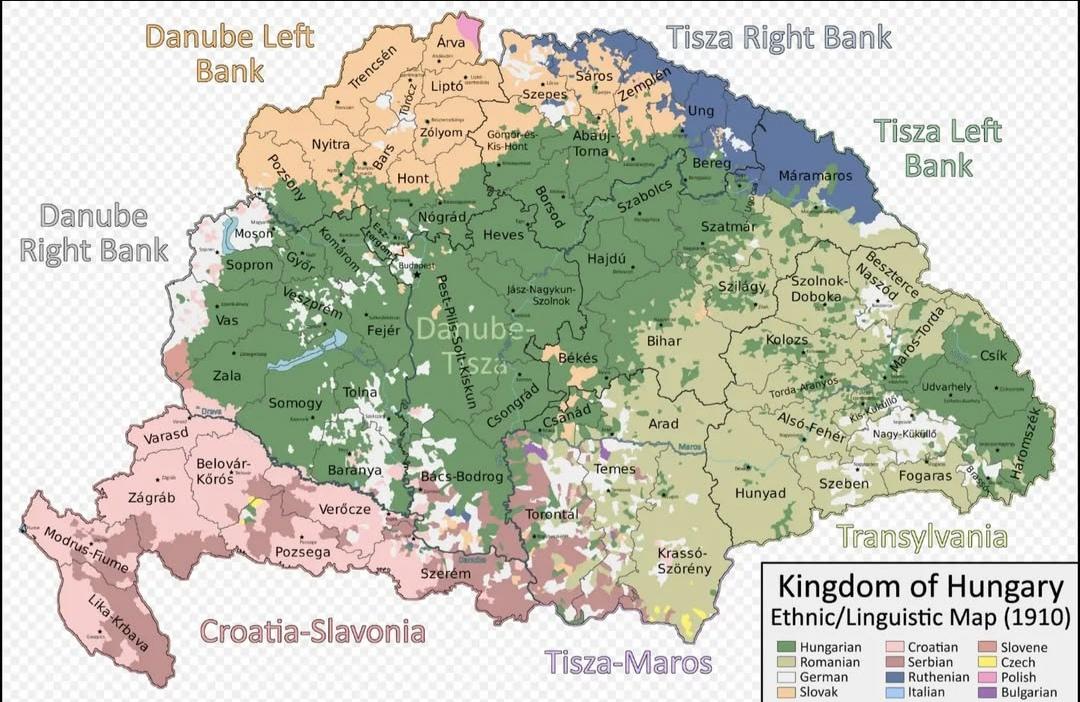
Ethnic Map of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1910

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Ethnic Map of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1910" provides a vivid representation of the diverse ethnic landscape of Hungary during the early 20th century. The map delineates various ethnic groups residing within the kingdom, highlighting their geographical distributions and concentrations across the region. This visualization serves as a valuable historical document that captures the complex tapestry of identities that existed in Hungary at a time when the Austro-Hungarian Empire was in its final years.
Deep Dive into Ethnic Diversity in Hungary
Hungary, particularly in 1910, was a melting pot of ethnicities, reflecting centuries of migration, conquest, and cultural exchange. The map showcases the presence of significant ethnic groups, including Hungarians, Slovaks, Romanians, Serbs, Croats, Germans, and others. Understanding this ethnic diversity is crucial for grasping the socio-political dynamics of the period.
Interestingly, the ethnic composition of Hungary was not uniform. The majority ethnic group was the Hungarians, who primarily inhabited the central regions, particularly around the capital, Budapest. However, the kingdom also included sizable populations of Slovaks in the north, Romanians in the east, and Serbs in the south. Each of these groups contributed to the region's cultural richness, which was reflected in traditions, languages, and social customs.
The Magyarization policies instituted by the Hungarian government in the late 19th and early 20th centuries aimed to promote Hungarian culture and language, often at the expense of minority groups. This created tensions that would later culminate in conflicts and struggles for autonomy. For instance, the Slovaks, concentrated in northern Hungary, were increasingly vocal about their cultural rights, leading to a push for greater recognition and representation.
Statistical data from the time indicated that ethnic Hungarians made up approximately 54% of the population, while the remaining 46% comprised various minority groups. The highest concentrations of ethnic minorities were found in regions such as Transylvania, which had a significant Romanian presence, and along the borders where Slavic populations resided. These demographics shaped local economies, educational systems, and even political structures, making Hungary a fascinating case study in ethnic relations.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map more closely, distinct regional patterns emerge that illustrate the complexities of Hungary's ethnic composition. For example, in the northern regions, the presence of Slovaks is notable, particularly in areas like the Upper Hungary (now Slovakia). These regions experienced significant cultural exchanges, with Slovak traditions influencing local customs and vice versa.
In contrast, the southern regions, particularly those bordering Serbia, were dominated by South Slavic peoples. This area became a hotspot for nationalistic sentiments, as ethnic Serbs sought greater autonomy from Hungarian rule. The mixed ethnic composition in these areas often led to a rich blend of cultural practices, but it was also a source of friction, especially as nationalism surged in the late 19th century.
Transylvania, which was part of the Kingdom of Hungary at the time, showcased a complex mosaic of ethnic groups, including Romanians, Hungarians, and Germans. The map illustrates how this region was characterized by a blend of ethnic communities, each with their own distinct identities. The historical ties and grievances in Transylvania continue to resonate in contemporary discussions about national identity and historical narratives.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ethnic landscape of Hungary in 1910 is significant for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insight into the historical roots of ethnic tensions that have persisted in the region long after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918. The map serves as a reminder of how diverse populations can coexist yet experience conflicting interests, especially in the face of national policies aimed at homogenization.
Moreover, the legacy of this ethnic diversity is still evident today. In contemporary Hungary, debates around minority rights, cultural preservation, and national identity often echo the historical dynamics illustrated in the 1910 map. The ethnic composition has shifted over the decades, but the importance of understanding these historical contexts remains critical for navigating current sociopolitical landscapes.
As we reflect on this map, it invites us to ponder: how do the historical narratives shaped by ethnic diversity influence our understanding of modern Europe? The ethnic map of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1910 is not just a historical artifact; it is a lens through which we can examine ongoing discussions about identity, belonging, and the challenges of multiculturalism in Europe today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 10, 2025
- Views
- 114
Comments
Loading comments...