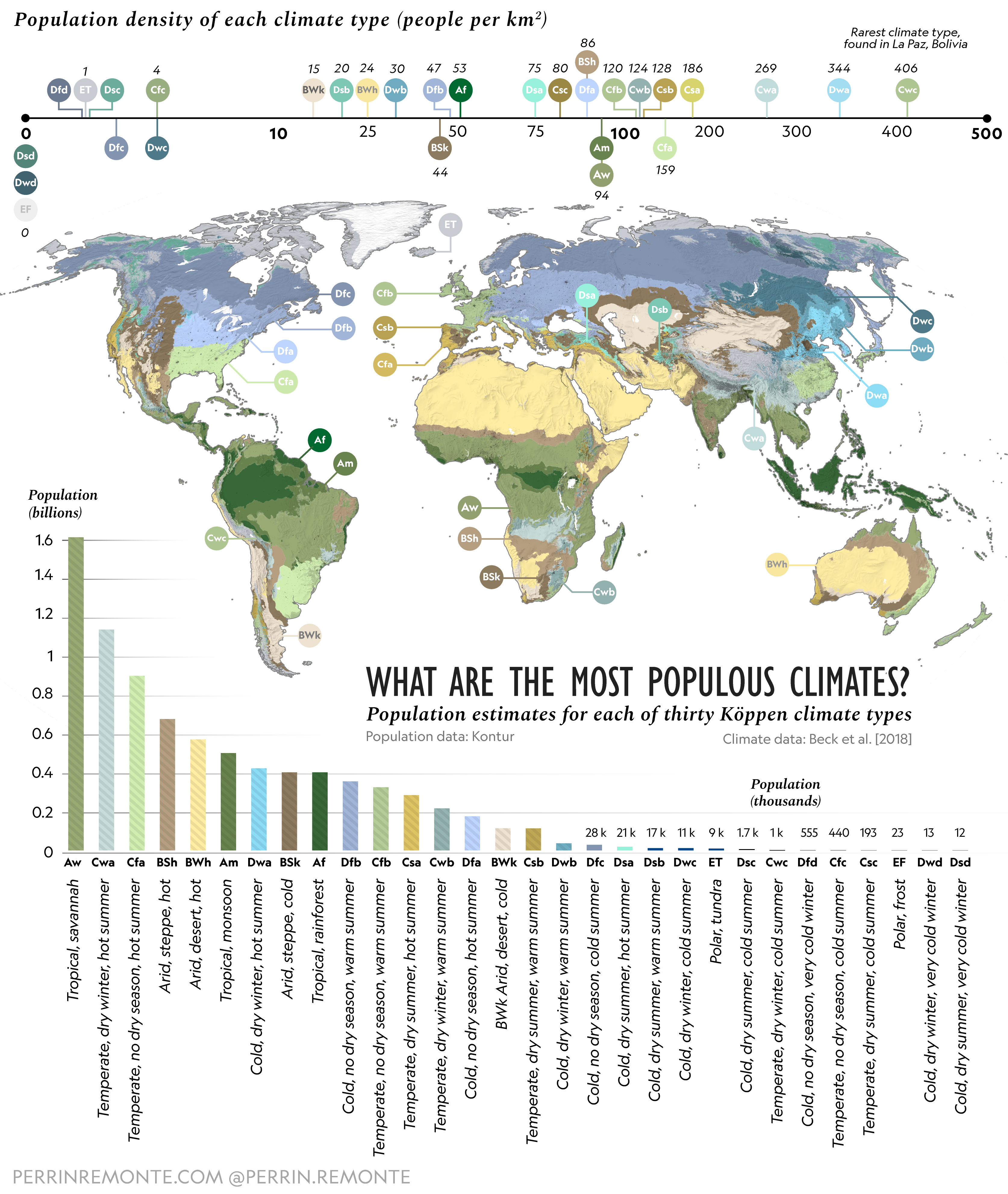
Most Populous Climates on Earth Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map provides an updated visualization of the most populous climates on Earth, highlighting the regions where human populations thrive in various climatic conditions. By examining the distribution of populations across different climate zones, this map sheds light on how environmental factors influence settlement patterns and demographic trends. From tropical rainforests to arid deserts, each climate zone plays a critical role in shaping the lives of the people who inhabit these areas.
Deep Dive into Climate and Population
Climate significantly impacts human populations in various ways. Different climates dictate not only the types of crops that can be grown but also the lifestyle, health, and economic activities of the inhabitants. For instance, tropical climates, characterized by high temperatures and significant rainfall, tend to support dense populations due to favorable agricultural conditions. Countries like Indonesia and Brazil exemplify this phenomenon, where fertile lands foster large communities engaged in farming and other related activities.
On the other hand, arid climates, such as those found in parts of the Middle East and North Africa, present challenges for settlement. However, despite the harsh conditions, cities like Cairo and Riyadh have emerged as populous urban centers. These cities often rely on advanced irrigation techniques and trade to sustain their populations, showcasing human adaptability in the face of environmental challenges.
Interestingly, temperate climates, which feature moderate temperatures and seasonal variations, also support significant populations. Regions such as Western Europe and parts of the United States have experienced substantial urban development, driven by a combination of favorable climate, rich natural resources, and historical migration patterns. For instance, cities like London and New York thrive not only because of their climate but also due to their roles as cultural and economic hubs.
As we delve deeper into this topic, it's essential to consider how climate change might alter these established patterns. Warmer temperatures could lead to shifts in agricultural productivity and alter migration trends. For example, areas currently deemed habitable could become less so, prompting populations to move toward more temperate regions.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely reveals distinct population patterns across various regions. In tropical climates, Southeast Asia stands out with significant population densities. Countries like Vietnam and Thailand are not only rich in biodiversity but also support millions of inhabitants due to their conducive climate for agriculture and trade.
Moving northward, we find temperate climates in Europe that have supported stable populations for centuries. Here, urban centers such as Berlin, Paris, and Amsterdam have thrived due to the combination of moderate weather, historical trade routes, and cultural significance. Comparatively, Eastern Europe experiences slightly lower population densities due to harsher winters and economic challenges.
In contrast, the map illustrates that populations in arid climates are often concentrated around water sources or urban centers, such as Las Vegas in the Mojave Desert. These areas typically exhibit a boom-and-bust population dynamic based on the availability of resources, underscoring the relationship between climate and human settlement.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the most populous climates on Earth is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps policymakers and urban planners make informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability. As climate change progresses, these factors will become even more critical, as populations may need to adapt to shifting climates and potential resource shortages.
Moreover, recognizing the interplay between climate and population can highlight vulnerabilities in certain regions. Areas with dense populations in high-risk climate zones may face challenges related to natural disasters, food security, and health issues. For instance, densely populated coastal cities are more susceptible to the impacts of rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
In conclusion, this map not only illustrates where people live in relation to climate but also serves as a reminder of the intricate relationship between our environment and human life. As we look to the future, understanding these dynamics will be vital in fostering resilience and sustainability in our rapidly changing world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 11, 2025
- Views
- 206
Comments
Loading comments...