Political Map of Prussia in 1900

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
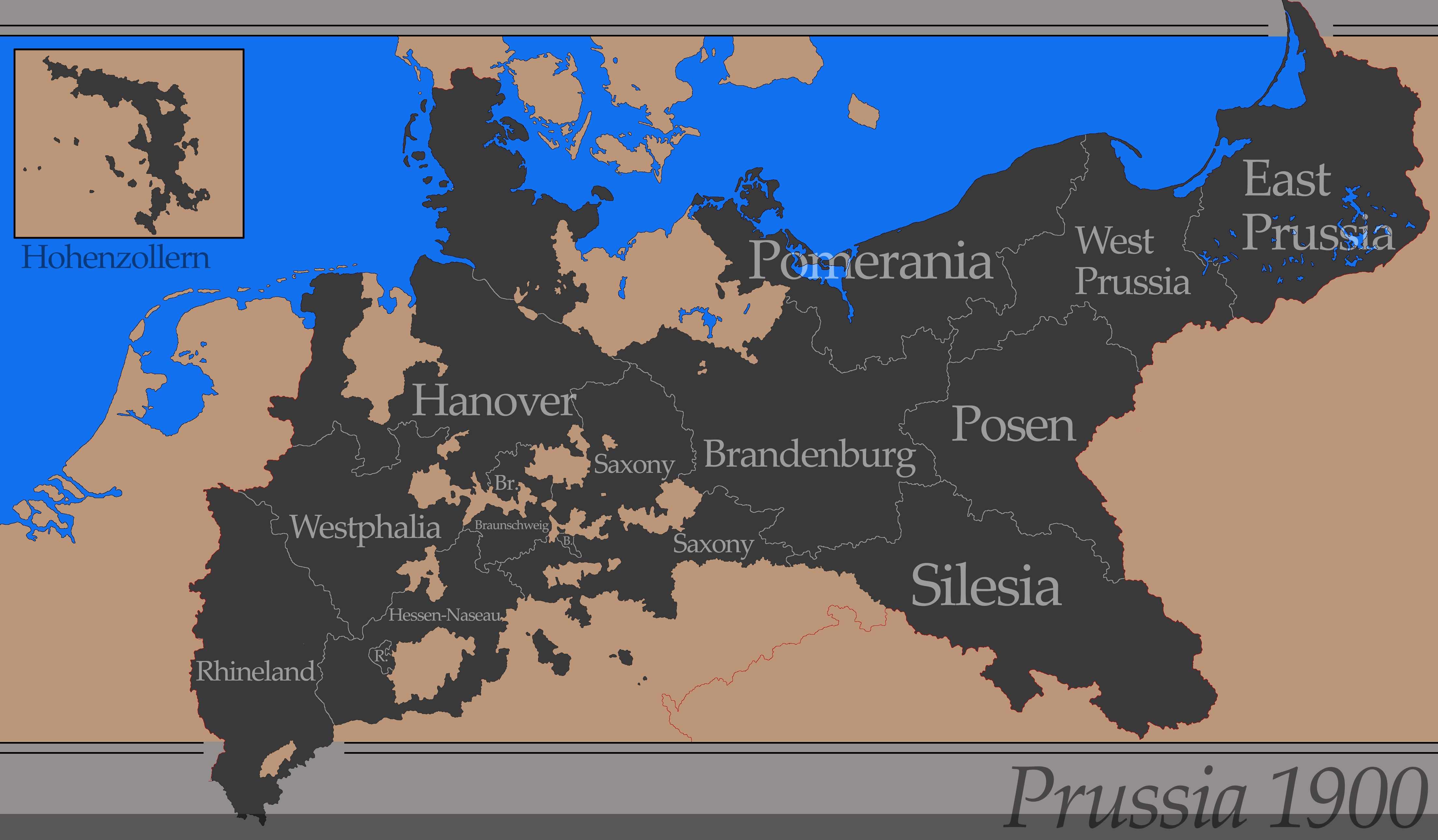
What This Map Shows
The "Simple Map of Prussia in 1900" visually represents the political boundaries and key geographical features of Prussia at the turn of the 20th century. This period marked a significant era in European history, especially for Prussia, which was a major player in the formation of modern Germany. The map outlines Prussia's extensive territories, including areas that today are part of Poland, Lithuania, and parts of western Russia. It highlights not just the borders but also the major cities, rivers, and other geographical landmarks that defined the region during this time.
Deep Dive into Prussian Geography
Prussia, known for its influential role in European politics and military power, had a unique geographical landscape that contributed to its status. By 1900, Prussia was not only the largest state in the German Empire but also a hub of economic and cultural development. One of the most striking features of Prussia's geography was its diverse topography. The northern regions were characterized by flat plains and coastal areas, while the south featured rolling hills and the famous Sudetes Mountains.
Interestingly, the geography of Prussia significantly impacted its population distribution and urban development. Major cities such as Berlin, Königsberg (now Kaliningrad), and Danzig (now Gdańsk) were not just political centers but also thriving economic hubs. Berlin, in particular, became the capital and a beacon of culture and innovation, boasting rapid industrial growth during this period. It is fascinating to note that the population of Berlin skyrocketed, making it one of the largest cities in Europe by the early 20th century.
In terms of demographics, Prussia was home to a diverse population that included Germans, Poles, Lithuanians, and Jewish communities. The map serves as a snapshot of these demographic trends in 1900, illustrating how national identities were shaped by geographical boundaries. For instance, the western parts of Prussia were predominantly German-speaking, while the eastern regions showed a higher concentration of Polish speakers, reflecting the complex ethnic tapestry of the area.
The rivers of Prussia, such as the Oder and the Vistula, played a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape. These waterways were vital for trade, transportation, and agriculture, allowing Prussia to flourish economically. The fertile plains along these rivers supported extensive agricultural activities, which were the backbone of the Prussian economy.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map more closely, we can identify distinct regional characteristics across Prussia. The eastern regions, comprising parts of modern-day Poland, were less industrialized compared to the western territories. Here, agriculture dominated, with small villages and farms prevalent. In contrast, the western regions, especially around the Ruhr area, showcased rapid industrialization, with coal and steel production driving urban growth.
Additionally, the map's portrayal of the border between Prussia and neighboring countries indicates the geopolitical tensions of the time. The border with Russia, for example, was heavily fortified, reflecting the rising tension between these two powers. The presence of various ethnic communities along these borders often complicated political relations, leading to conflicts that would later be exacerbated by World War I.
Significance and Impact
The geographical layout of Prussia in 1900 holds significant historical importance. Understanding the map not only provides insight into Prussian political boundaries but also illuminates the socio-economic dynamics that shaped Central Europe. The implications of Prussia's geography were profound; they influenced the rise of nationalism, the push for unification in Germany, and the eventual conflicts that arose in the 20th century.
What's fascinating is that the legacy of Prussia's geography still impacts our world today. The borders established at this time laid the groundwork for modern political divisions in Europe. As we reflect on these historical contexts, it’s crucial to consider how geography continues to play a role in shaping cultural identities and political landscapes across the globe. In a contemporary setting, the study of Prussia's geographical and political evolution can provide valuable lessons about nationalism, identity, and the complexities of borders in our increasingly interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 6, 2025
- Views
- 110
Comments
Loading comments...