Geographical Length of Chile Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
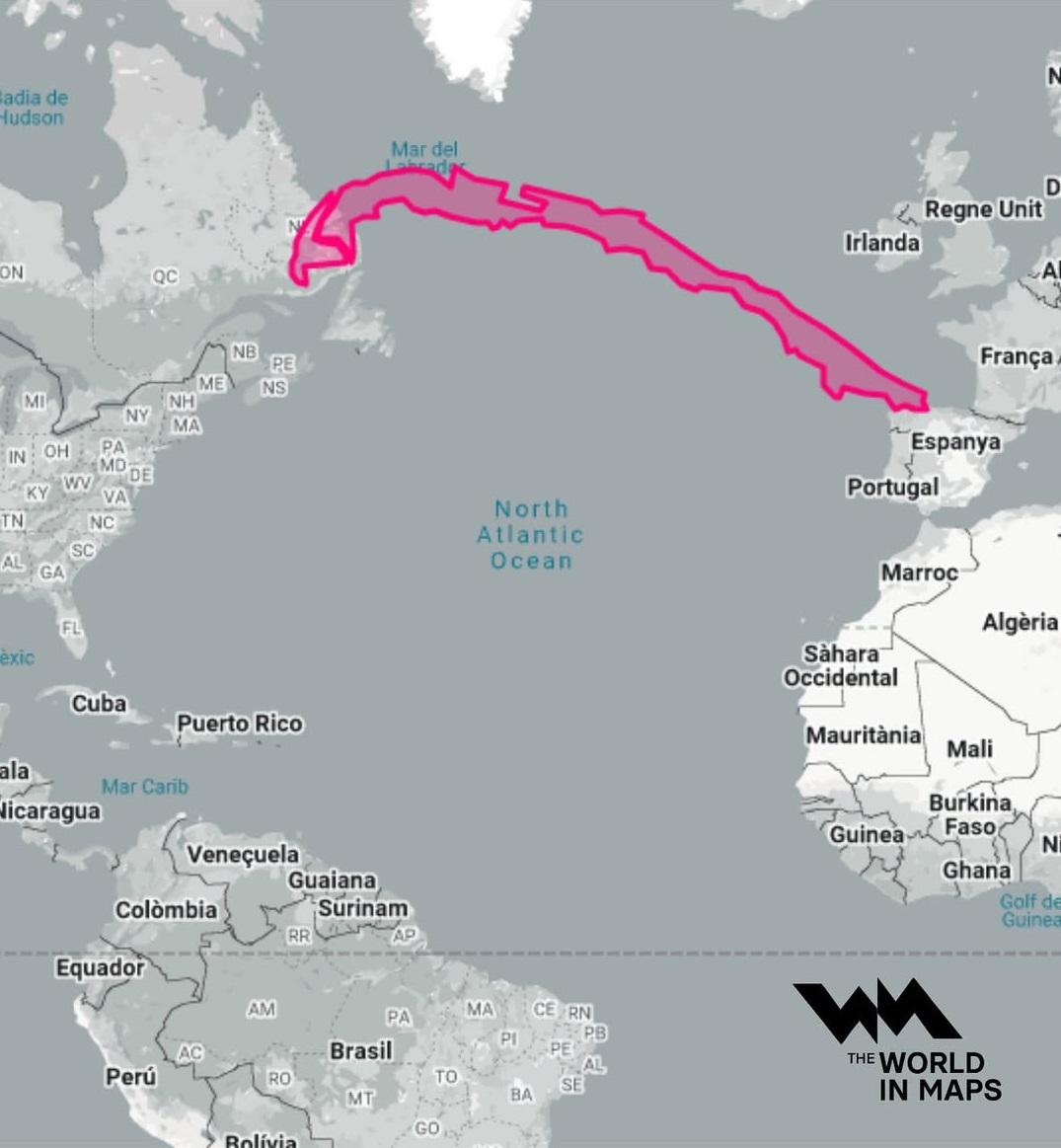
What This Map Shows\nThis map illustrates the remarkable geographical length of Chile, which extends over 4,300 kilometers (about 2,670 miles) from its northern border with Peru to its southern tip at Cape Horn. Interestingly, this elongated shape makes Chile one of the longest north-south countries in the world, comparable to the distance between Canada and Spain across the Atlantic Ocean. This visualization highlights how Chile's unique geography can serve as a metaphorical bridge across vast distances, demonstrating its geographical significance on a global scale.
Deep Dive into Chile's Geography\nChile's unique geographical positioning is not just a matter of distance; it profoundly influences its climate, biodiversity, and population distribution. The country’s length means that it encompasses a wide range of climatic zones, from the arid Atacama Desert in the north to the temperate rainforests of the south. This variation creates diverse ecosystems and habitats, making Chile one of the most ecologically rich countries in the world.
The northern region of Chile is known for the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth, where annual rainfall is less than 1 millimeter in some areas. Interestingly, this desert climate supports unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions and is home to some of the world’s largest copper reserves, significantly contributing to Chile's economy.
As we move south, the landscape transforms dramatically. The central region, which includes the capital city of Santiago, is characterized by a Mediterranean climate, making it suitable for agriculture, especially wine production. Chilean wines have gained international acclaim, bolstered by the region’s favorable climate and diverse terroirs.
Further south, the geography begins to shift into a cooler, temperate climate. The southern regions experience significant rainfall and are home to lush forests, glacial lakes, and fjords. This area is a biodiversity hotspot, hosting unique species such as the endangered Chilean flamingo and the huemul deer. The presence of the Andes mountain range, which runs along the eastern border, creates a rain shadow effect, leading to stark climatic variations within relatively short distances.
Chile's vast length also impacts its demographics. The population is concentrated in central regions, particularly around Santiago, where urban development has flourished. However, the southern parts remain sparsely populated, with communities that often rely on fishing and agriculture. Have you noticed how the culture and lifestyle can differ dramatically between these regions? The northern areas, heavily influenced by mining, contrast sharply with the southern regions, where indigenous cultures and traditions are more pronounced.
Regional Analysis\nExamining Chile by regions reveals significant variations in climate, population density, and economic activities. The northern region is dominated by mining, particularly copper extraction, which is vital for the national economy. In contrast, the central region thrives on agriculture and viticulture, benefiting from its more temperate climate. The southern regions, with a focus on tourism, especially in Patagonia, attract visitors seeking adventure in nature, from trekking to glacial explorations.
Interestingly, regions like Magallanes in the south have much lower population densities compared to the metropolitan area of Santiago, which is one of the most densely populated urban areas in South America. This disparity highlights the impact of geography on human settlement patterns and economic opportunities. The urban sprawl in Santiago presents challenges such as pollution and congestion, while rural areas face issues like lack of infrastructure and access to services.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding Chile's geographical length and diversity is crucial for various reasons. Firstly, it emphasizes the need for tailored policies that address the unique challenges faced by different regions. For instance, sustainable development in the north must consider the environmental impact of mining, while the south requires investment in infrastructure to support tourism and local communities.
Moreover, as climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the distinct climates across Chile suggest that different regions will face unique challenges. The northern deserts may suffer from increased temperatures and water scarcity, while the southern areas might experience shifts in rainfall patterns that could affect biodiversity.
In conclusion, Chile’s geographical length serves as a fascinating lens through which to view not only the physical landscape but also the socio-economic dynamics that arise from such diversity. As we navigate future developments, recognizing the importance of geography is vital for planning sustainable growth and preserving the rich cultural and ecological heritage of this remarkable country.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 10, 2025
- Views
- 324
Comments
Loading comments...