Global Population Distribution Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
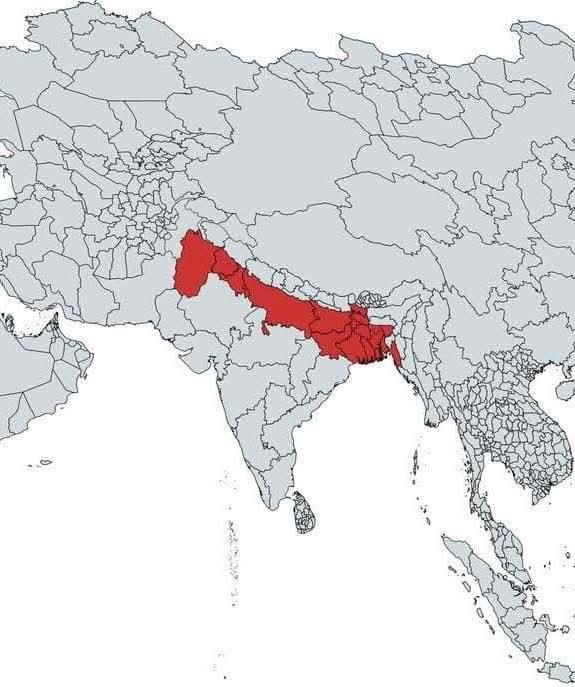
What This Map Shows
The map highlights a significant area in red, representing approximately 890 million people, which is about 11% of the world's total population. Interestingly, this figure exceeds the entire population of Europe by 140 million, making this region a critical focal point for understanding global demographics. The visualization serves as a stark reminder of how population density is concentrated in specific areas, influencing everything from resource distribution to political power.
Deep Dive into Global Population Distribution
When we consider global population distribution, we're diving into a complex web of dynamics influenced by geography, history, economy, and culture. The red area on the map encapsulates diverse nations and regions, each with unique characteristics that contribute to their population figures.
One striking aspect of population distribution is urbanization. Historically, cities have attracted people seeking better economic opportunities, education, and healthcare. For instance, mega-cities like Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai are among the most populous, each housing tens of millions of residents. Urban areas tend to have higher population densities compared to rural areas, which can lead to various challenges such as housing shortages, traffic congestion, and increased pollution.
In contrast, some regions are sparsely populated due to geographical barriers like mountains or deserts, or socio-economic factors that limit development. For example, only a fraction of the population dwells in vast areas of Central Asia, where harsh climates and limited infrastructure deter large settlements.
Demographics play a crucial role in shaping the population structures within these areas. For instance, countries like India and China have significant populations that are relatively young, which can impact their workforce and economic growth. On the other hand, many European countries are facing aging populations, leading to potential economic challenges in terms of labor shortages and increased healthcare costs.
Moreover, migration patterns significantly affect population distribution. People often move from rural areas to cities or from one country to another in search of better living conditions. The recent global events, including economic shifts and climate change, have prompted new waves of migration, further altering the demographic landscape.
Regional Analysis
Diving deeper into the regions covered in the red area, we can see distinct population characteristics. For example, in South Asia, particularly in India and Bangladesh, population density is exceptionally high, with urban centers overflowing with residents. The urbanization rate is compounded by a high birth rate, leading to a youthful demographic eager for opportunities.
Conversely, in regions like North Africa, while countries such as Egypt have considerable populations, they face challenges like water scarcity and political instability that impact growth rates and urban development. Interestingly, North Africa’s urbanization differs significantly from that of Sub-Saharan Africa, where cities often grow rapidly but lack the necessary infrastructure to support such growth effectively.
In Southeast Asia, countries like Indonesia and Vietnam showcase a blend of rural and urban populations, with rapid urbanization transforming landscapes. This region is particularly fascinating as it balances a youthful demographic with a rich cultural history, making it a vibrant area for both economic and social development.
Significance and Impact
Understanding global population distribution is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it has significant implications for resource allocation. Countries with high population densities often face pressure on their natural resources, necessitating sustainable management strategies. Have you noticed how countries like India and China are investing heavily in renewable energy to meet the needs of their growing populations?
Moreover, population distribution influences political power dynamics. Regions with larger populations tend to have more representation in global affairs, affecting international relations and trade agreements. As migration continues to reshape demographics, nations must consider the implications of welcoming newcomers, balancing cultural integration with economic needs.
Looking forward, trends such as aging populations in developed countries and youthful demographics in developing nations will likely shape global economic and social landscapes. Understanding these patterns will be essential for governments and organizations aiming to address future challenges effectively.
In conclusion, the red area depicted on the map serves as a reminder of the complexities of human geography. It underscores the importance of understanding where people live and how that impacts their lives, economies, and the environment. As we move forward into an increasingly interconnected world, recognizing these patterns will be vital for fostering sustainable development and improving quality of life globally.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 9, 2025
- Views
- 106
Comments
Loading comments...