Topographic Map of the US

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
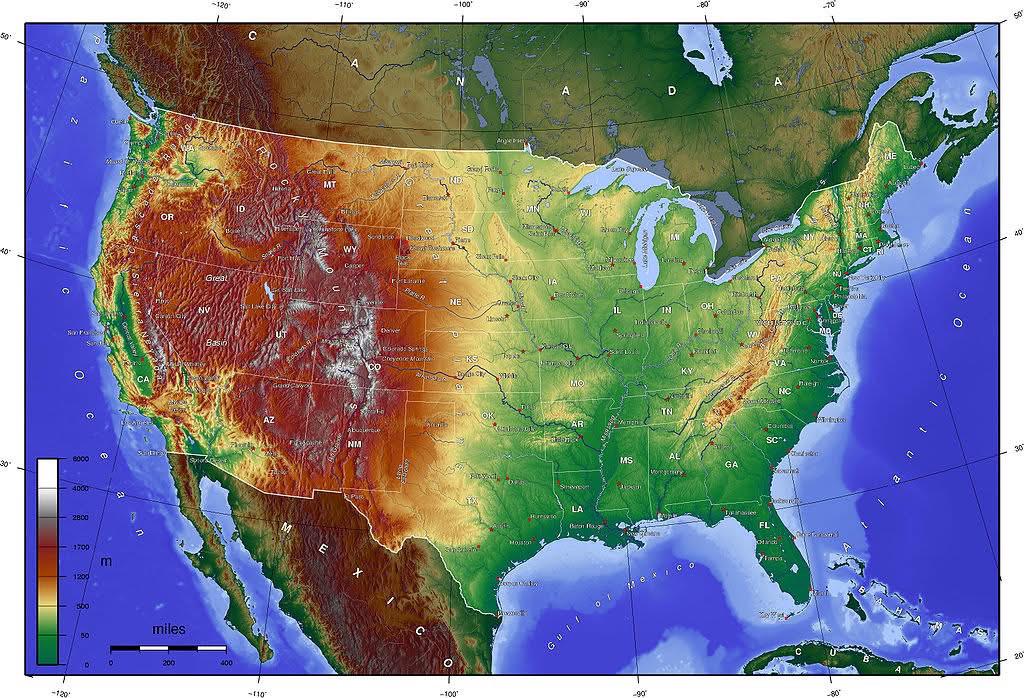
What This Map Shows\nThe topographic map of the United States provides a detailed representation of the country’s varied terrain. It highlights significant physical features such as mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus, utilizing contour lines to illustrate elevation changes across different regions. Additionally, it demarcates hydrographic features like rivers and lakes, giving viewers a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Transitioning from visualization to the actual topic, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of topography and its implications on various aspects of life in the U.S.
Deep Dive into Topography\nTopography plays a crucial role in defining not only the natural environment but also human activities, ecosystems, and climate. The United States boasts a diverse topography that ranges from the towering Rocky Mountains in the west to the flat plains of the Midwest, and from the Appalachian Mountains in the east to the coastal lowlands of the southeast.
One of the most striking features of the U.S. topography is the Rocky Mountain range, which extends over 3,000 miles from Canada down to New Mexico. This mountainous region is characterized by high peaks, deep canyons, and alpine lakes, making it a hotspot for outdoor recreation and biodiversity. Interestingly, these mountains not only influence local weather patterns by creating rain shadows but also serve as a natural barrier that historically shaped human settlement and movement throughout the continent.
In contrast, the Great Plains, known for their vast flatlands and fertile soil, are an agricultural powerhouse. Stretching from Texas up to Canada, these plains are pivotal for crop production, particularly for wheat and corn. The topography here allows for extensive farming practices, contributing significantly to the U.S. economy. Have you ever wondered why certain regions are more agriculturally productive than others? It often boils down to the underlying topography and soil types.
Furthermore, the coastal regions of the U.S. present a different topographical landscape. The Atlantic Coast features a series of estuaries and barrier islands, while the Pacific Coast is marked by rugged cliffs and deep bays. The influence of the ocean on these areas is profound, affecting climate, vegetation, and human activity, from tourism to fishing industries.
Regional Analysis\nWhen analyzing the topography of the United States, it’s crucial to consider the distinct regions it encompasses. The Pacific Northwest, characterized by its mountainous terrain and lush forests, contrasts sharply with the arid deserts of the Southwest.
In the Northeast, the Appalachian Mountains provide a scenic backdrop and have historically influenced settlement patterns. States like Vermont and New Hampshire are known for their beautiful mountainous landscapes, which attract tourists year-round. On the other hand, states in the Midwest, such as Nebraska and Kansas, are defined by their flat topography, heavily influencing agricultural practices.
Interestingly, you can see how the elevation changes dramatically when traveling from the East to the West. For instance, Colorado boasts the highest average elevation of any state, largely due to the Rocky Mountain range. In contrast, the elevations in Florida are among the lowest in the nation, resulting in a different ecological and climatic profile.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the topography of the United States is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. The diverse landscapes influence everything from climate patterns to economic activities such as agriculture, tourism, and resource extraction. For example, mountainous regions are often rich in minerals and resources, leading to mining activities that can significantly impact local ecosystems.
Moreover, climate change poses challenges to various topographical regions. Rising sea levels threaten coastal areas, while increased flooding can alter river patterns in the Midwest. The adaptation and management of these topographical features are essential for sustainable development and disaster preparedness. What's fascinating is how topography can shape cultural identities and lifestyles, from the outdoor enthusiasts in mountainous regions to the farming communities in the plains.
In conclusion, the topographic map of the U.S. unveils more than just the physical landscape; it tells a story of how geography influences life, economy, and the environment. As we continue to study and understand these dynamics, we can better appreciate the intricate relationship between the earth and its inhabitants.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 10, 2025
- Views
- 112
Comments
Loading comments...